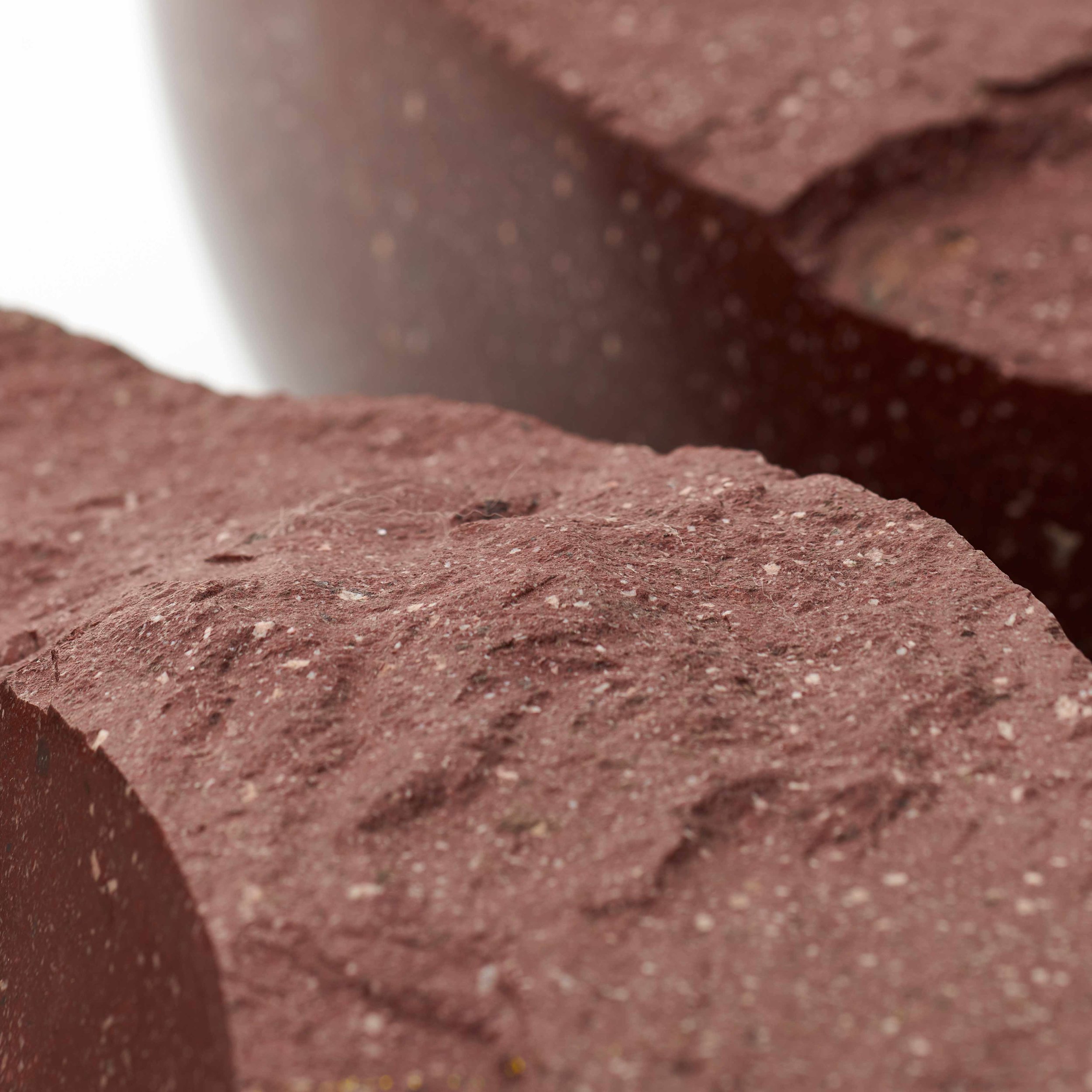
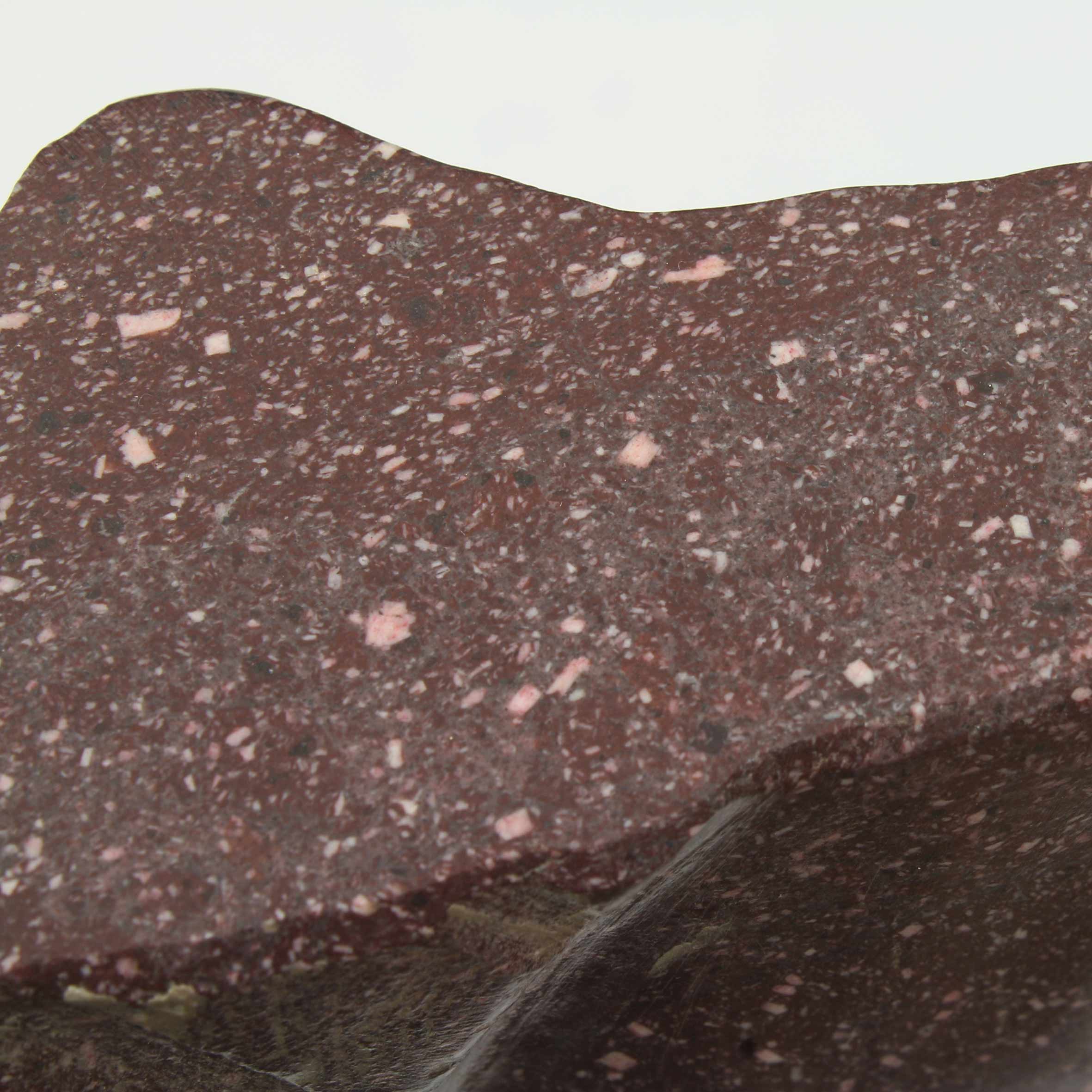
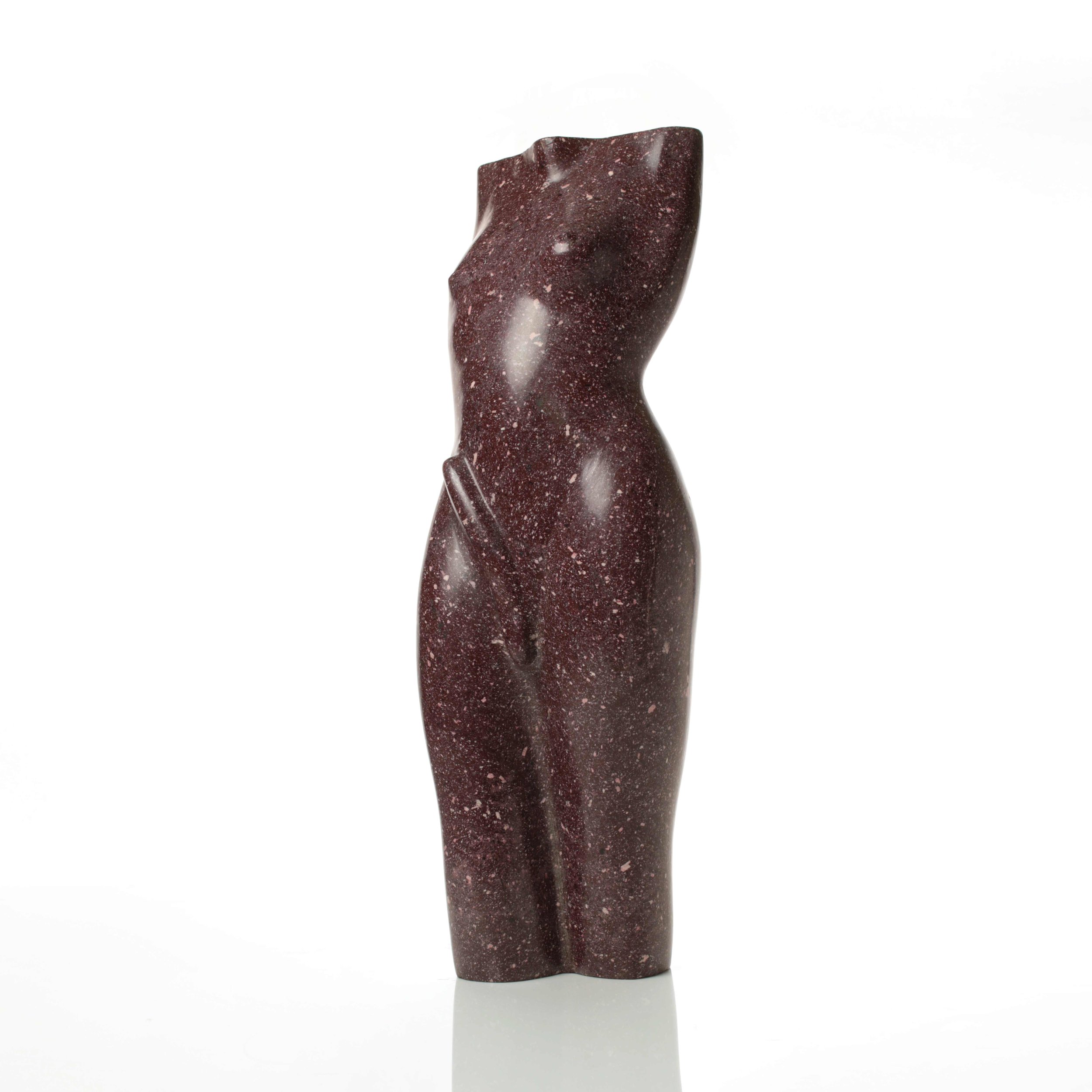
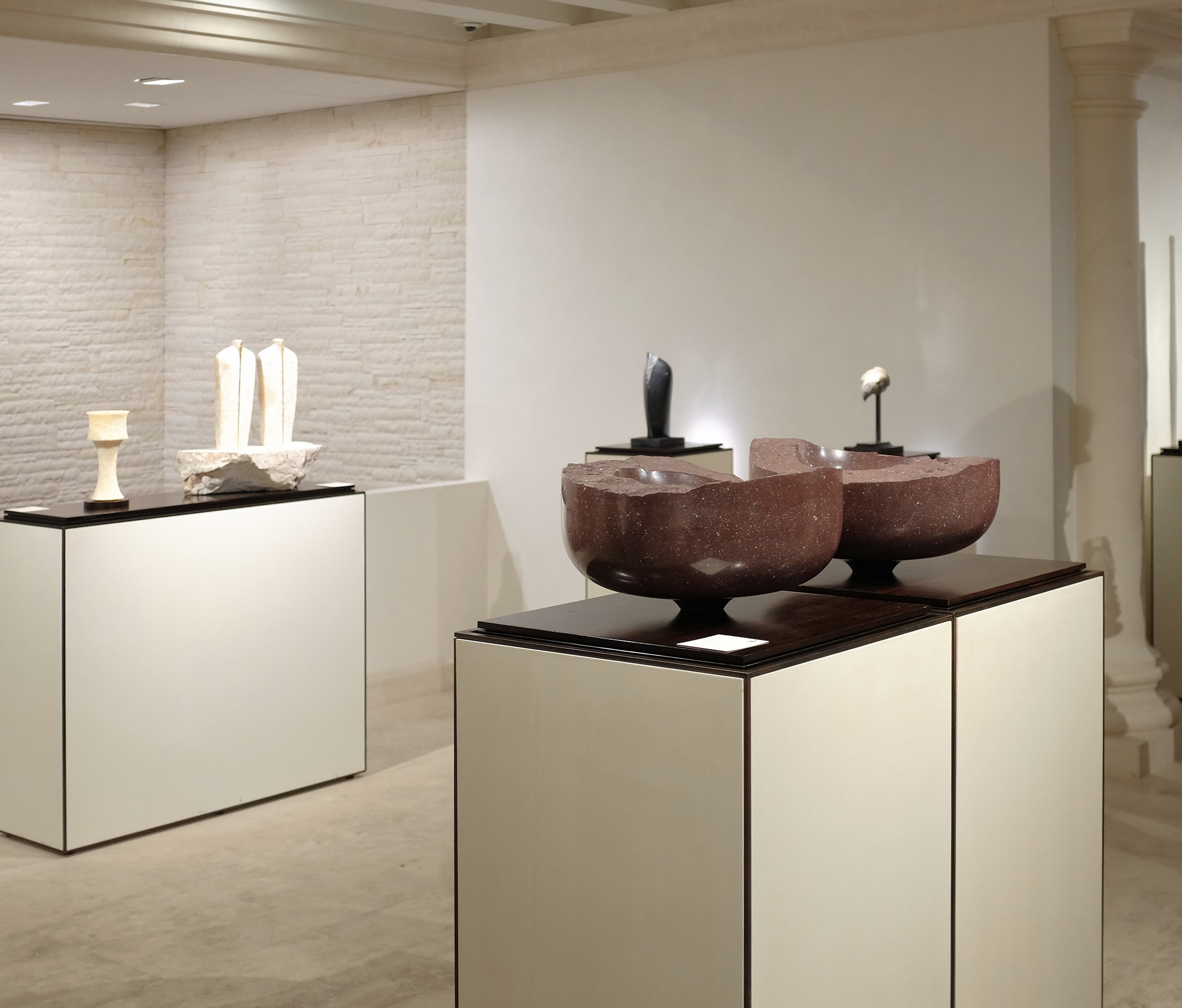
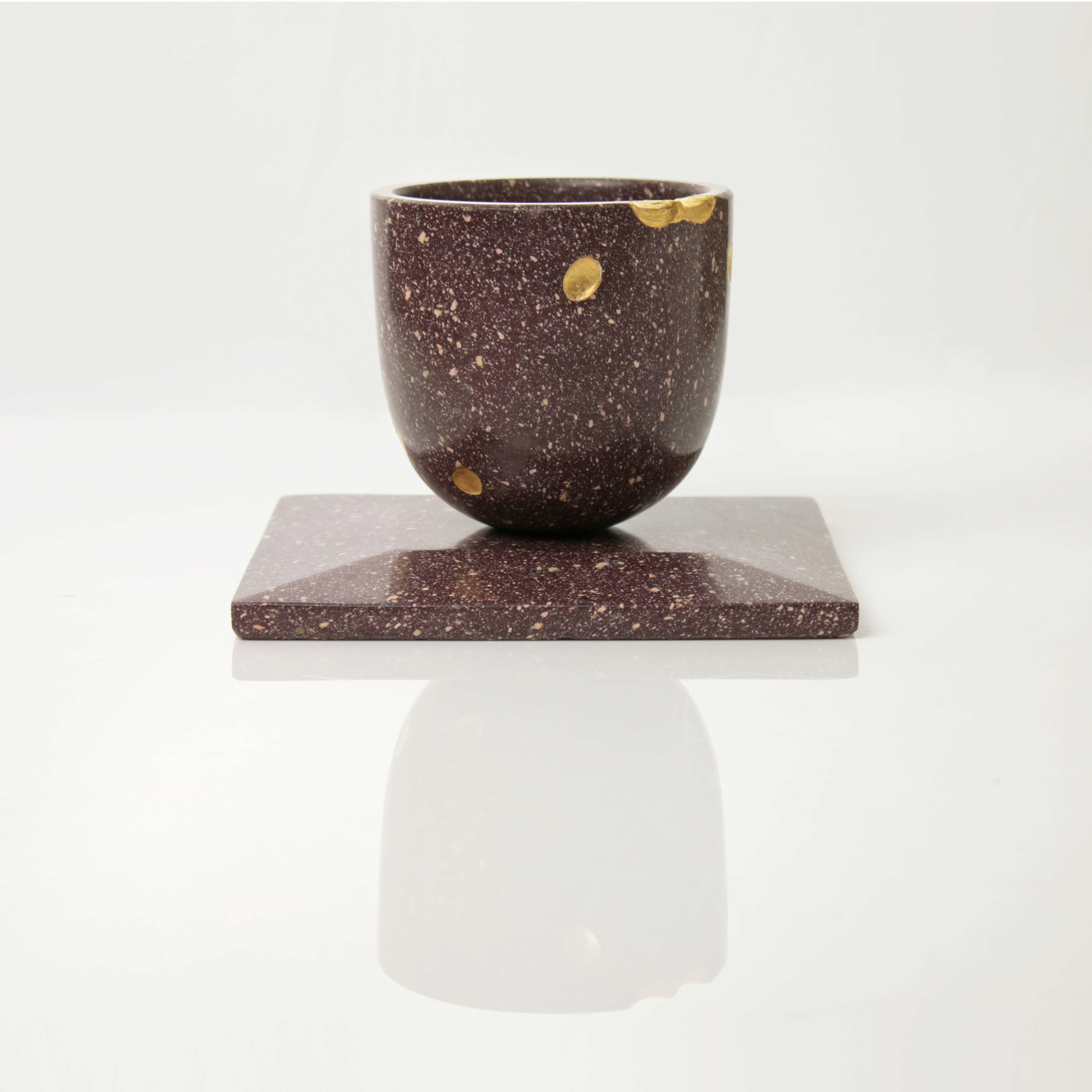
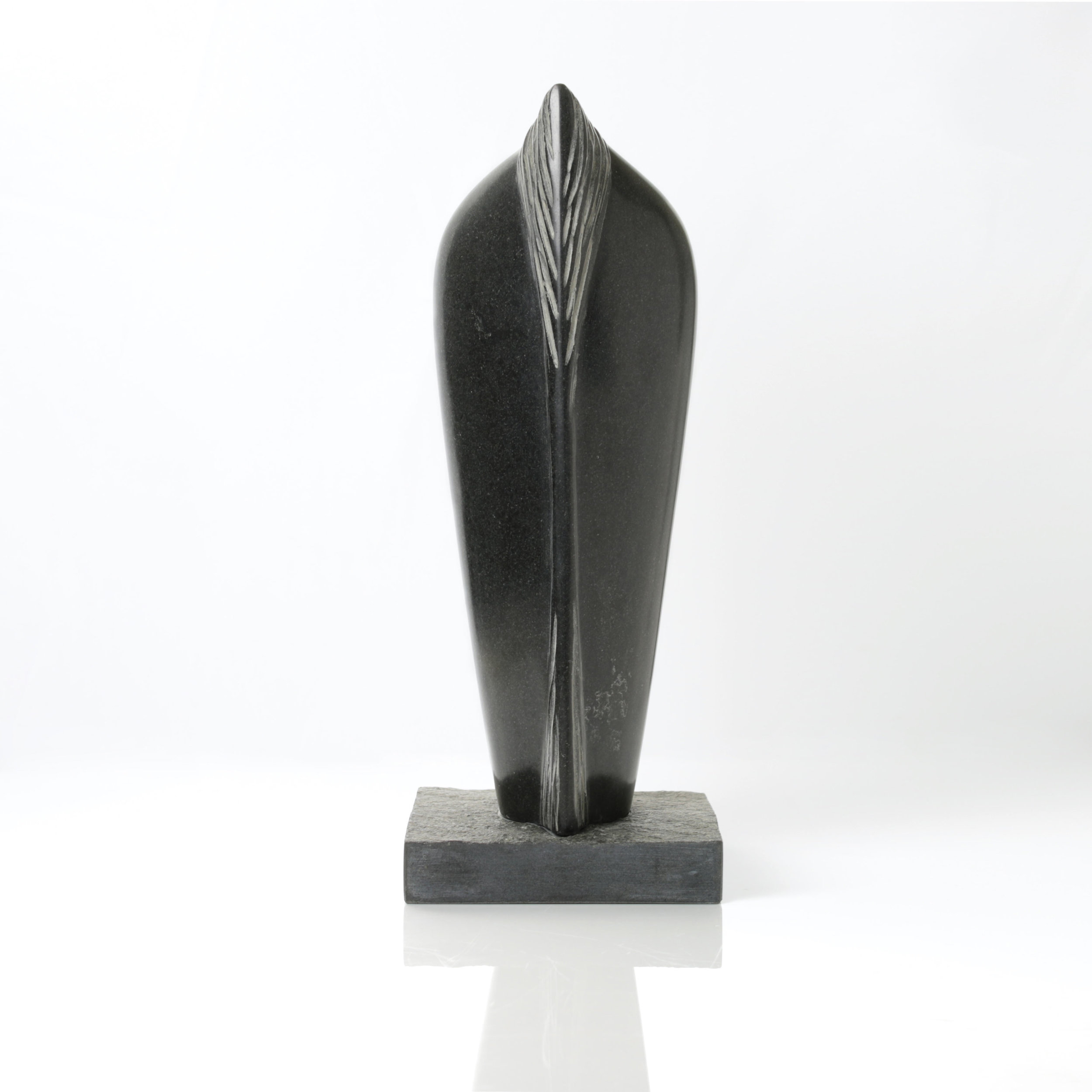
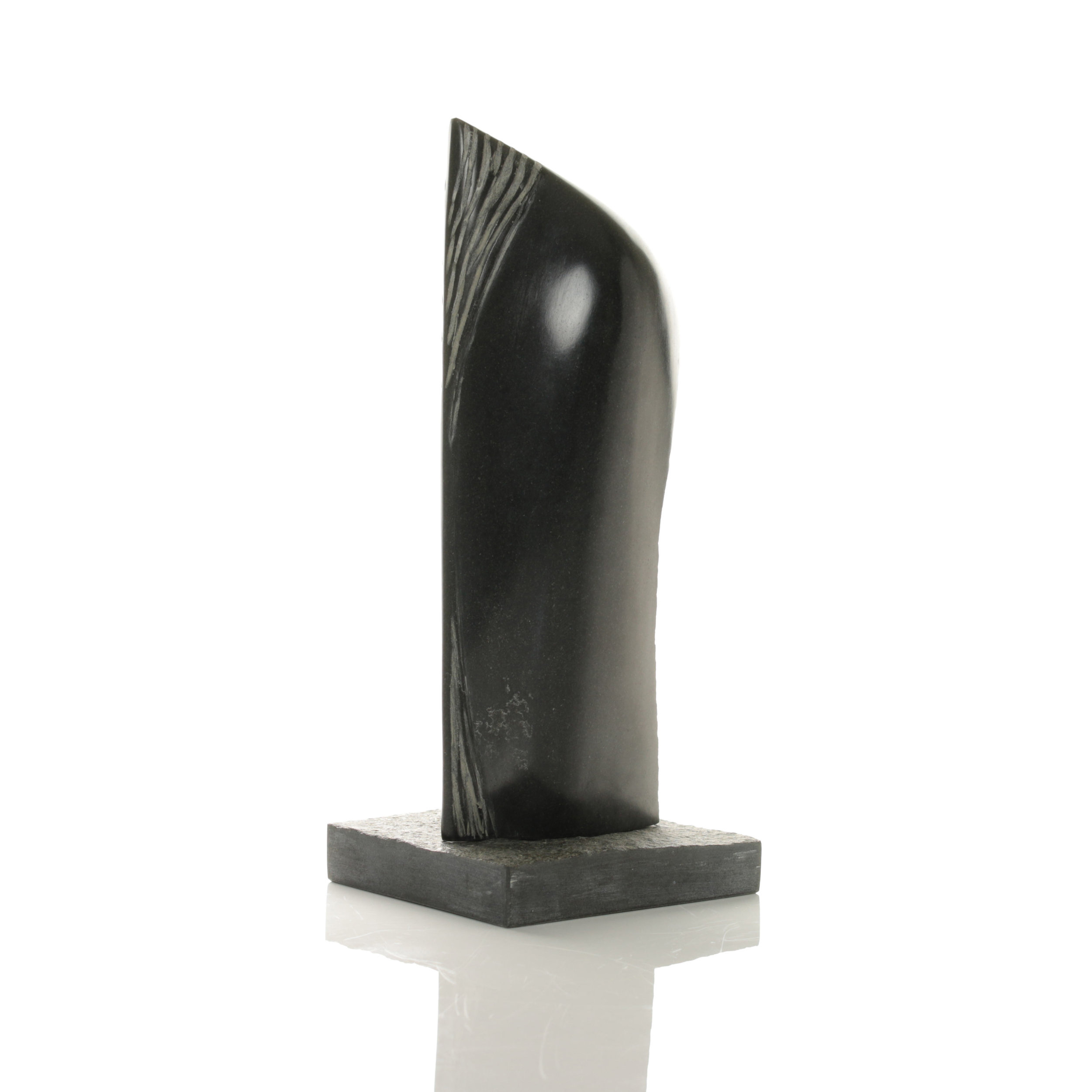
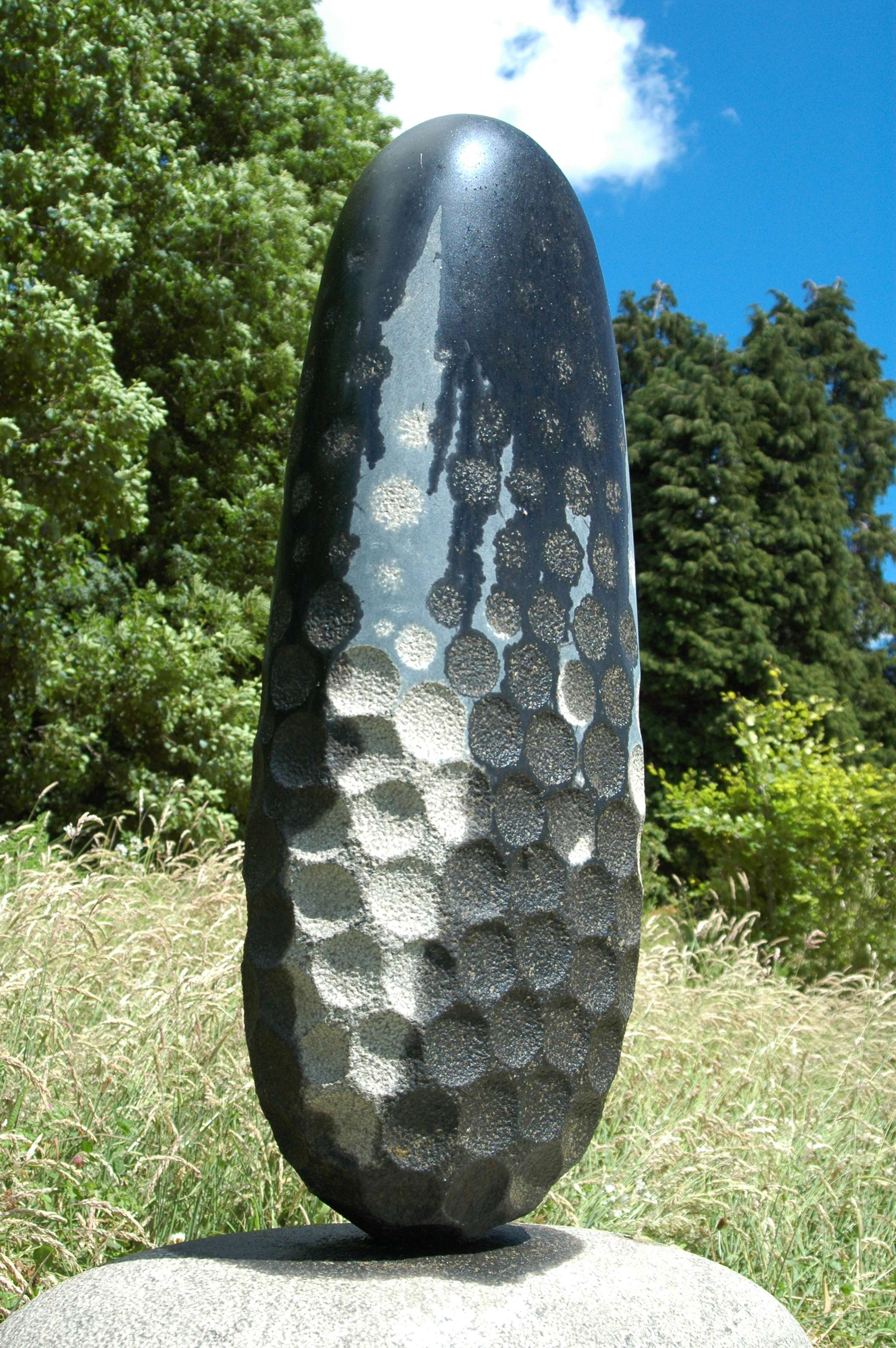
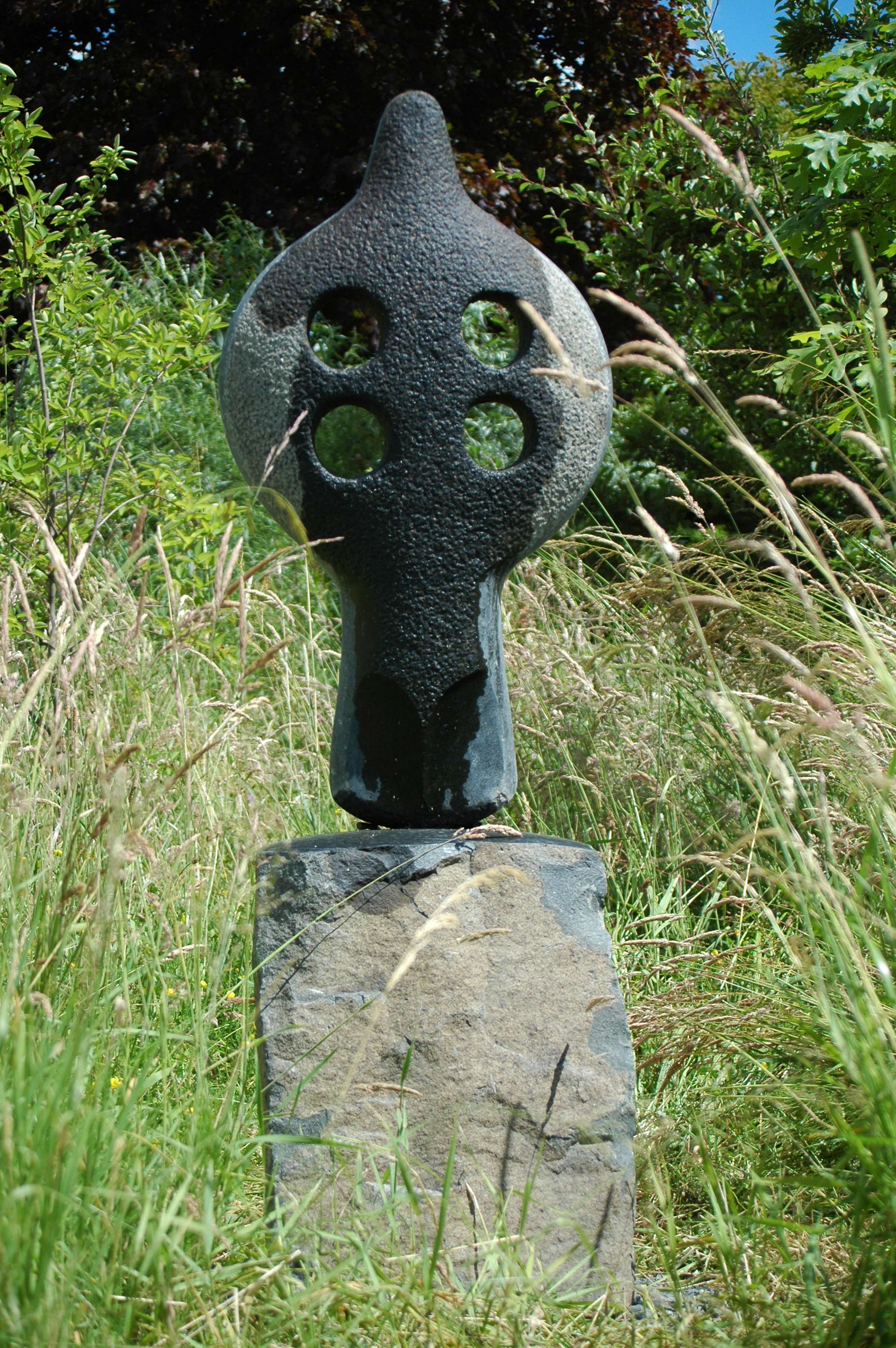
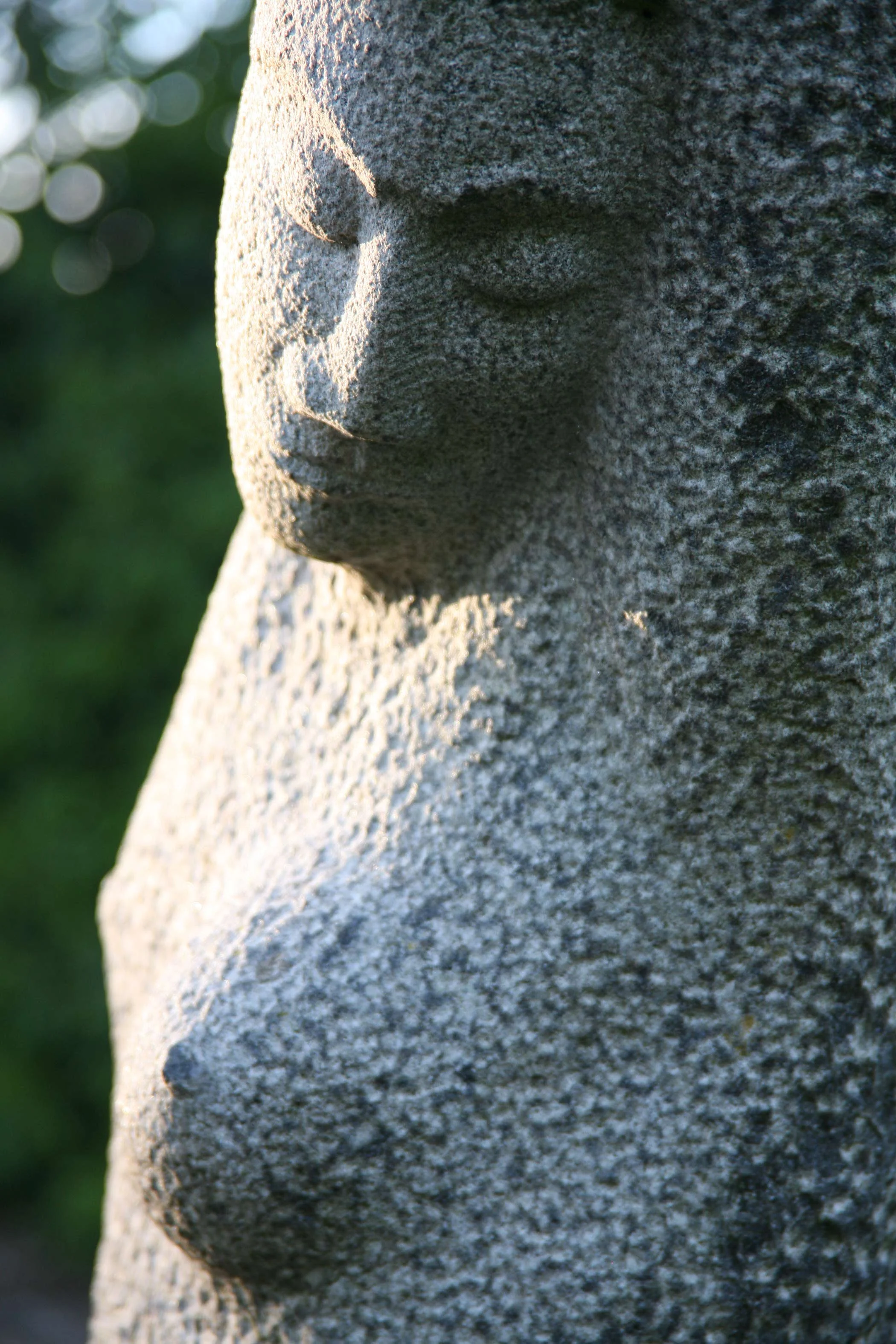
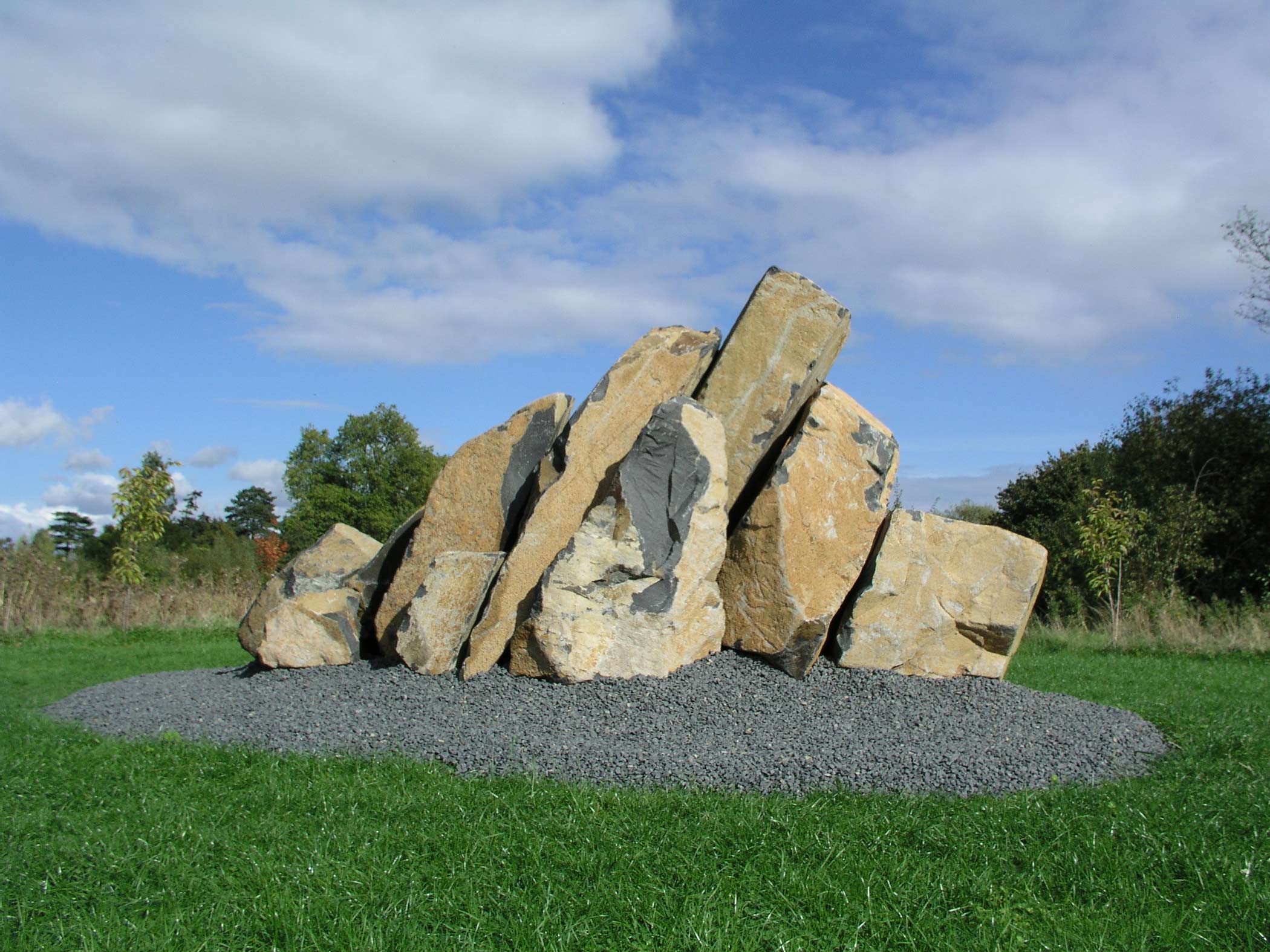
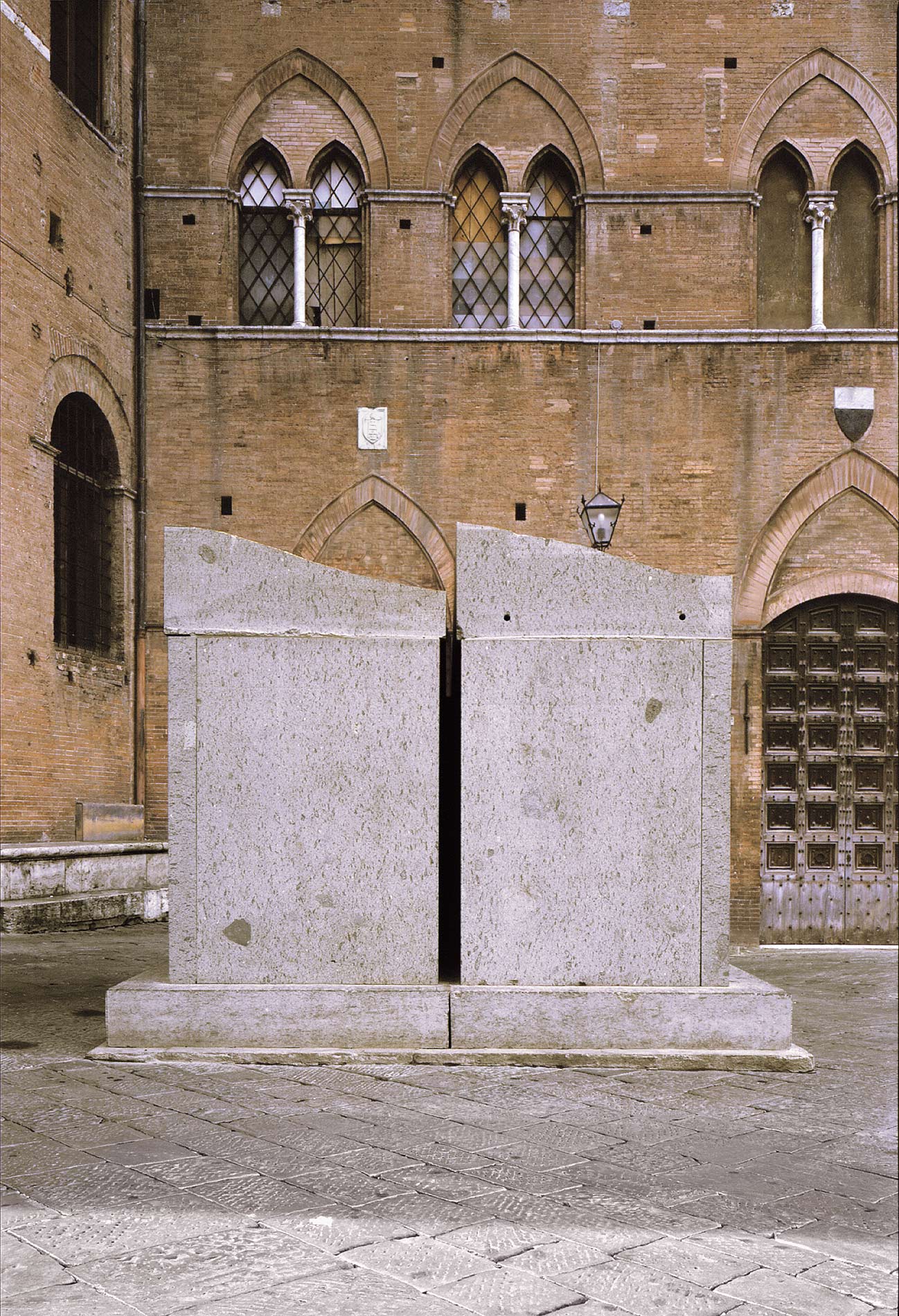
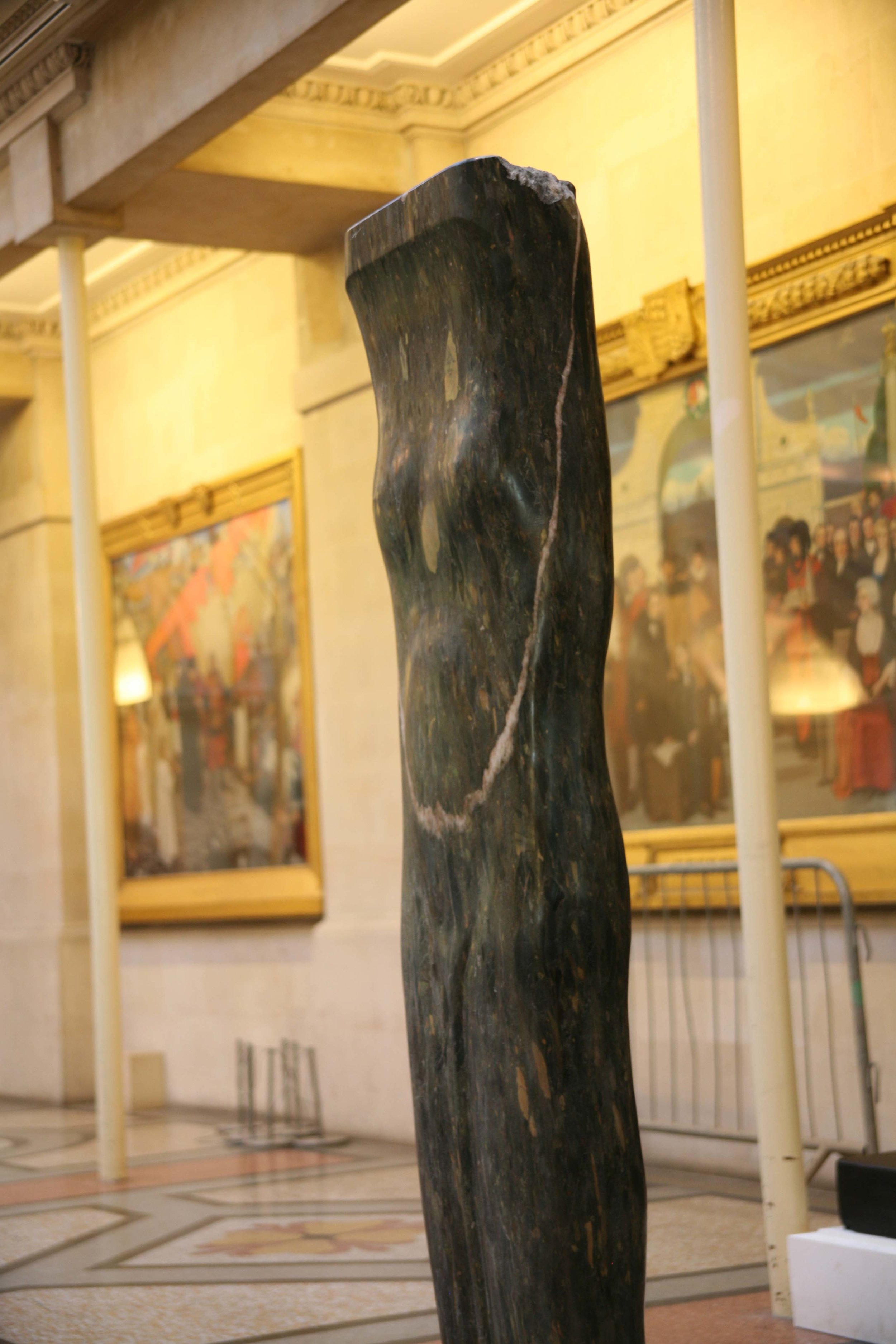Stephen Cox: Myth
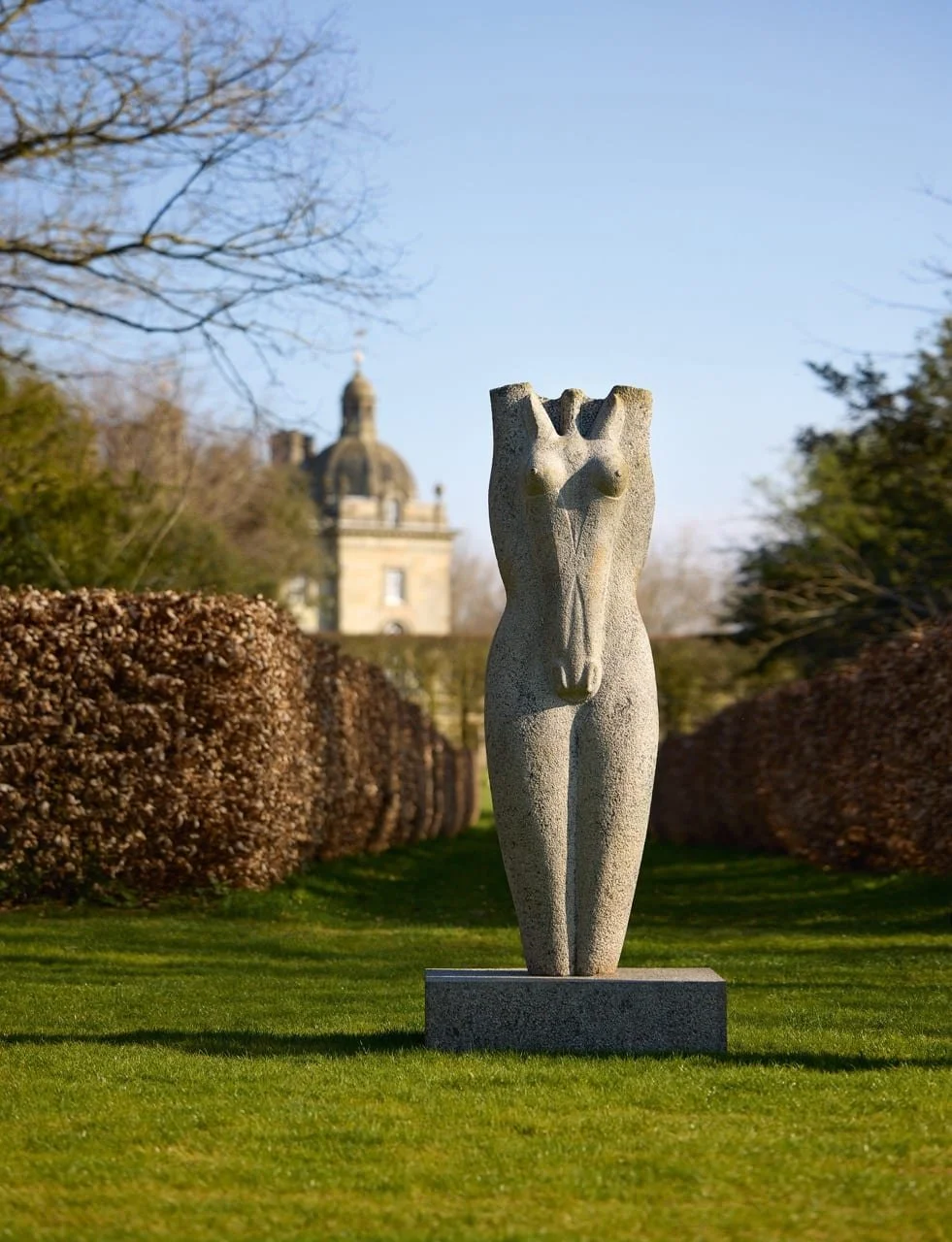
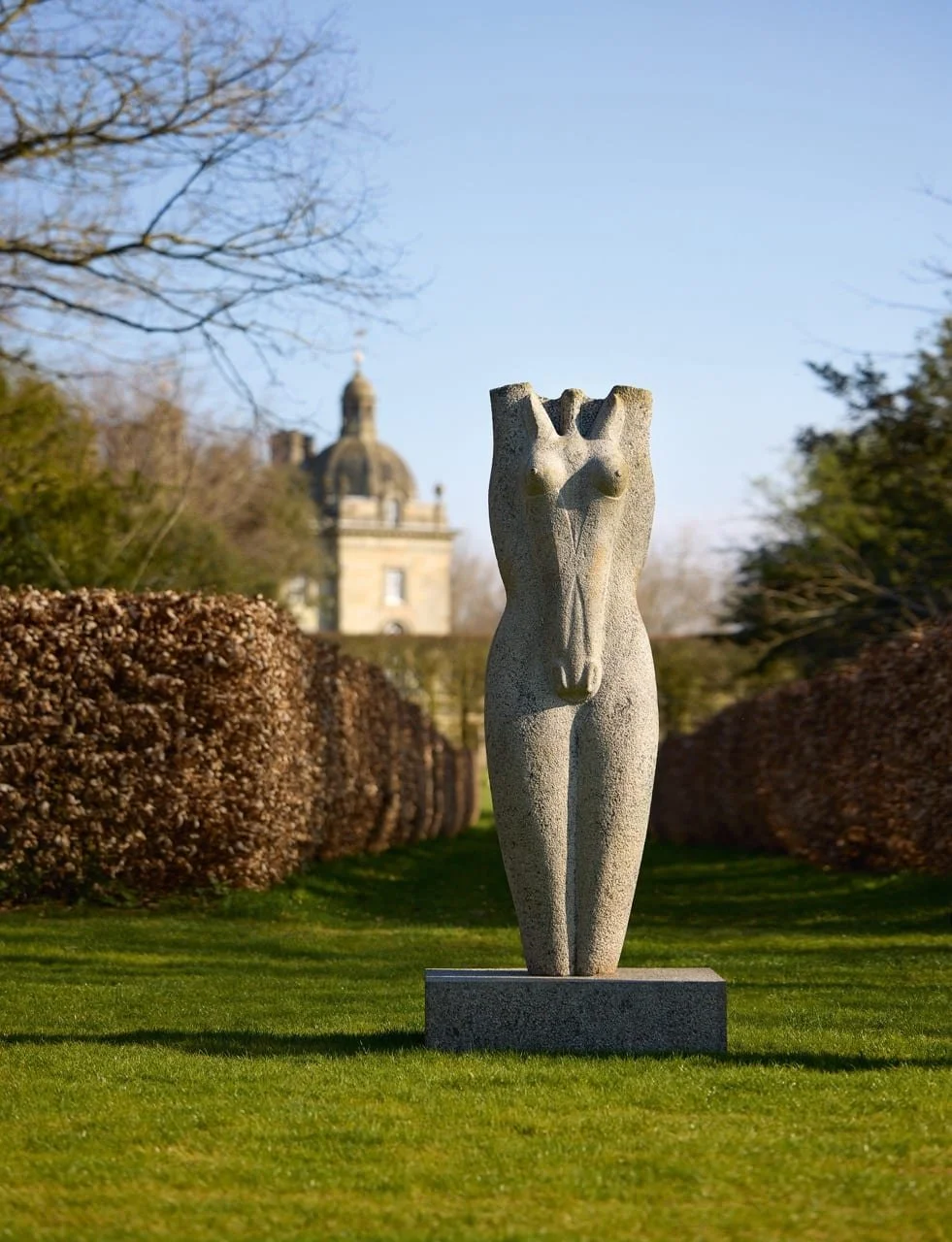
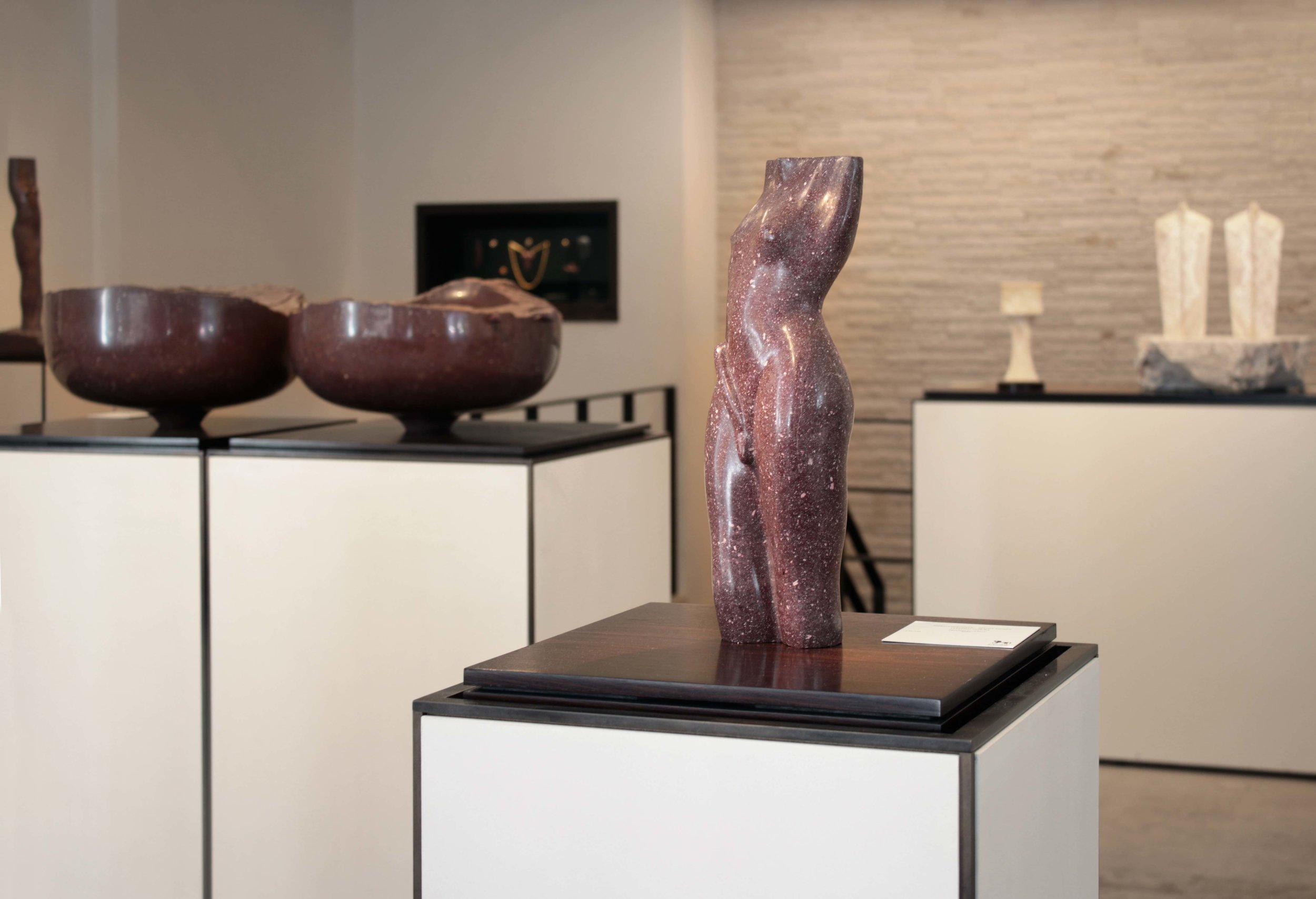
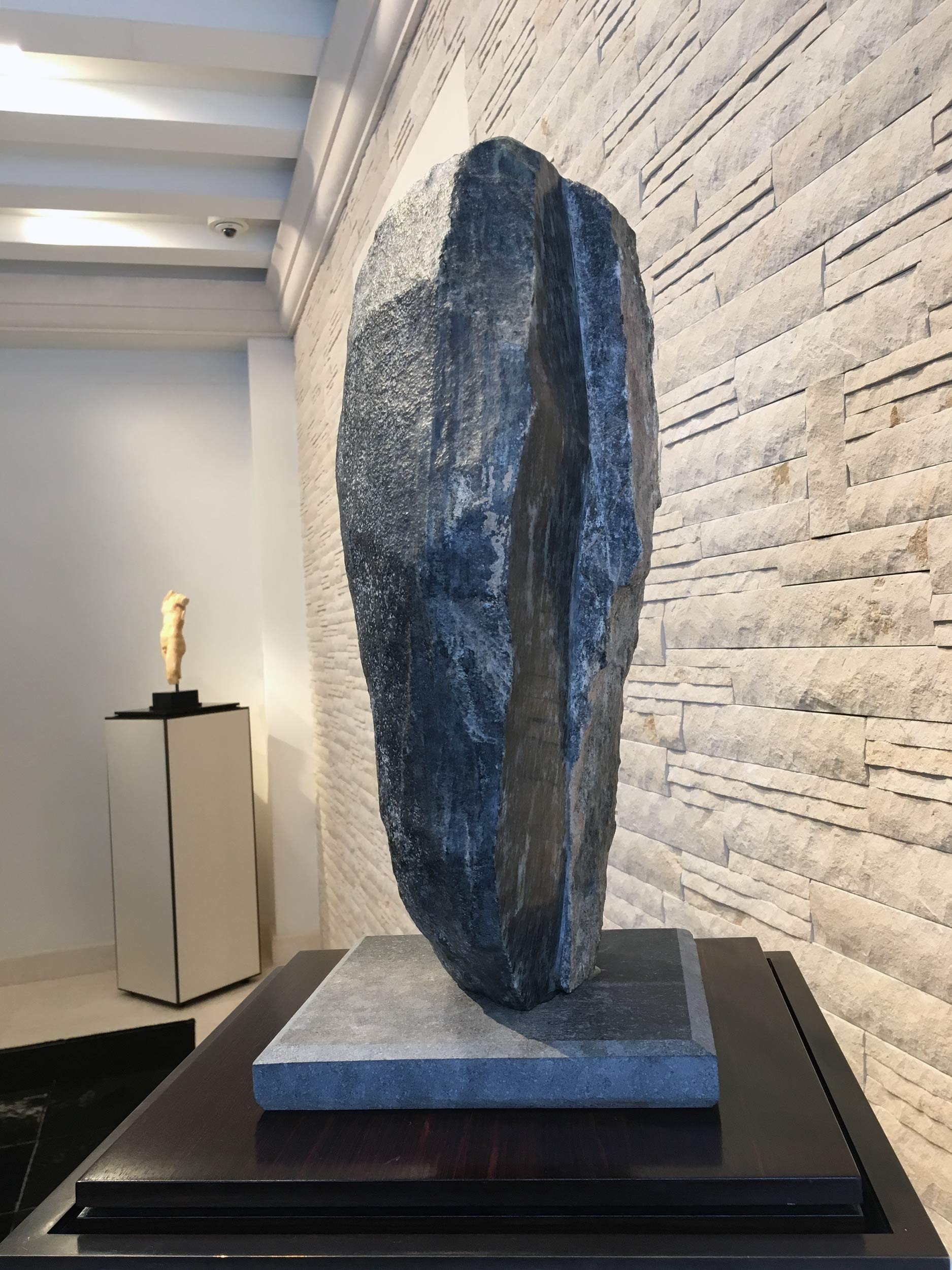
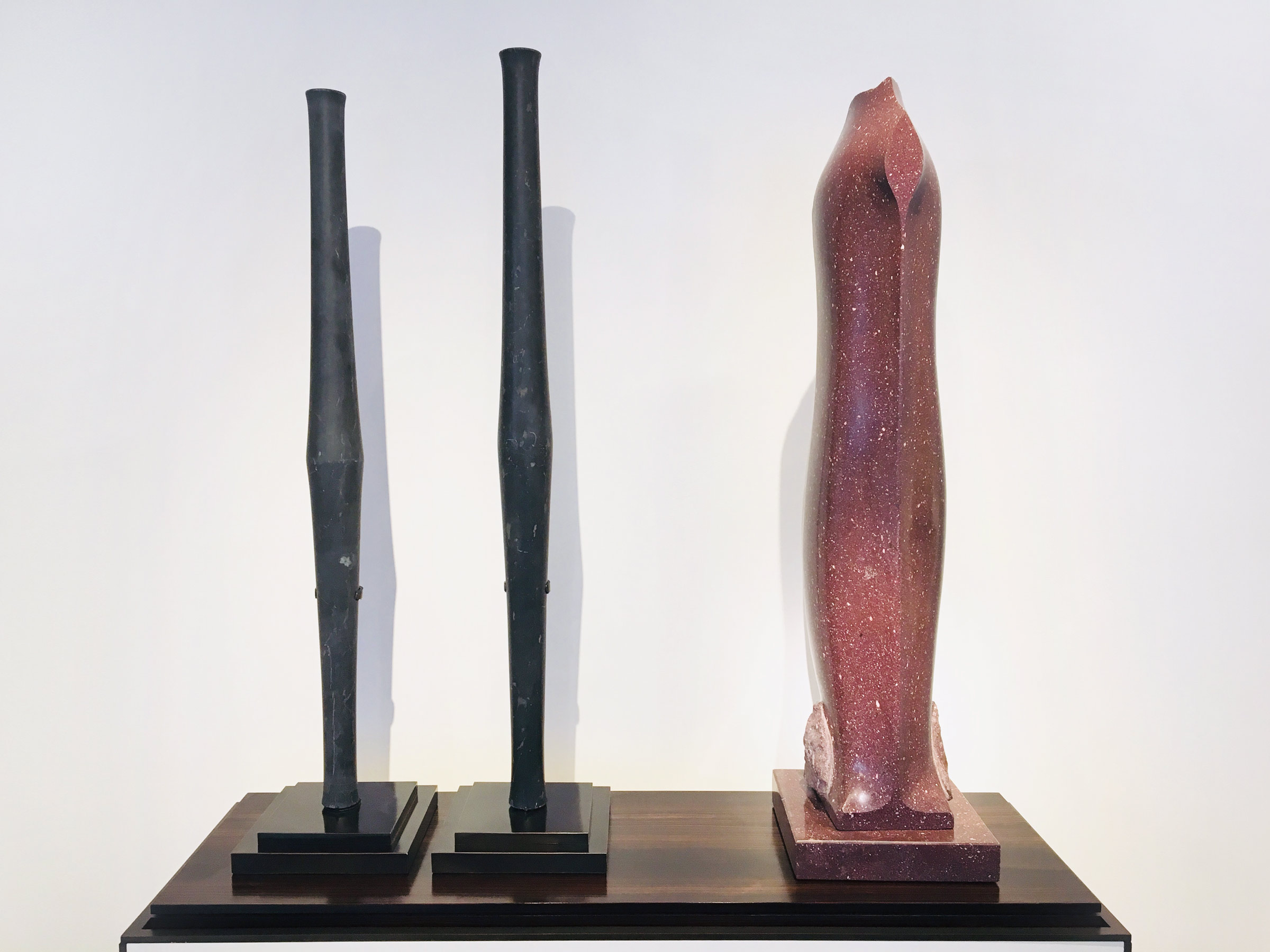
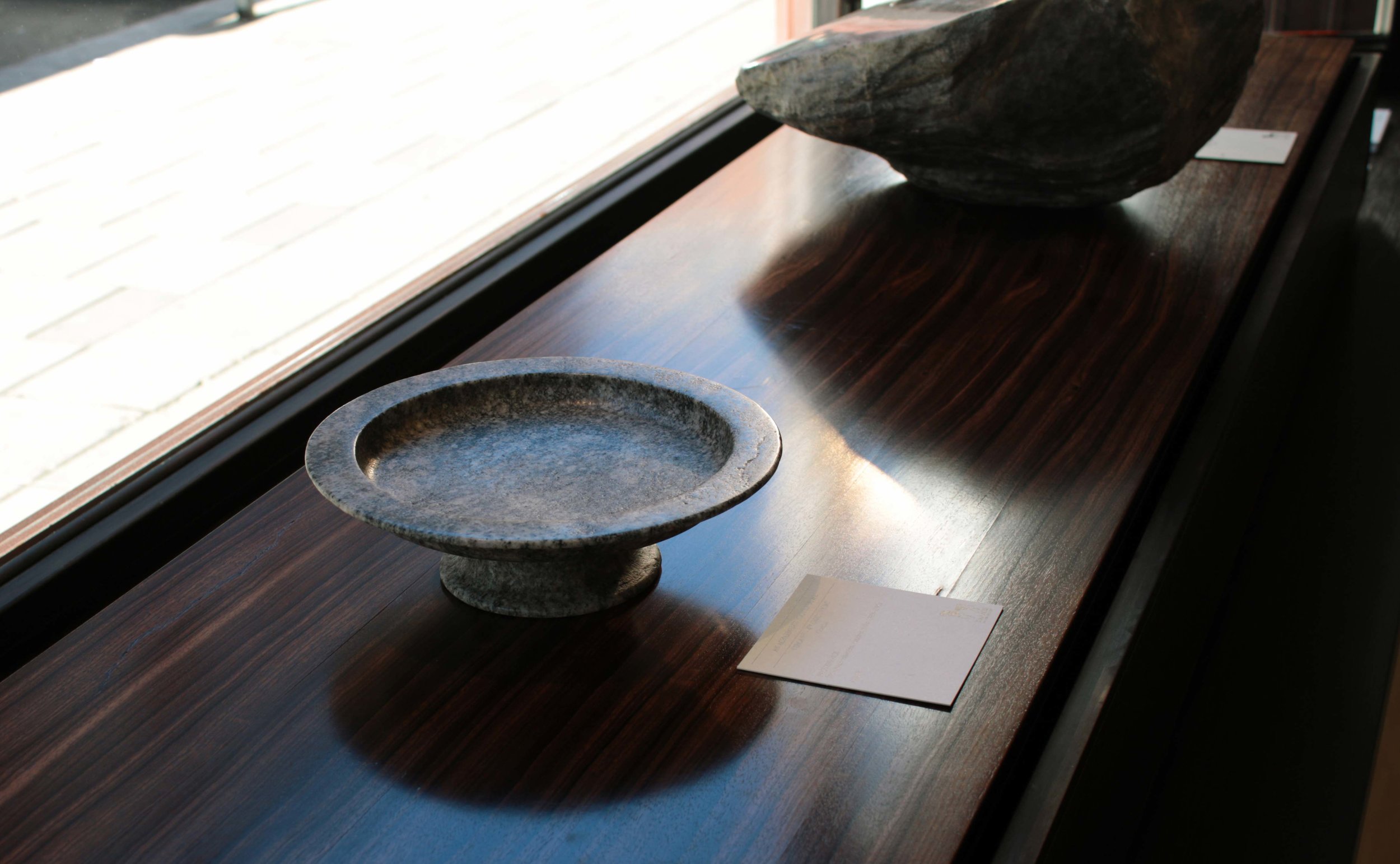
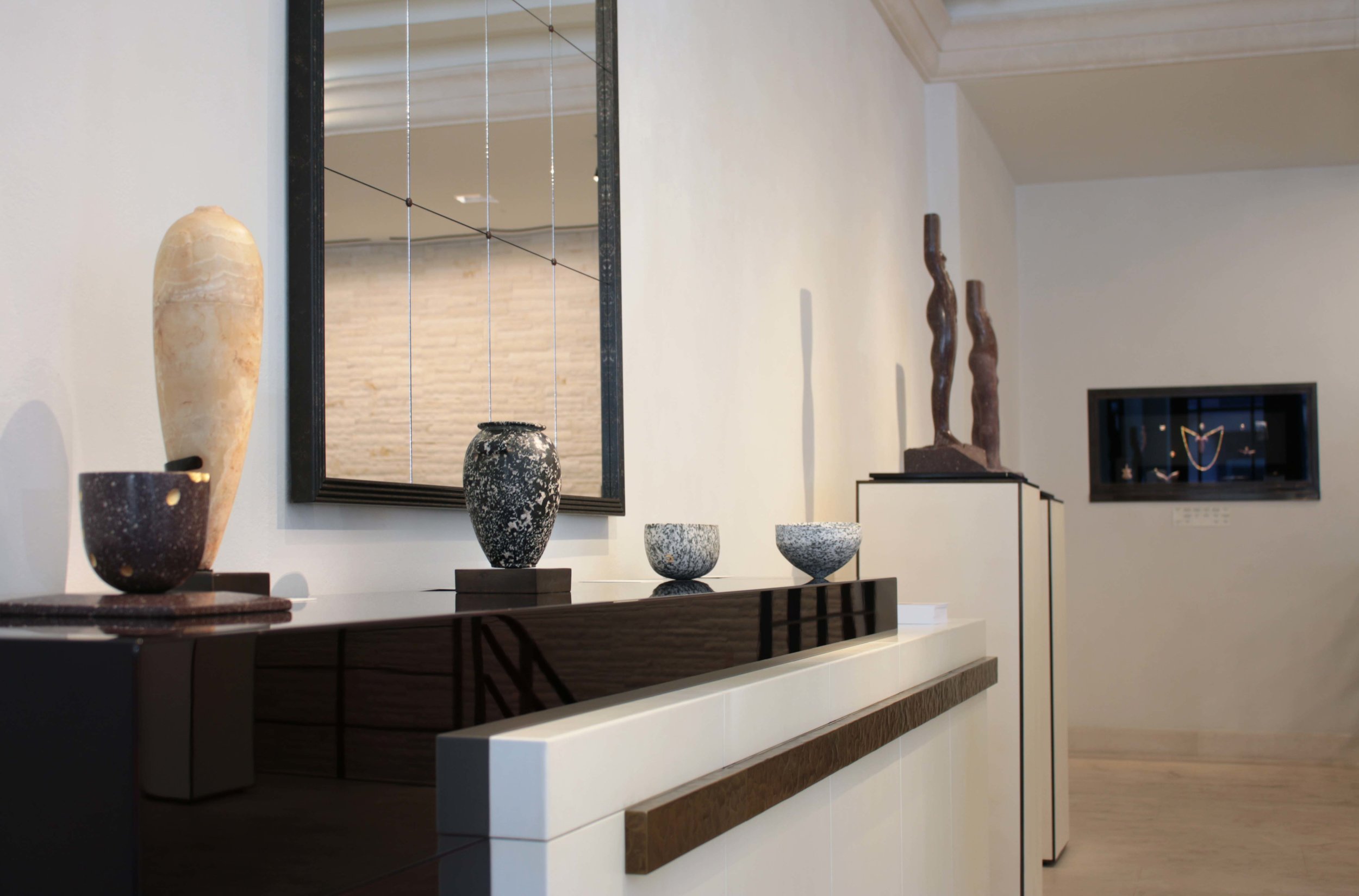
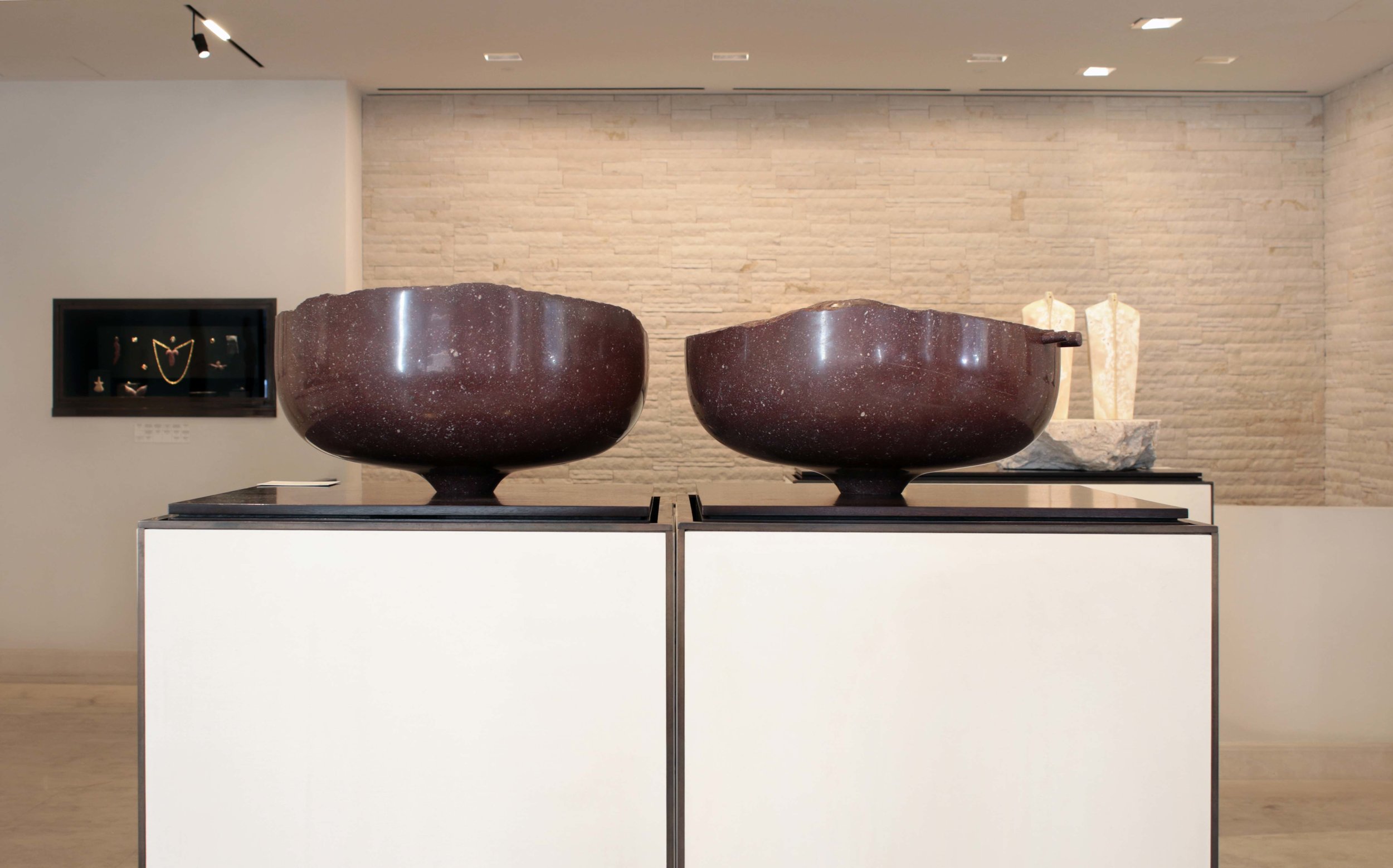
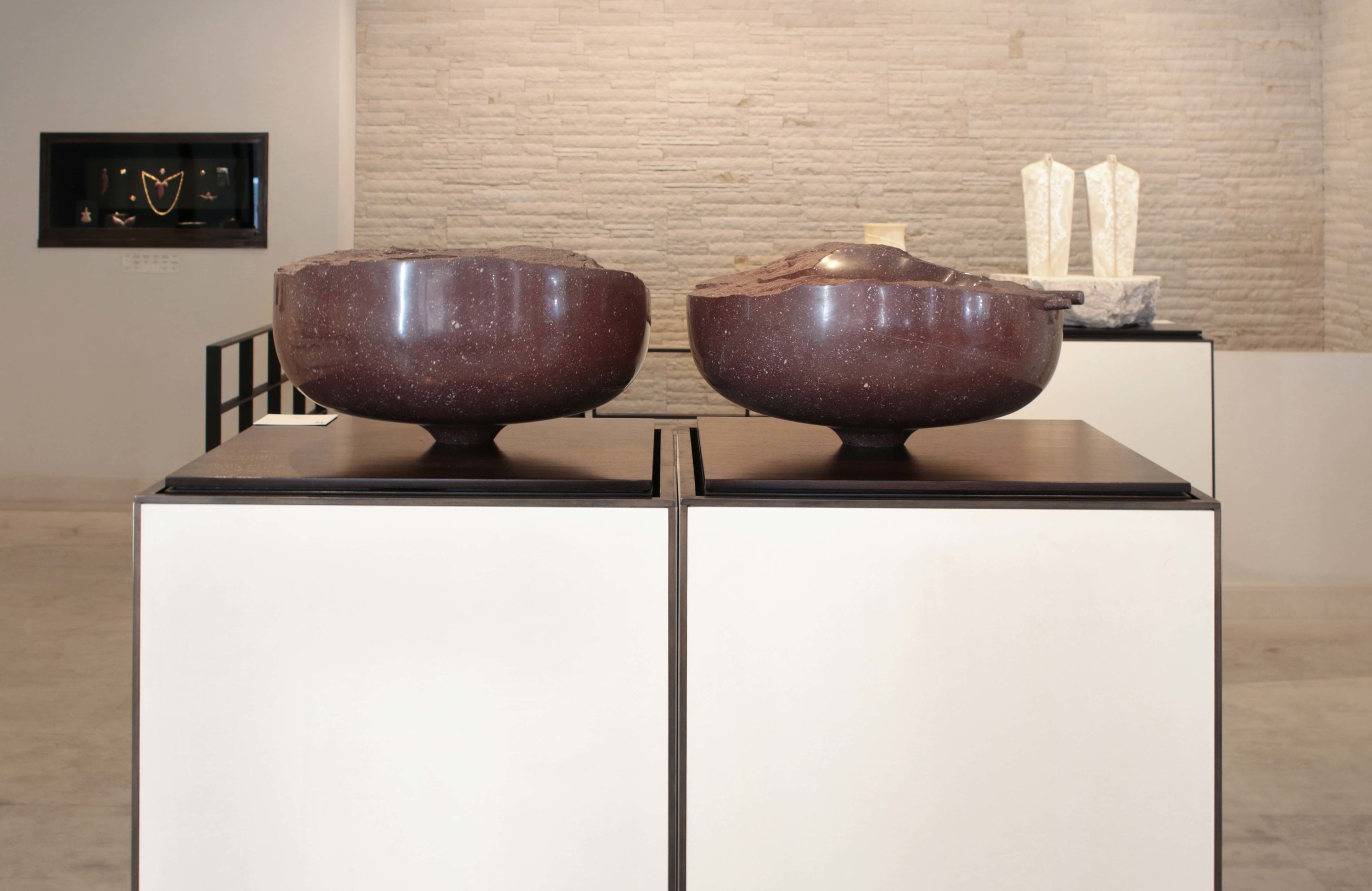
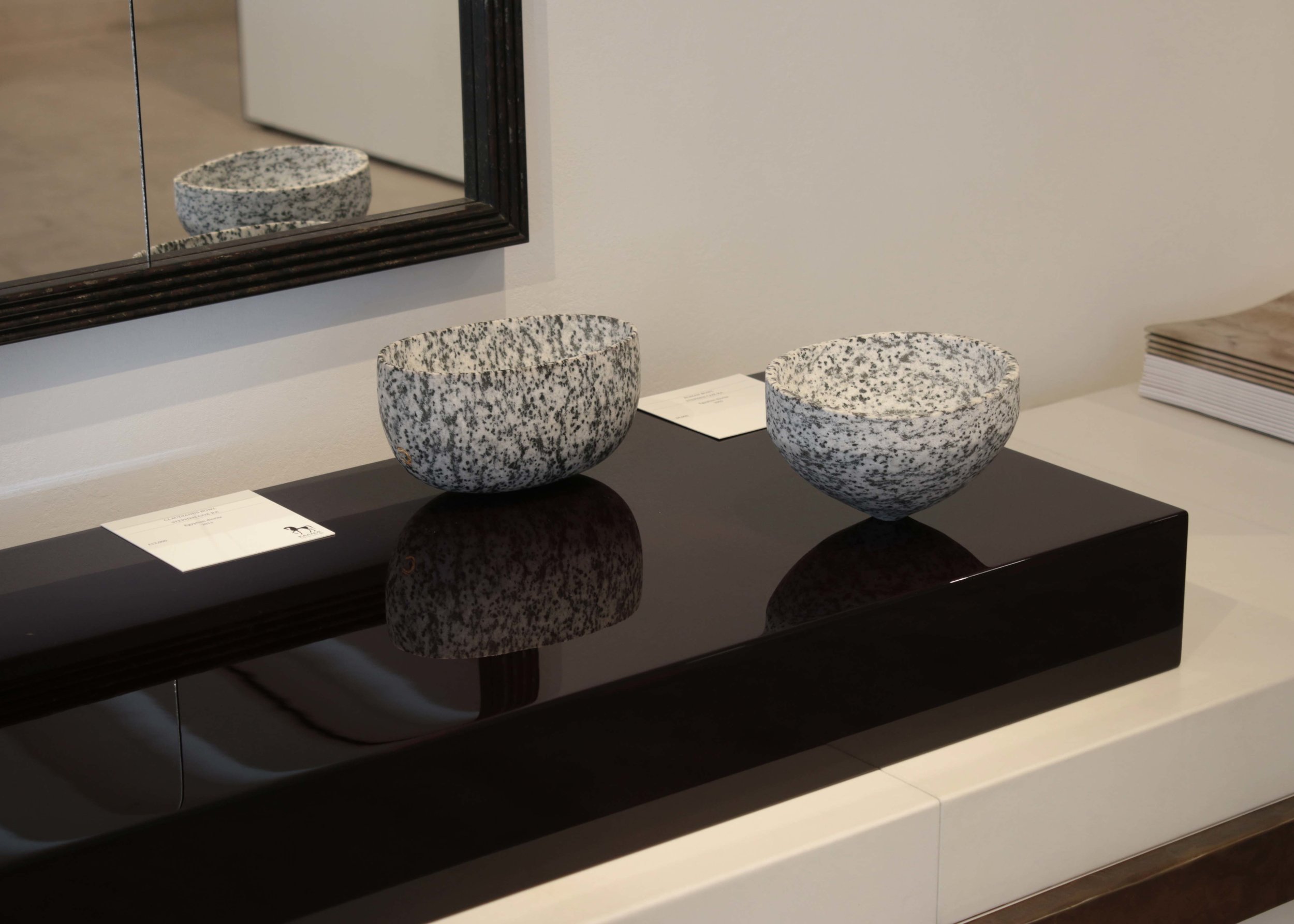
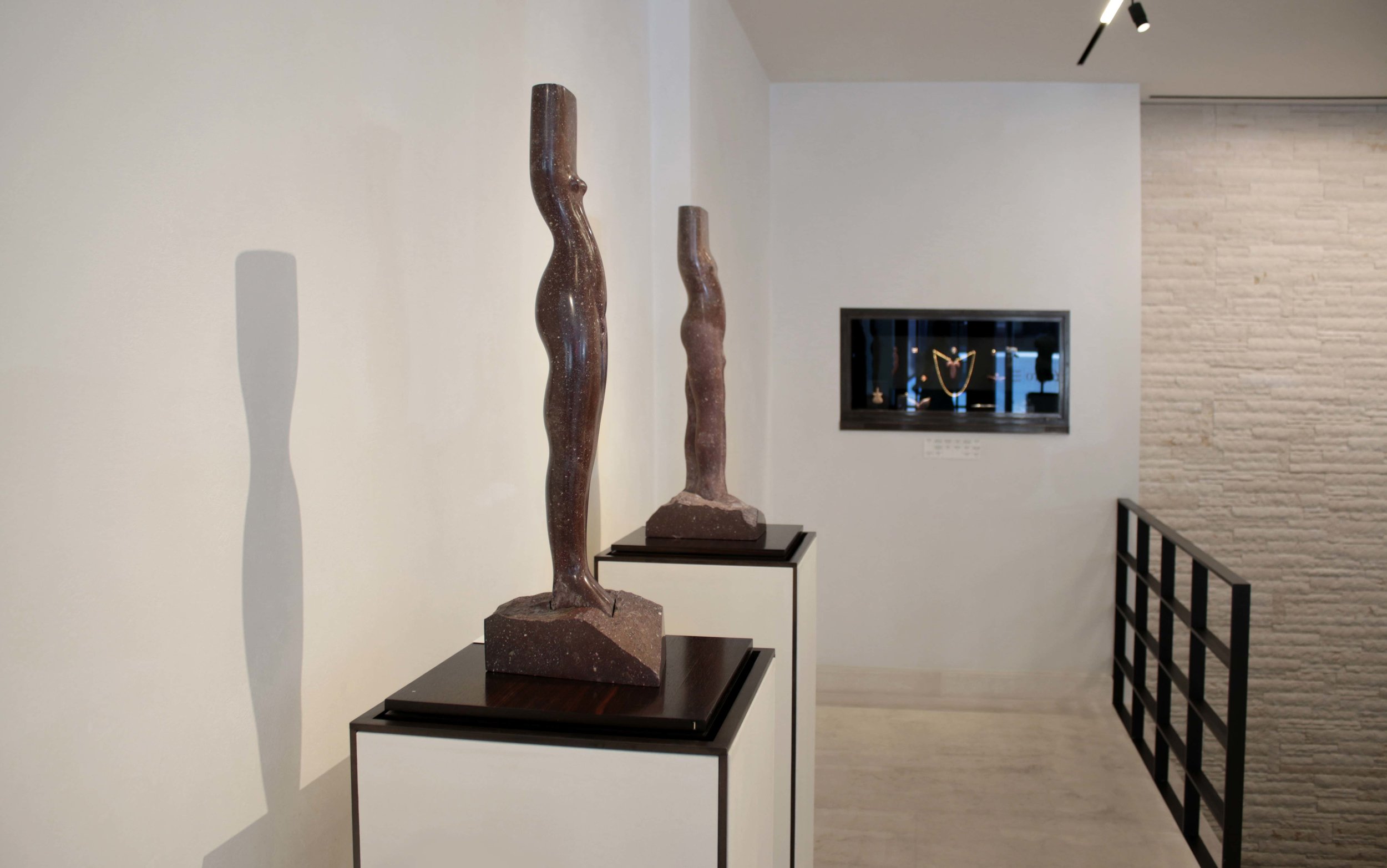
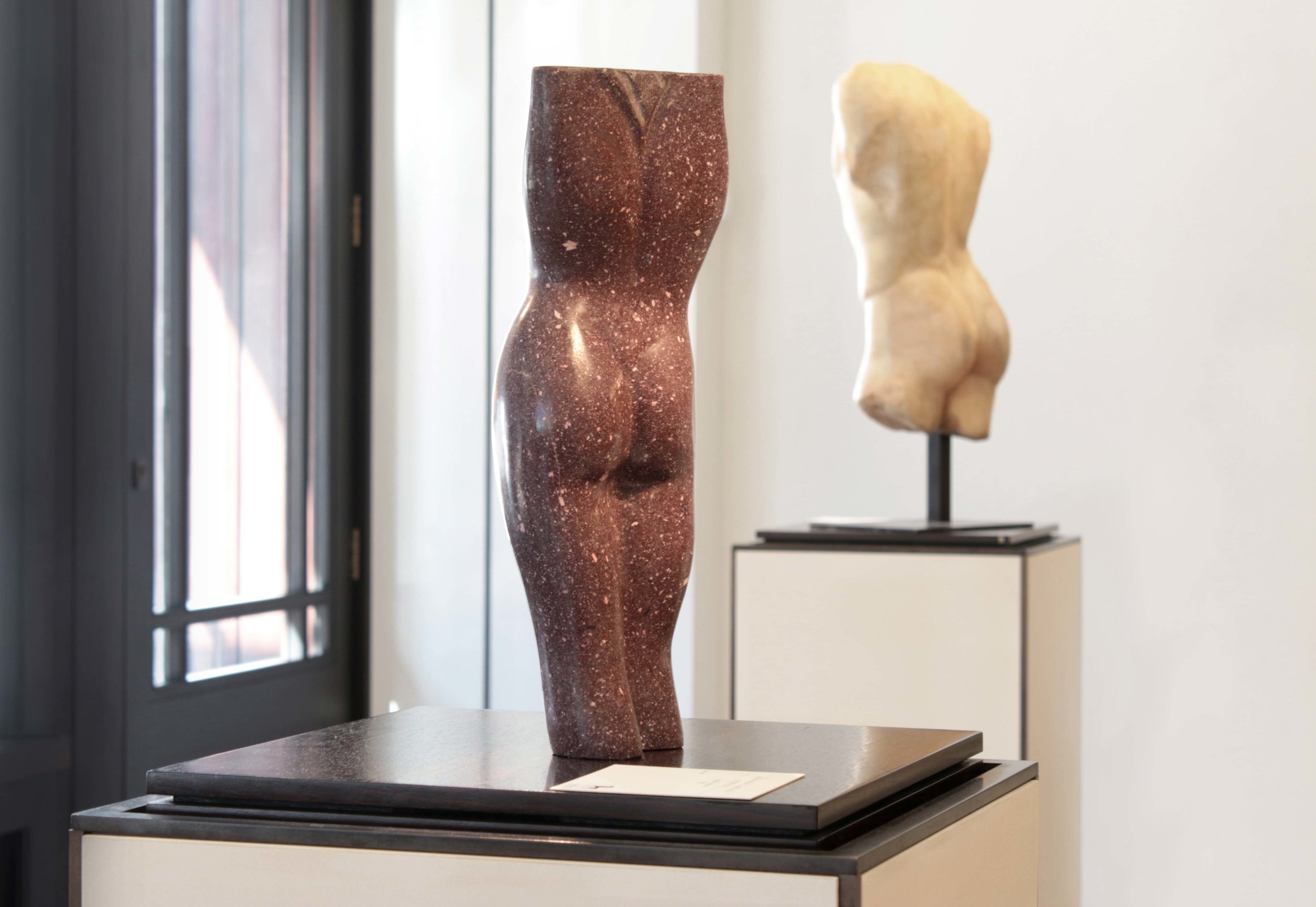
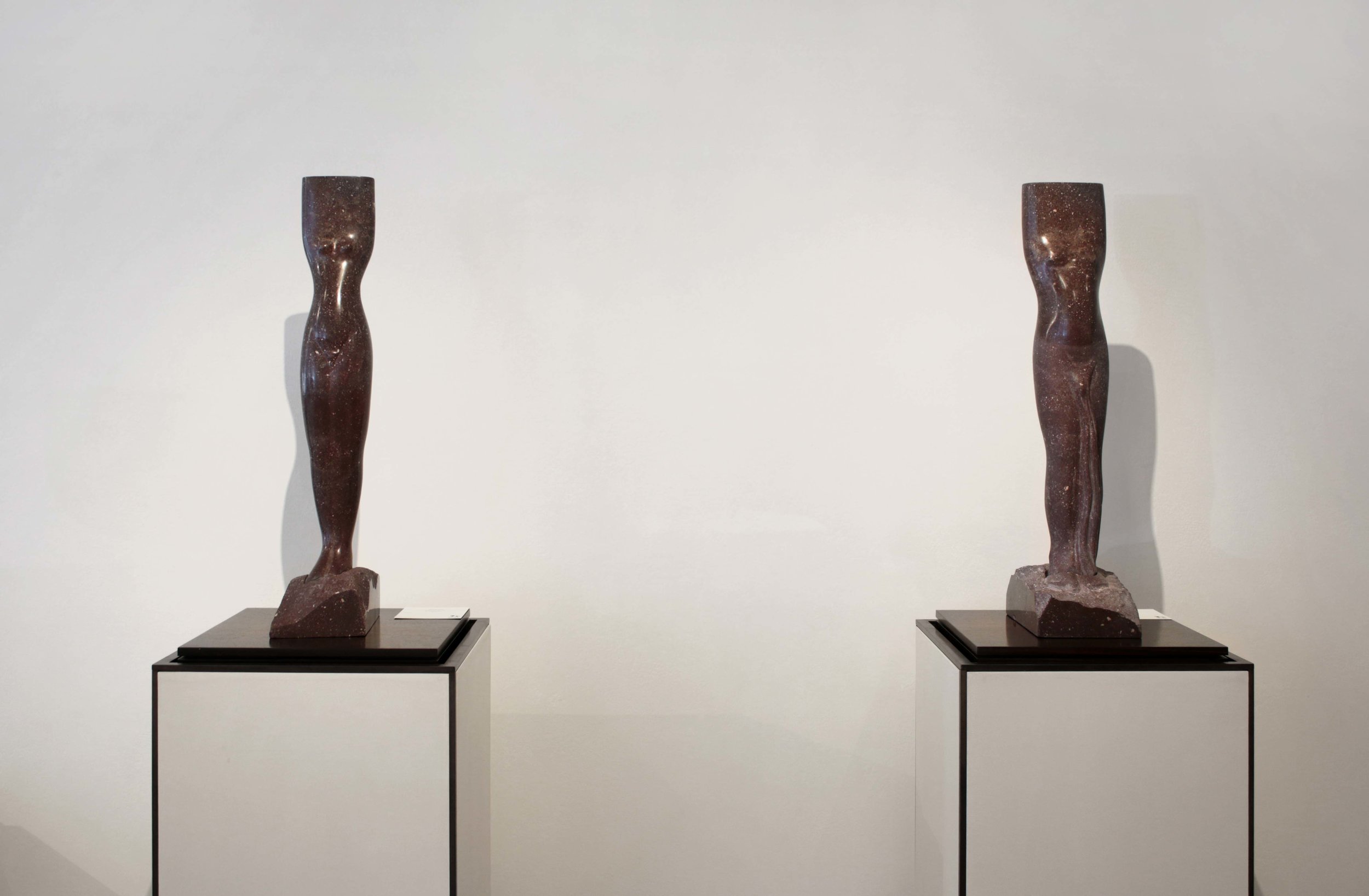
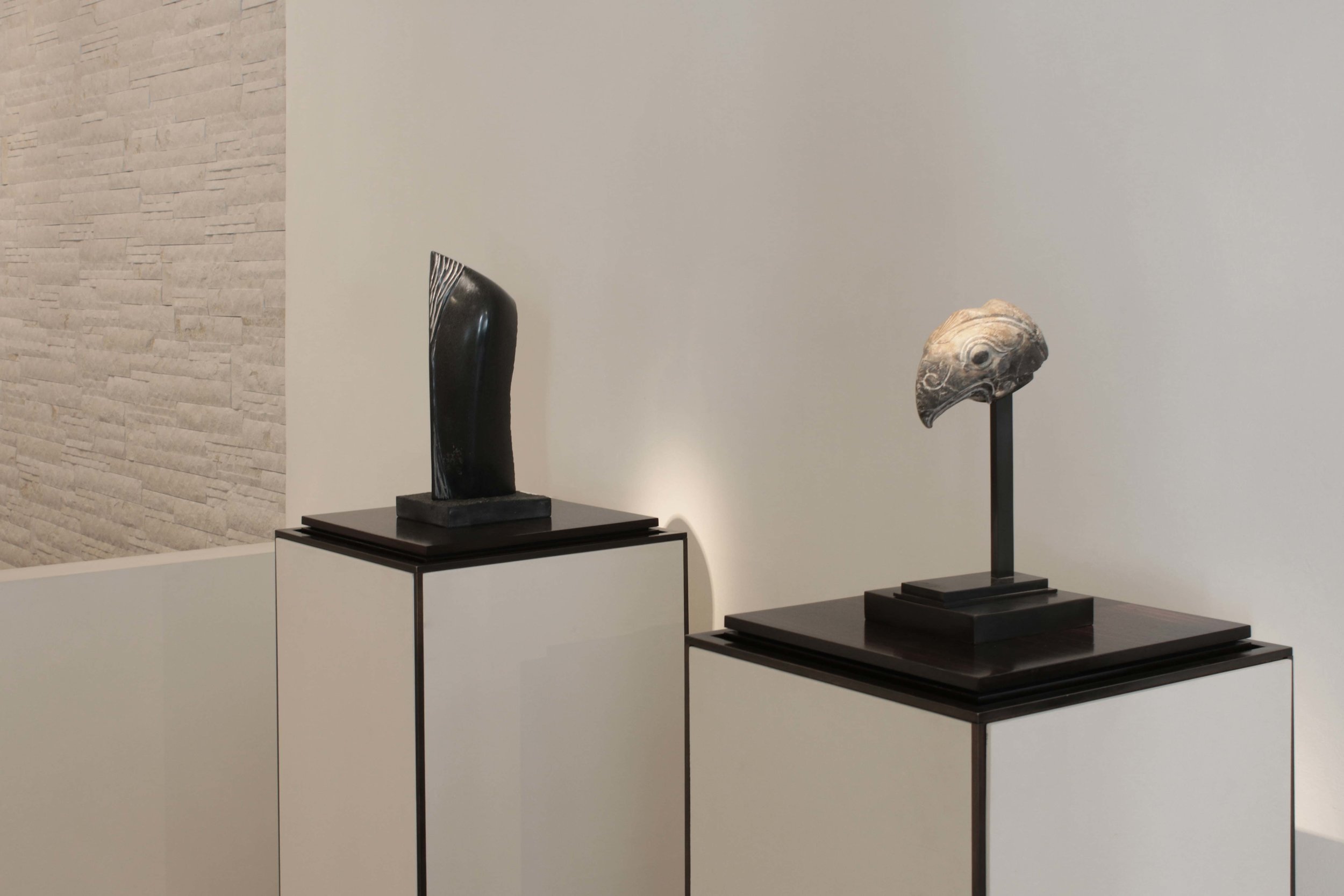
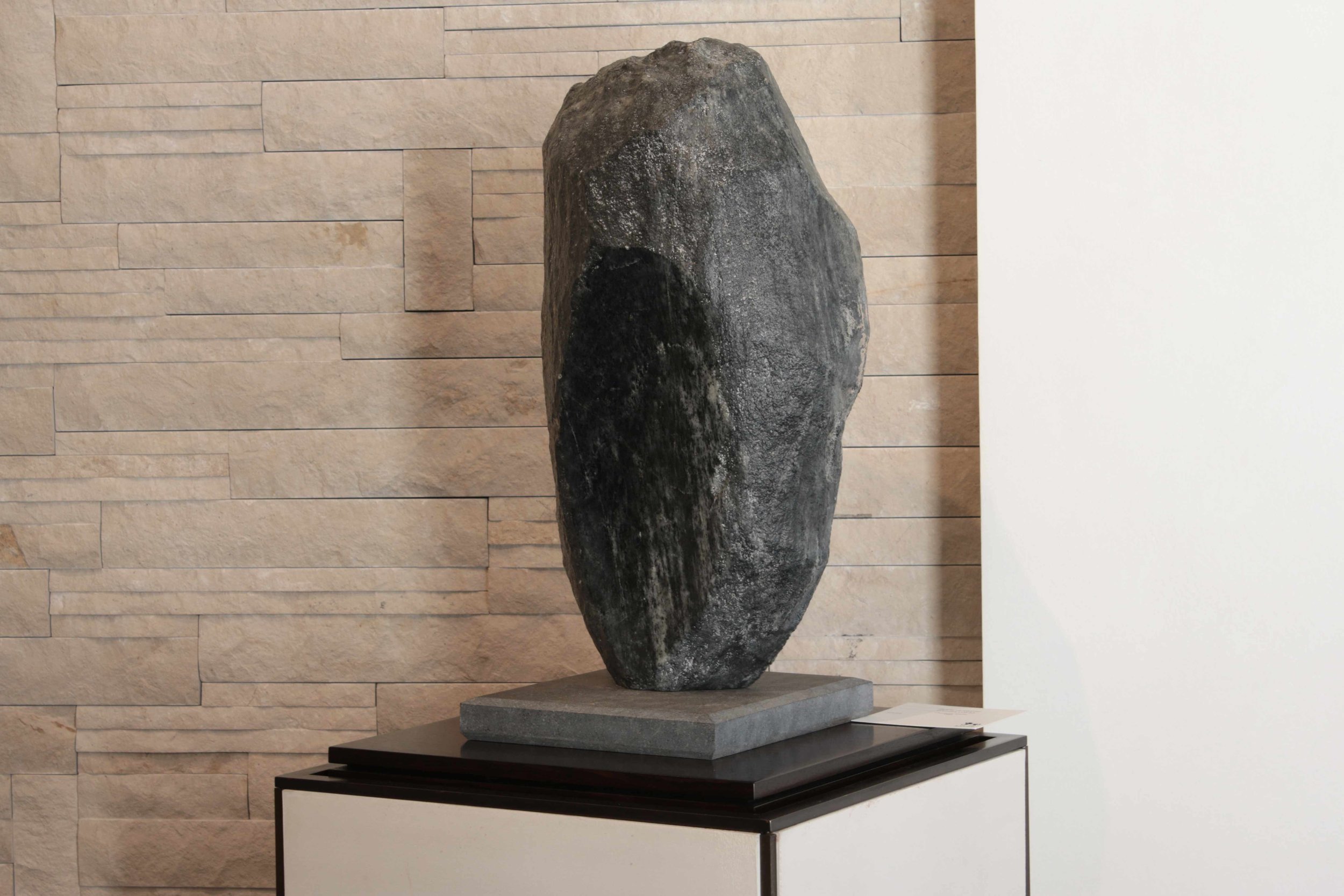
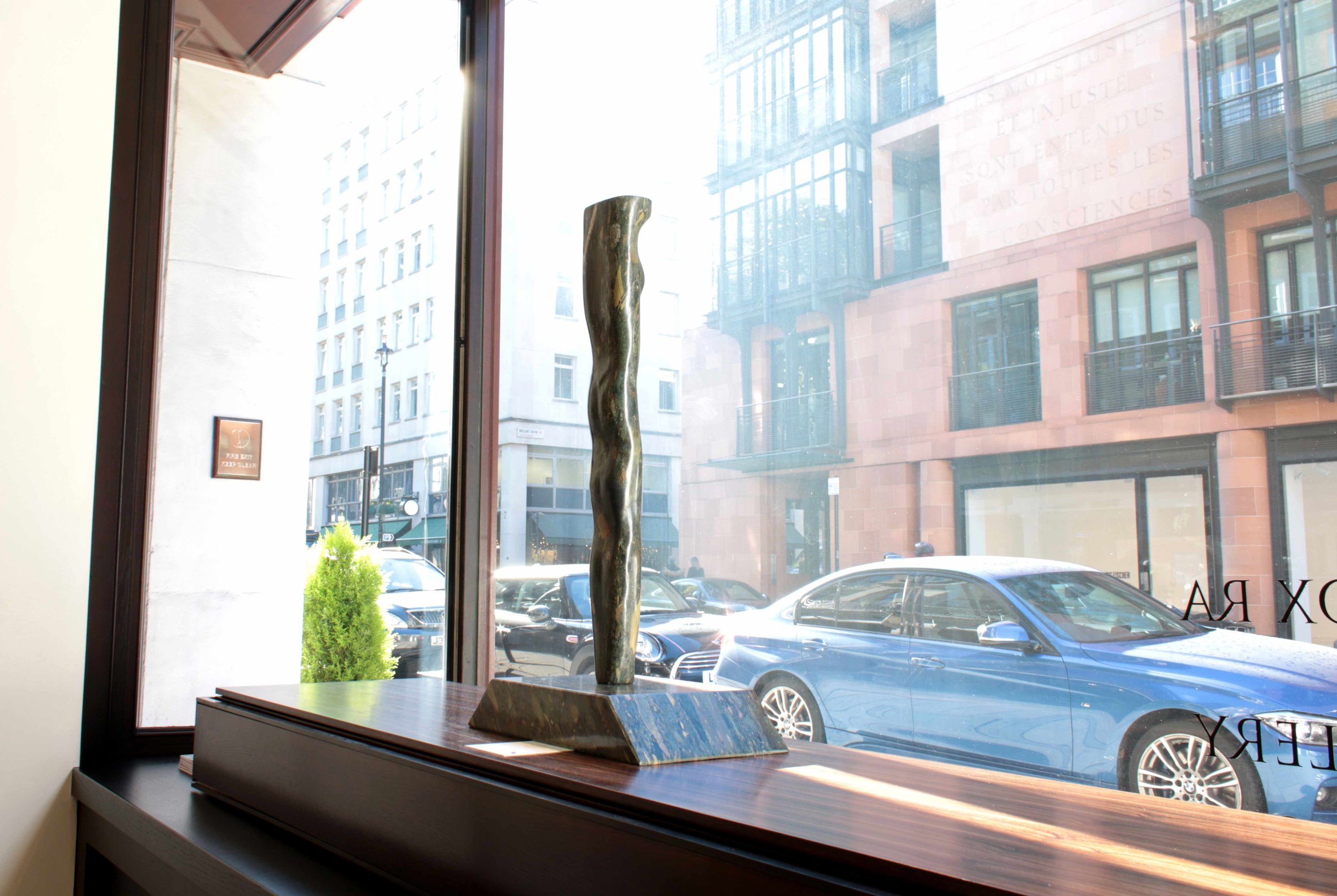
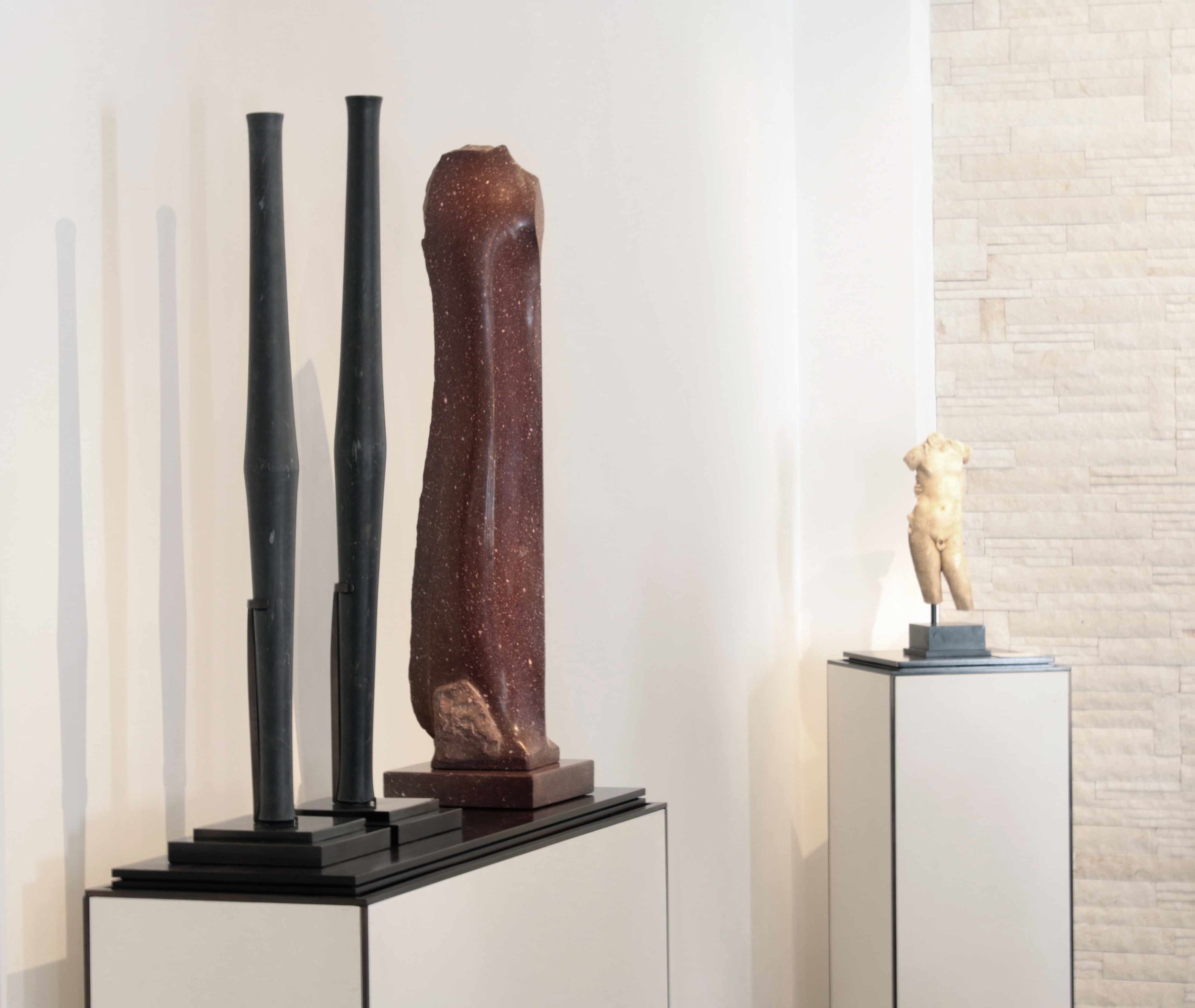
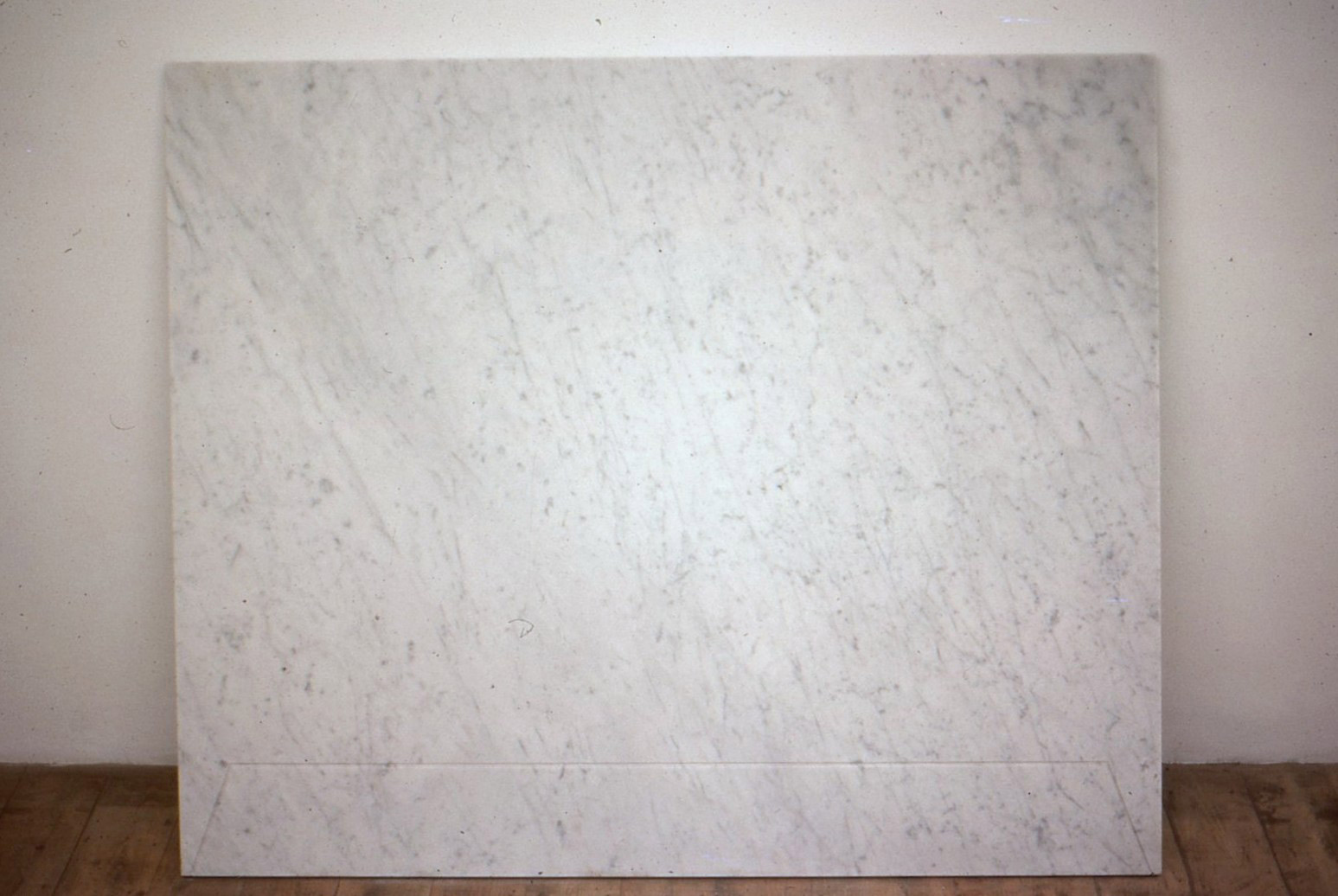
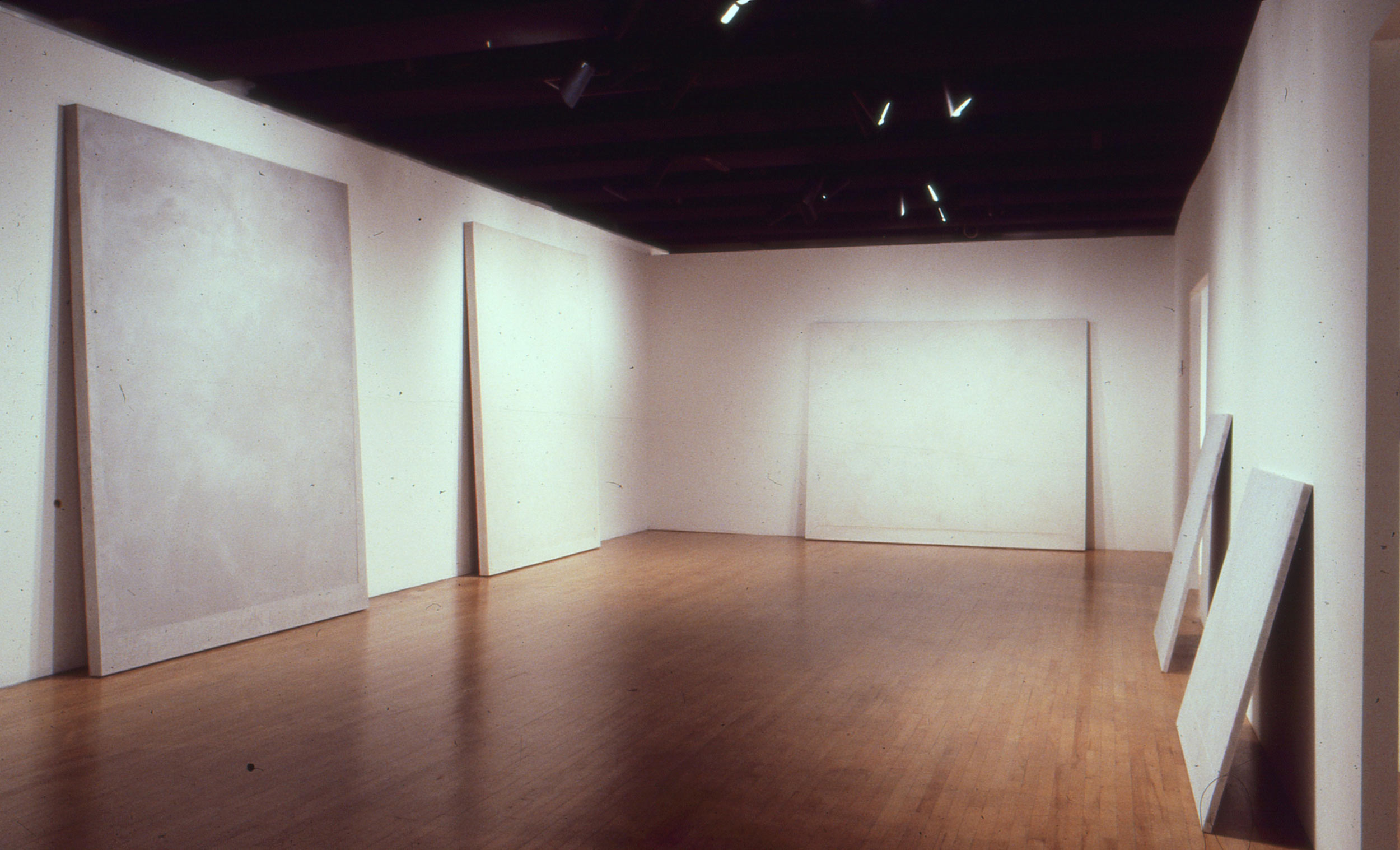
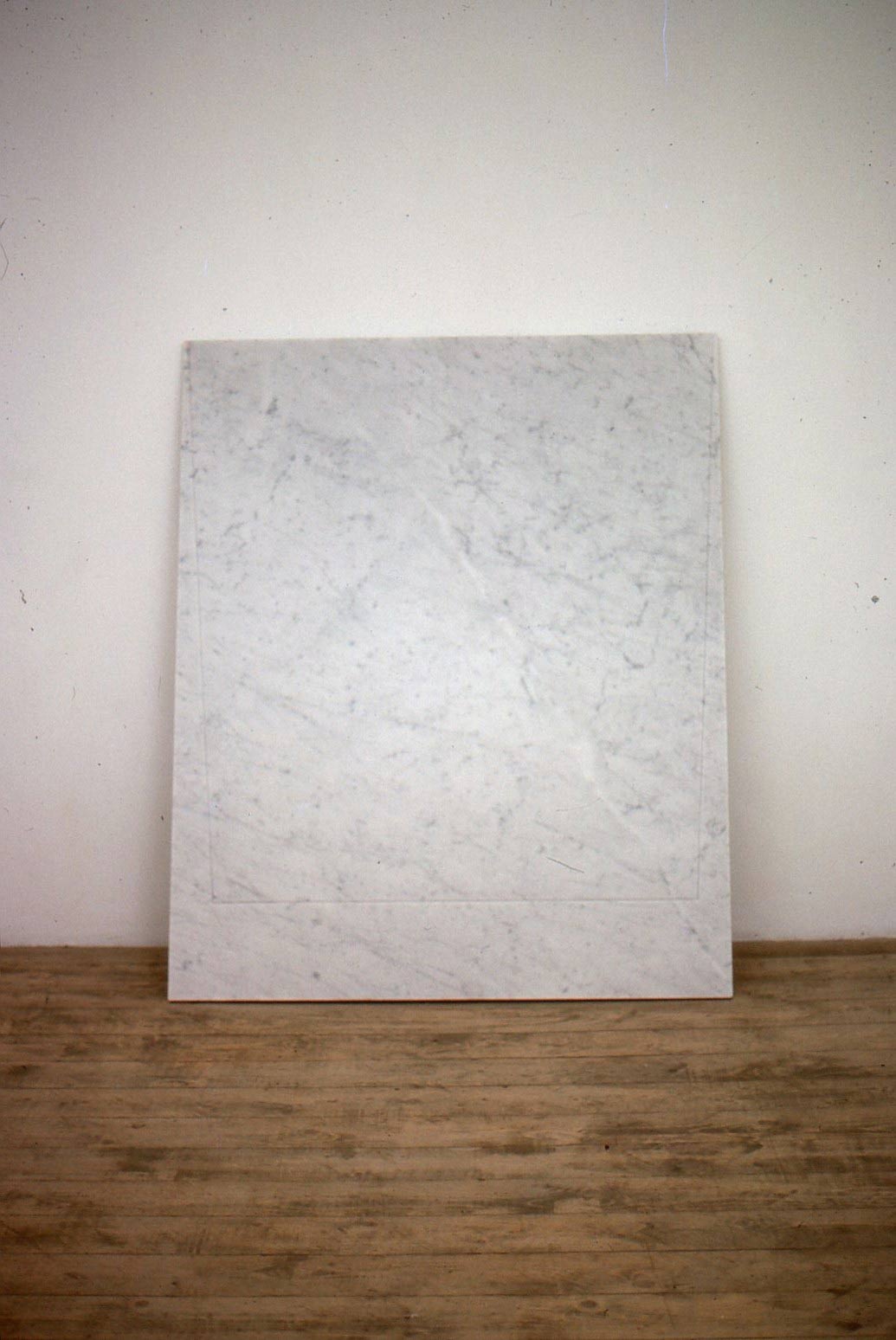
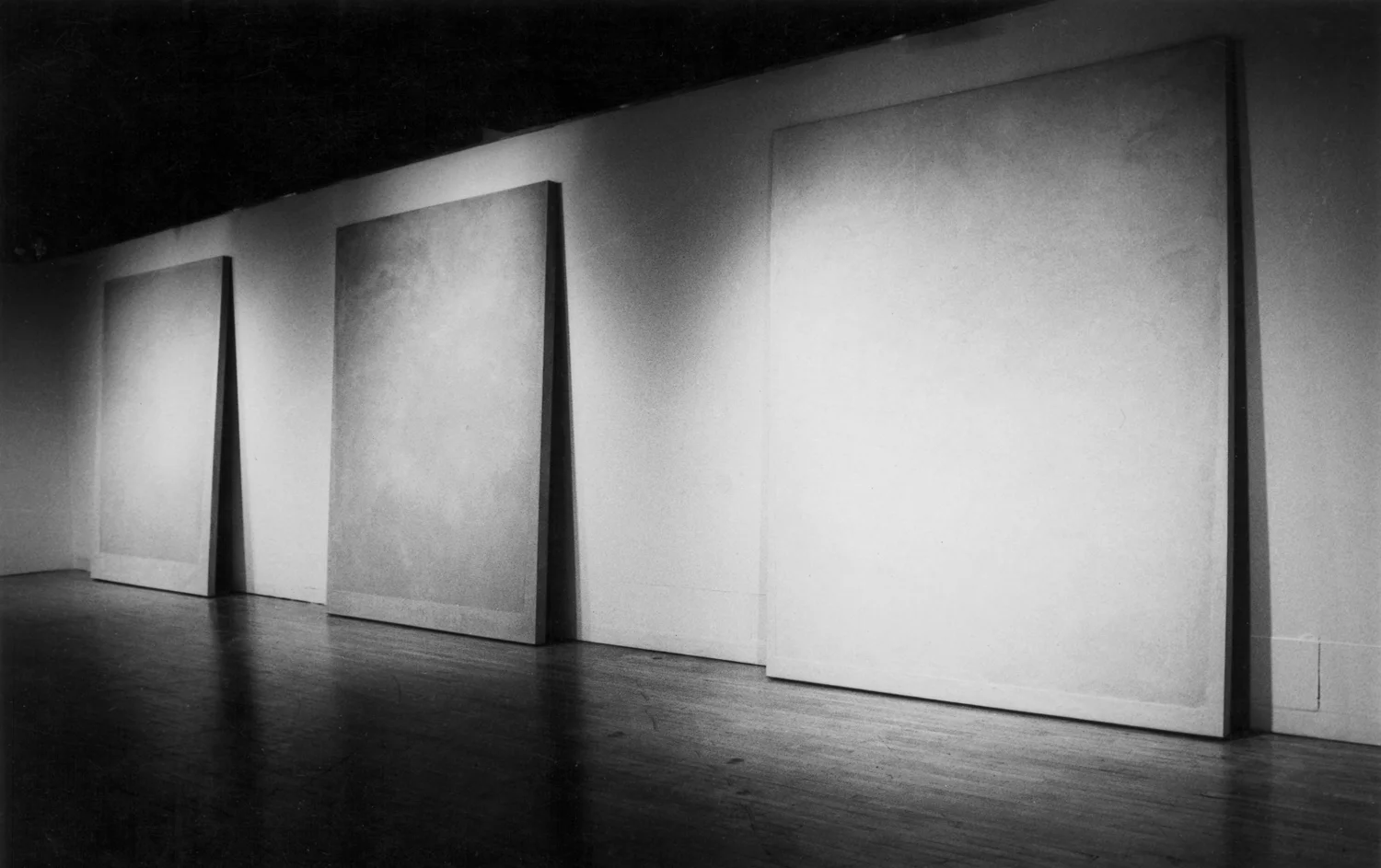
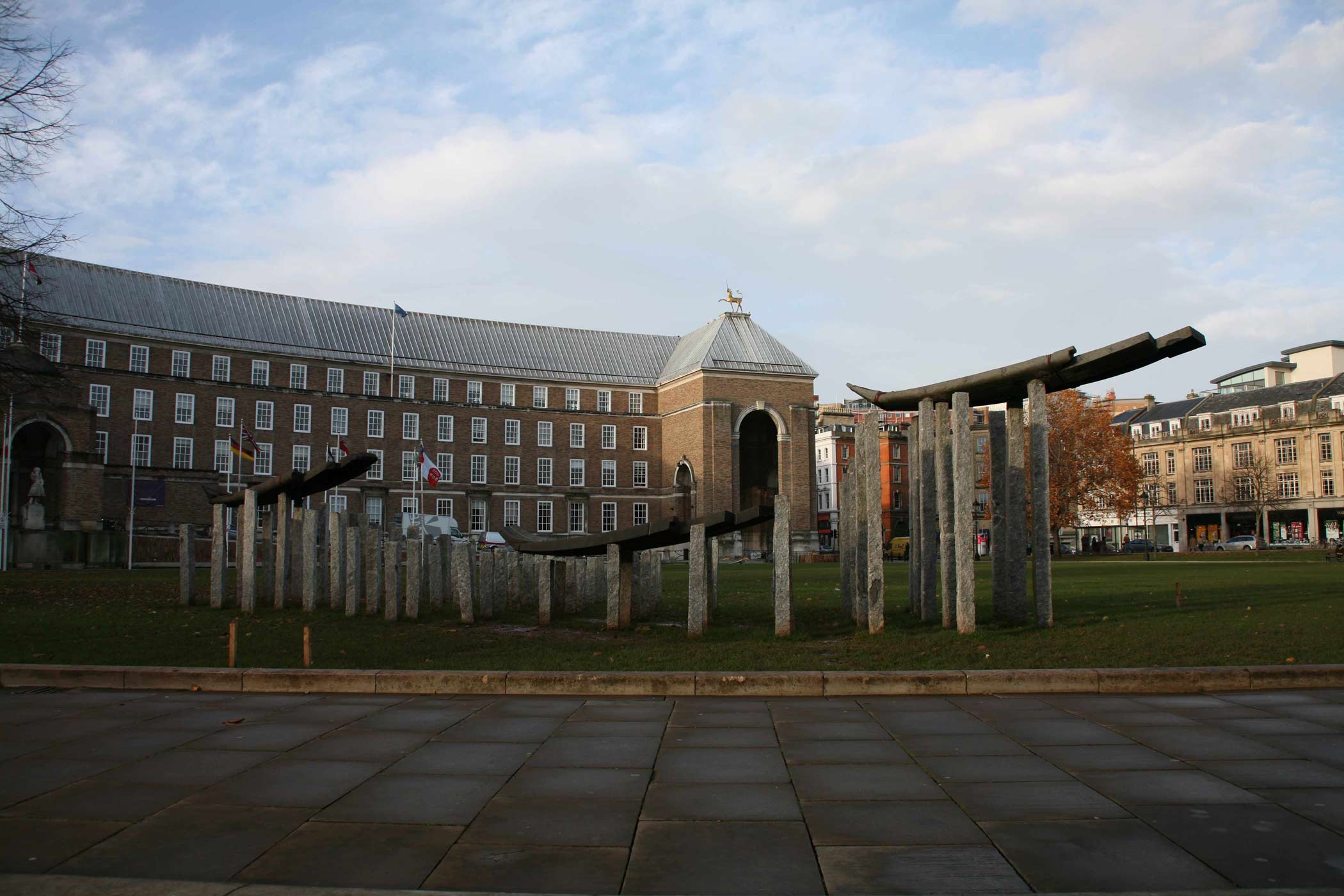
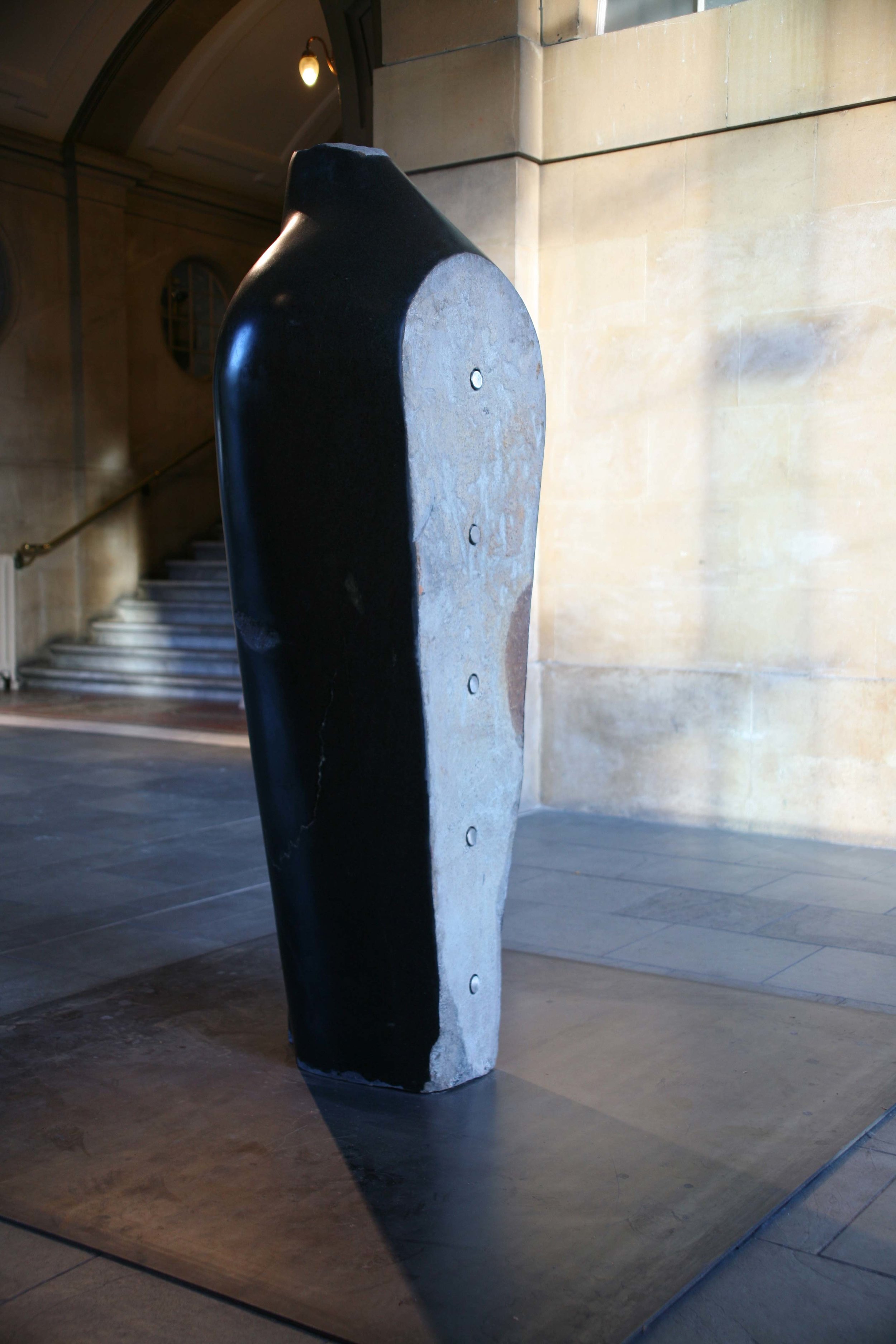
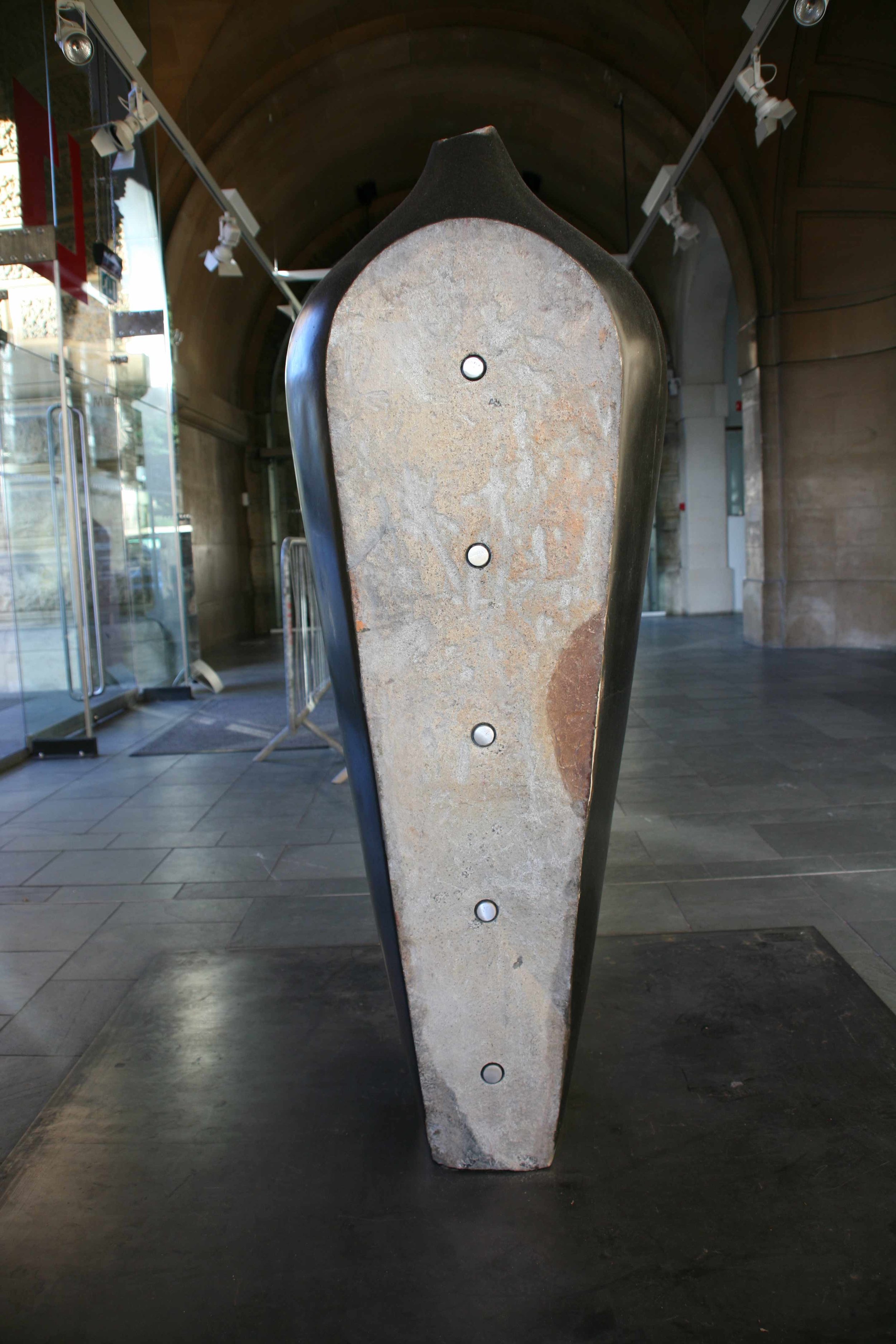
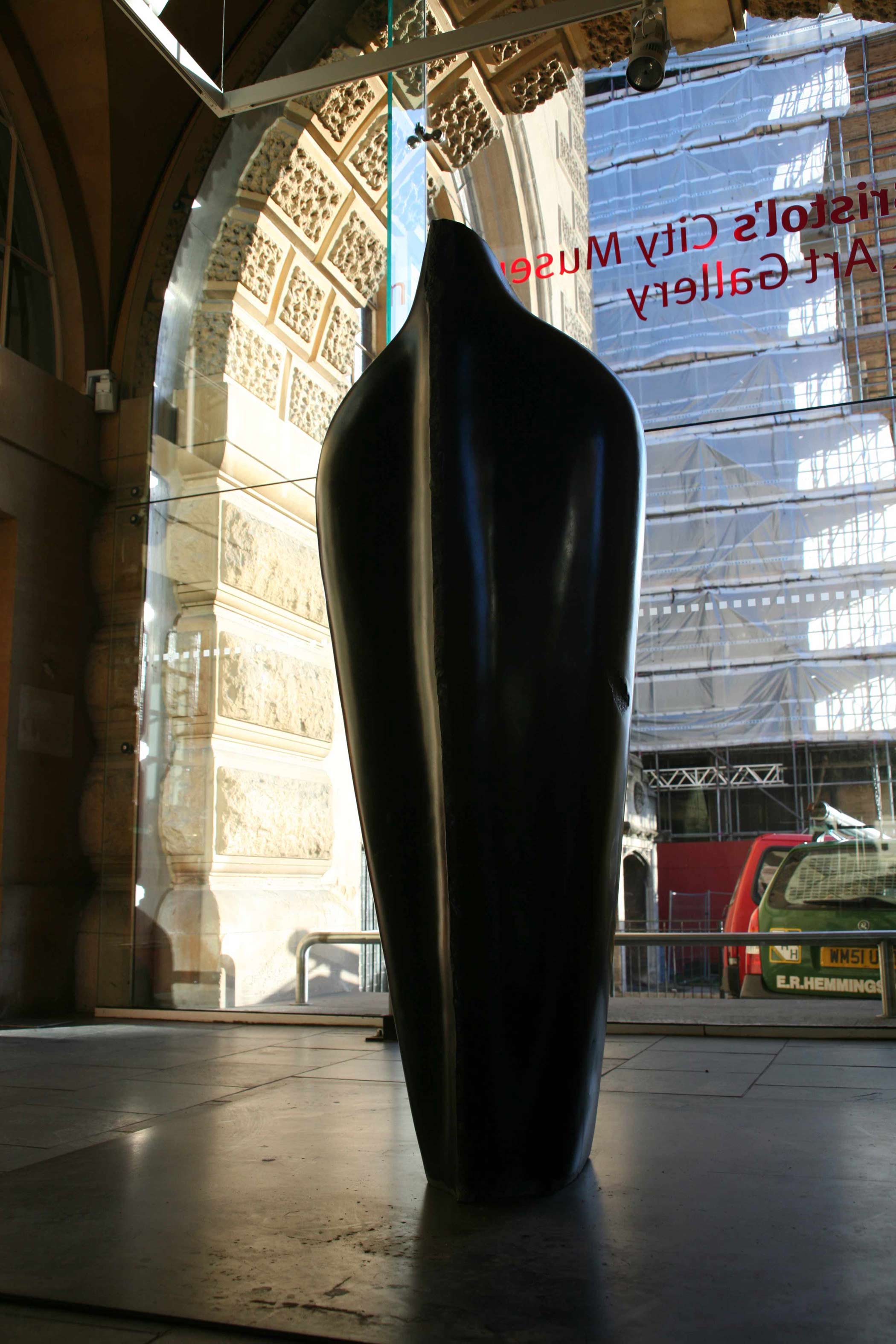
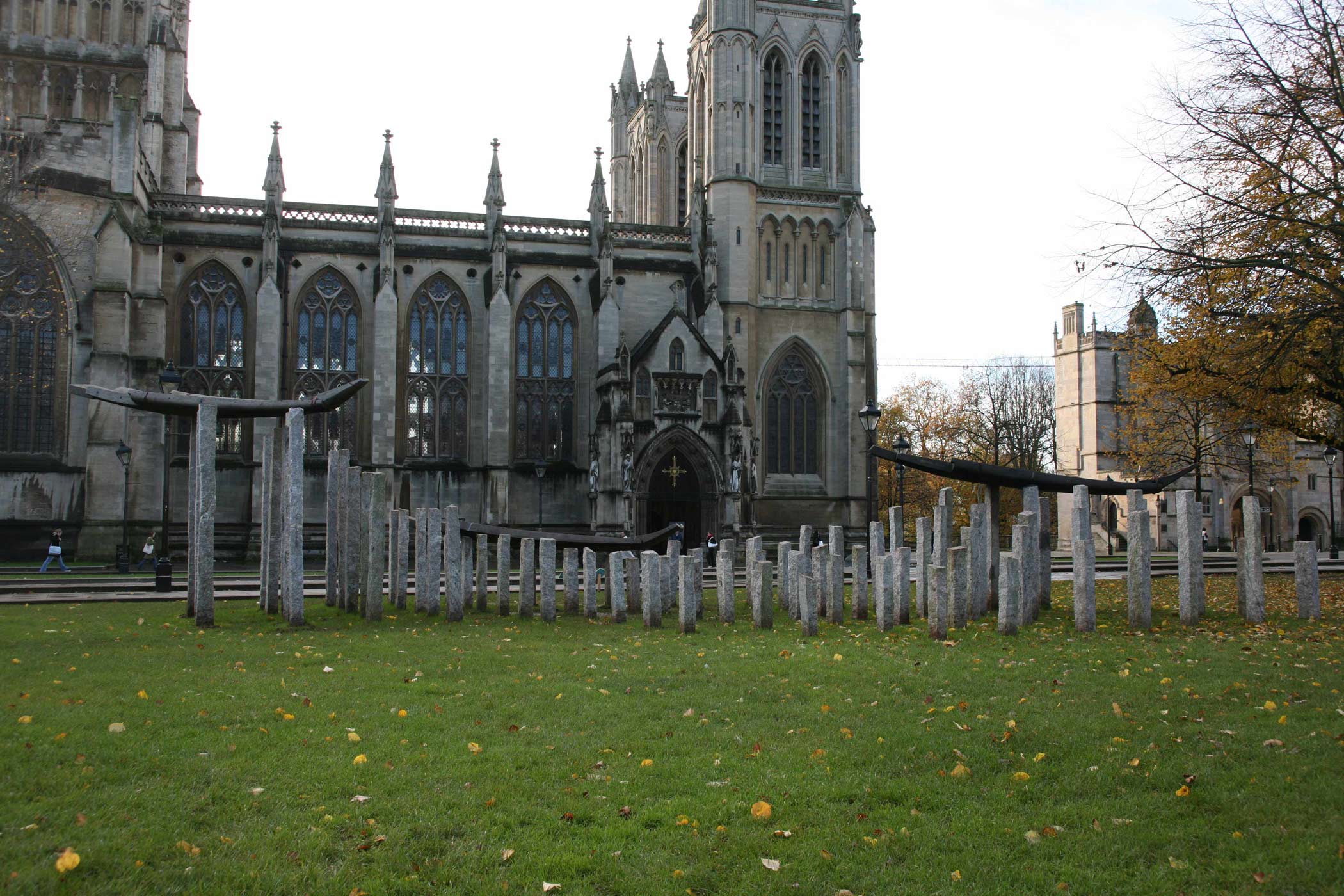
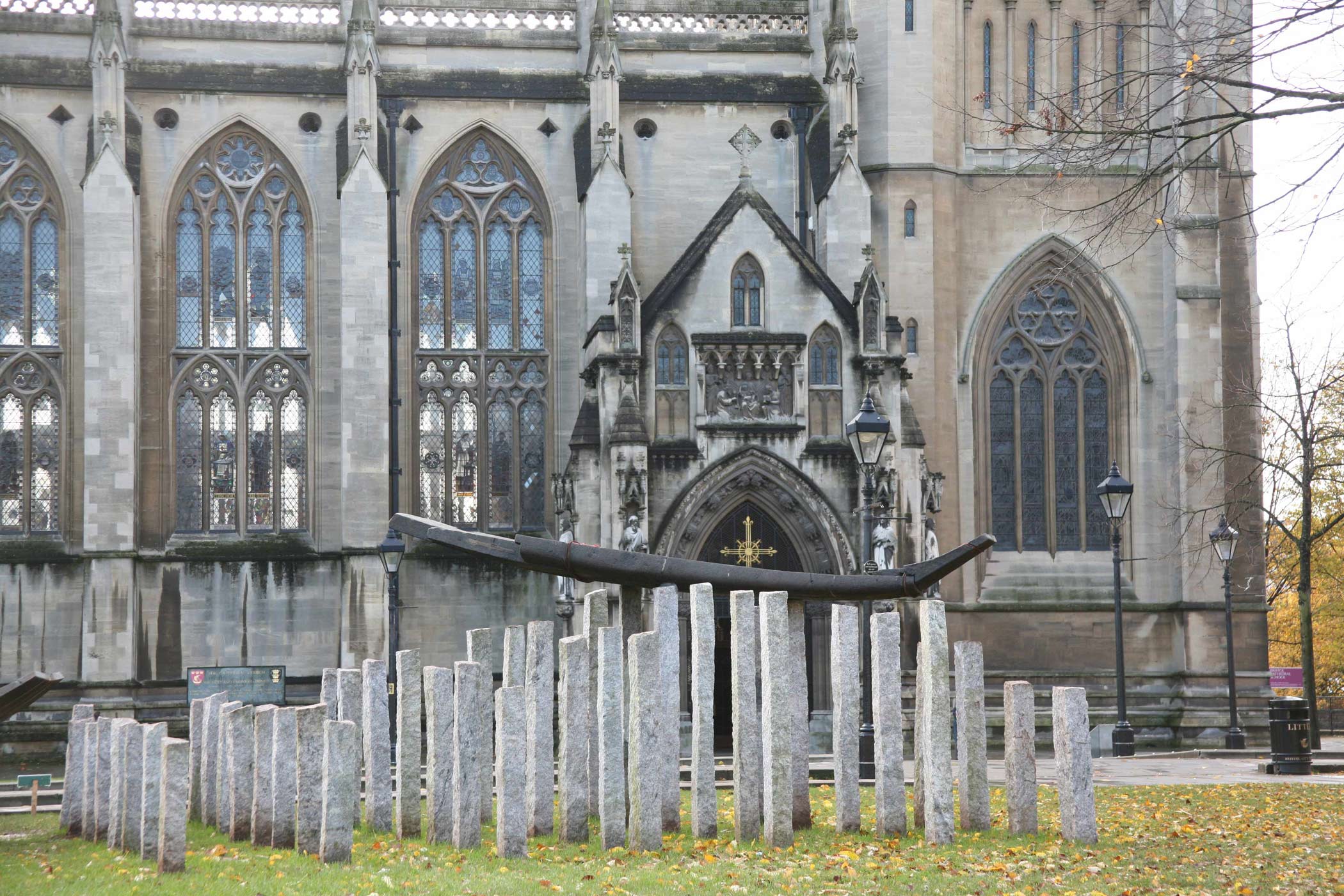
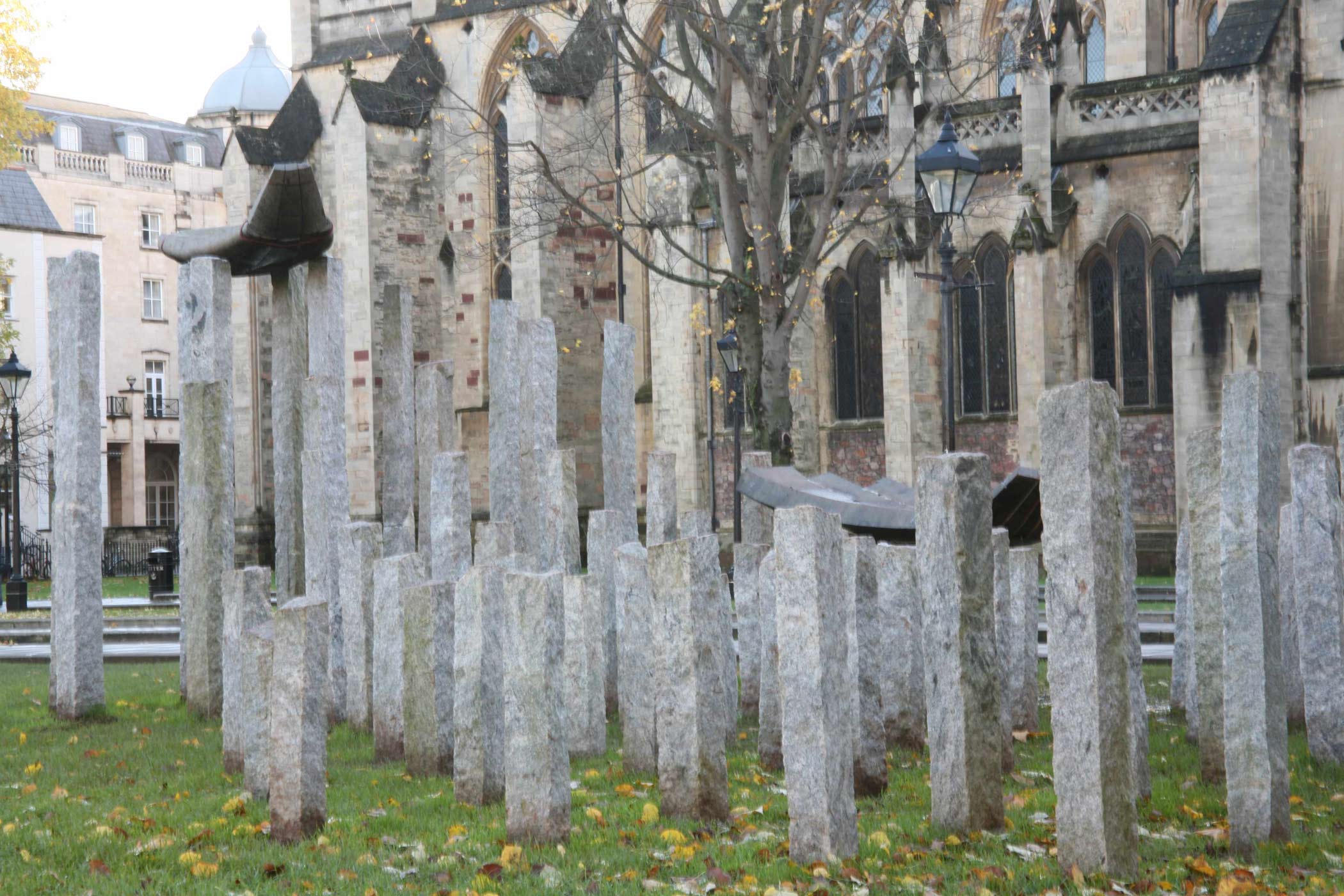
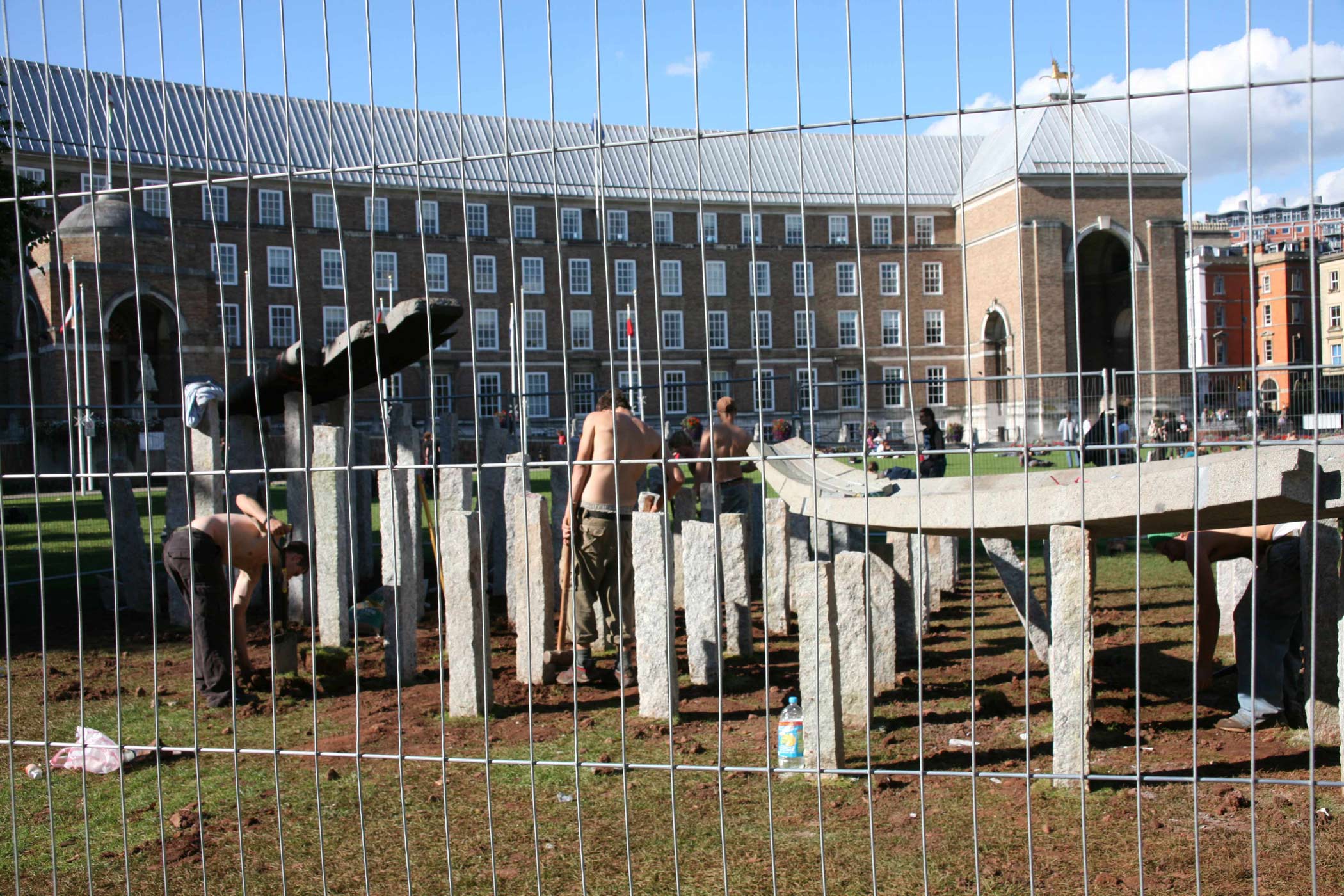
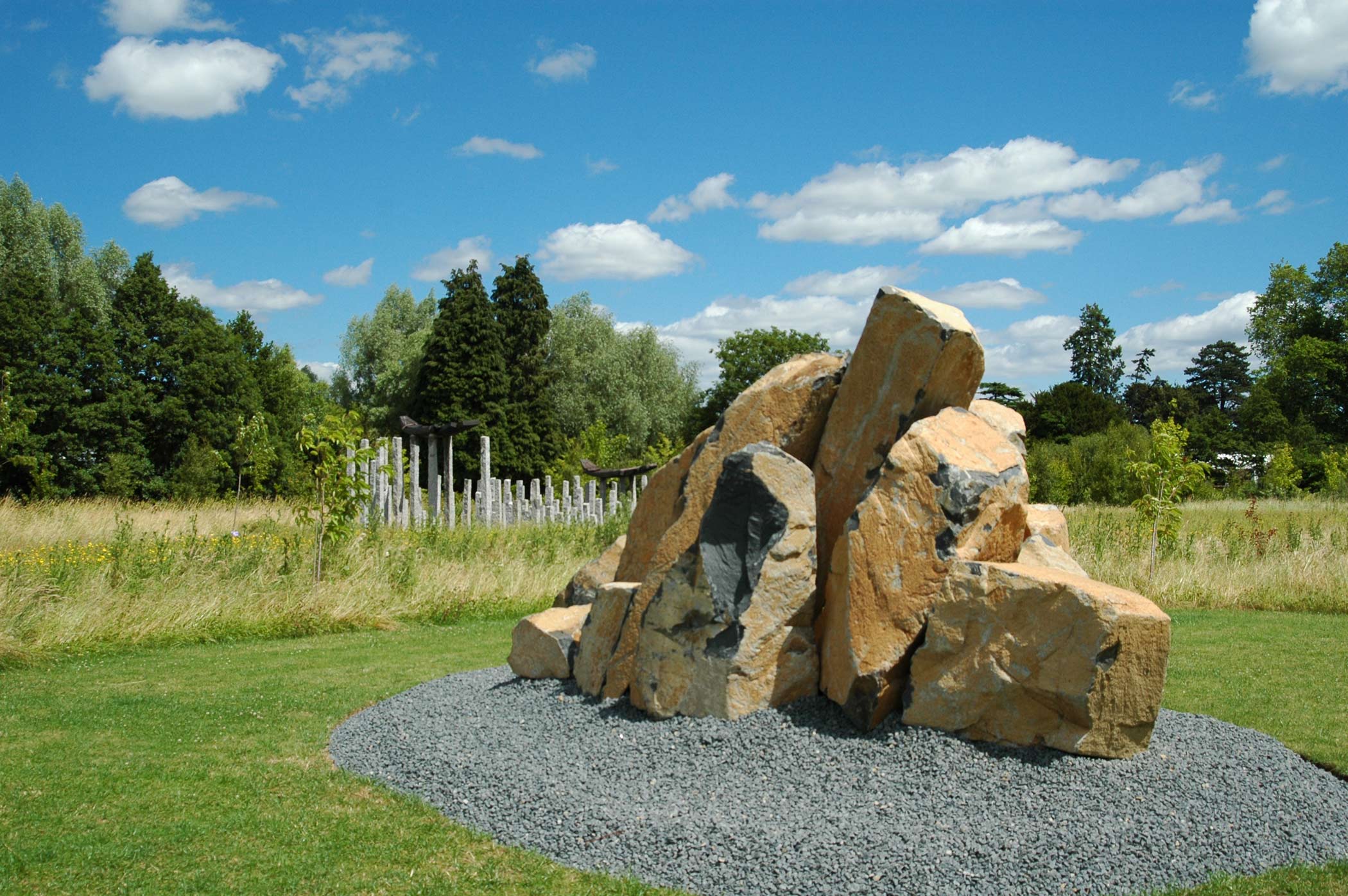
Stephen Cox: Myth is a major exhibition presented across the park, gardens and interiors of Houghton Hall, running from 4 May to 28 September.
The exhibition represents the largest and most comprehensive group of work the artist has ever shown. Spanning over 40 years, it includes work conceived and produced all over the world from India to Egypt, Italy and the UK.
Stephen Cox: Myth is a major exhibition presented across the park, gardens and interiors of Houghton Hall, running from 4 May to 28 September.
The exhibition represents the largest and most comprehensive group of work the artist has ever shown. Spanning over 40 years, it includes work conceived and produced all over the world from India to Egypt, Italy and the UK.
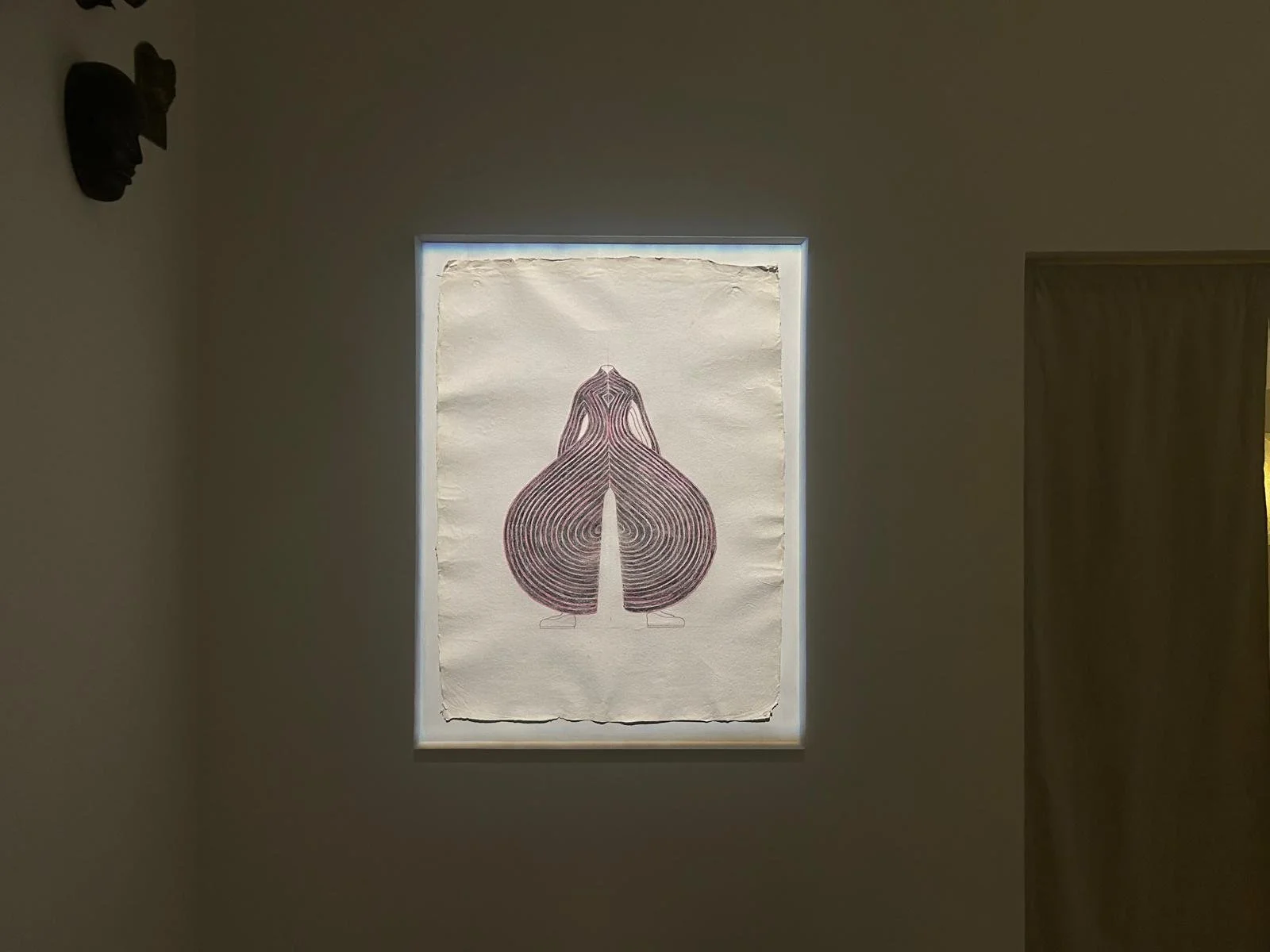
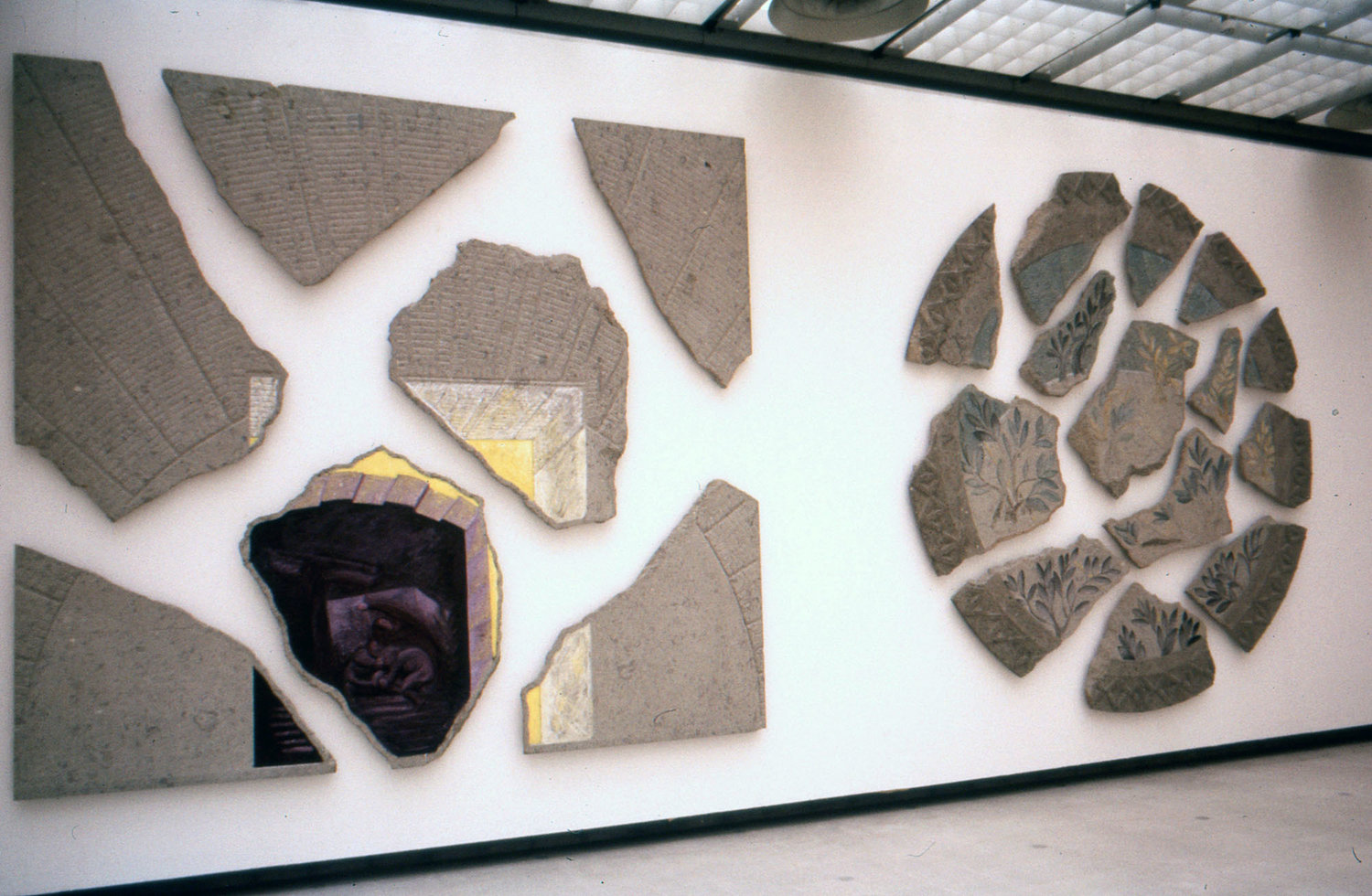
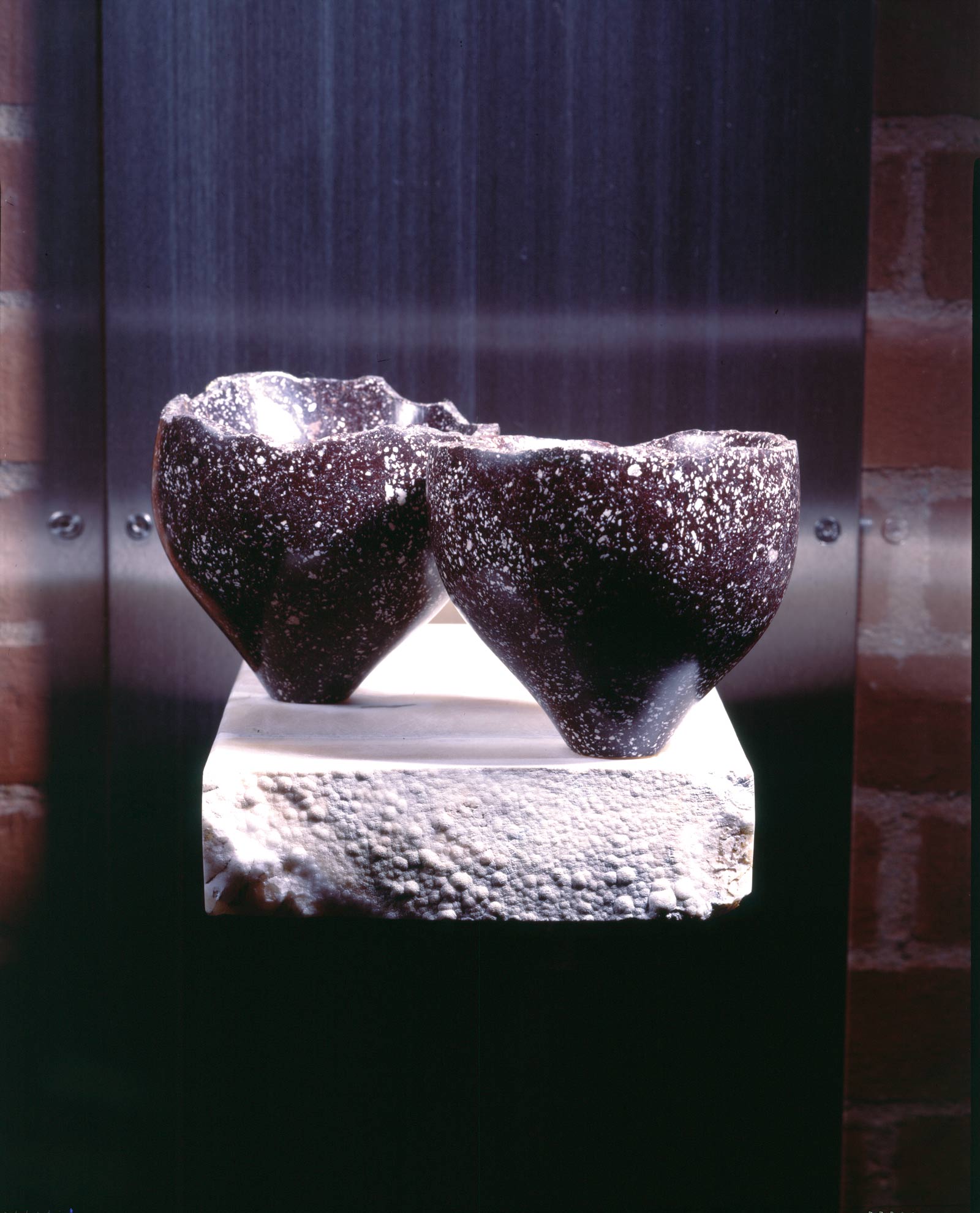
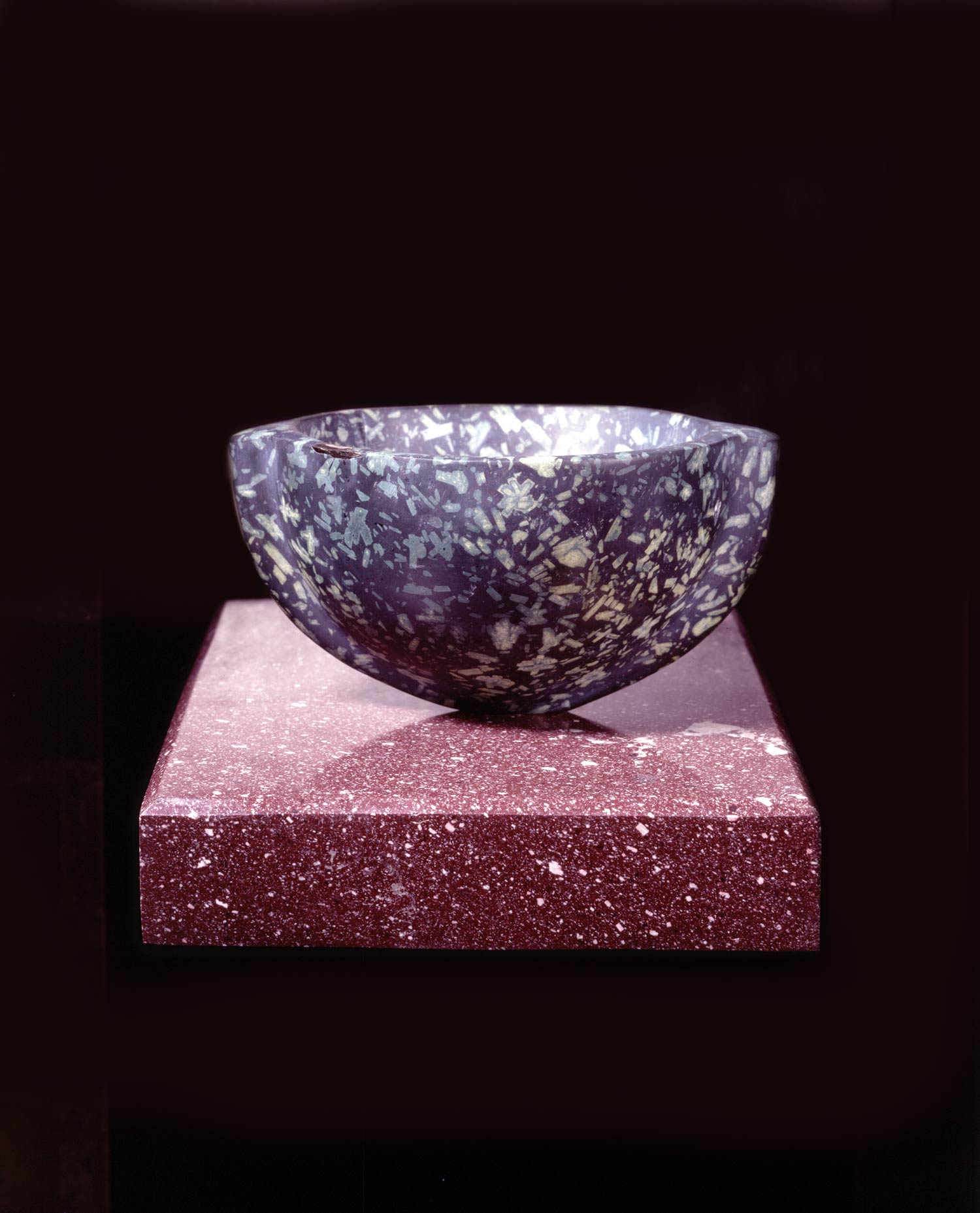
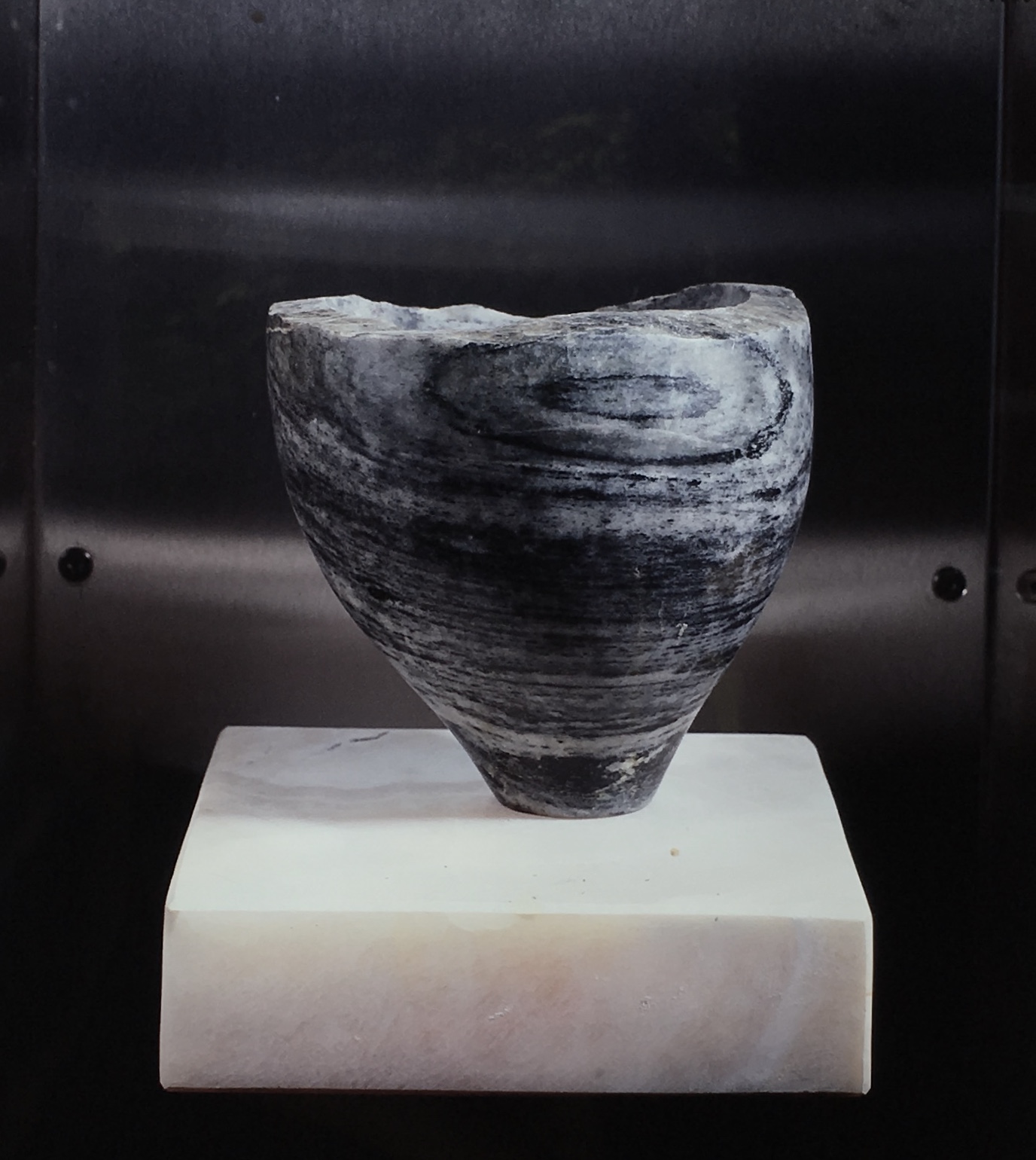
More than 20 sculptures in marble and stone have been placed in the landscape, while smaller works are installed in the State Rooms on the first floor of the house, where William Kent’s exuberant decorative scheme has hardly changed since it was created in the early 18th century. A modern gallery space in the South wing of the house houses a group of works on paper together with a large marble and porphyry sculpture, Shrine, which was created for the celebrated Encounters exhibition at the National Gallery in 2000.
Houghton Hall
4 May to 28 September 2025
Photography by Pete Huggins © Houghton Hall
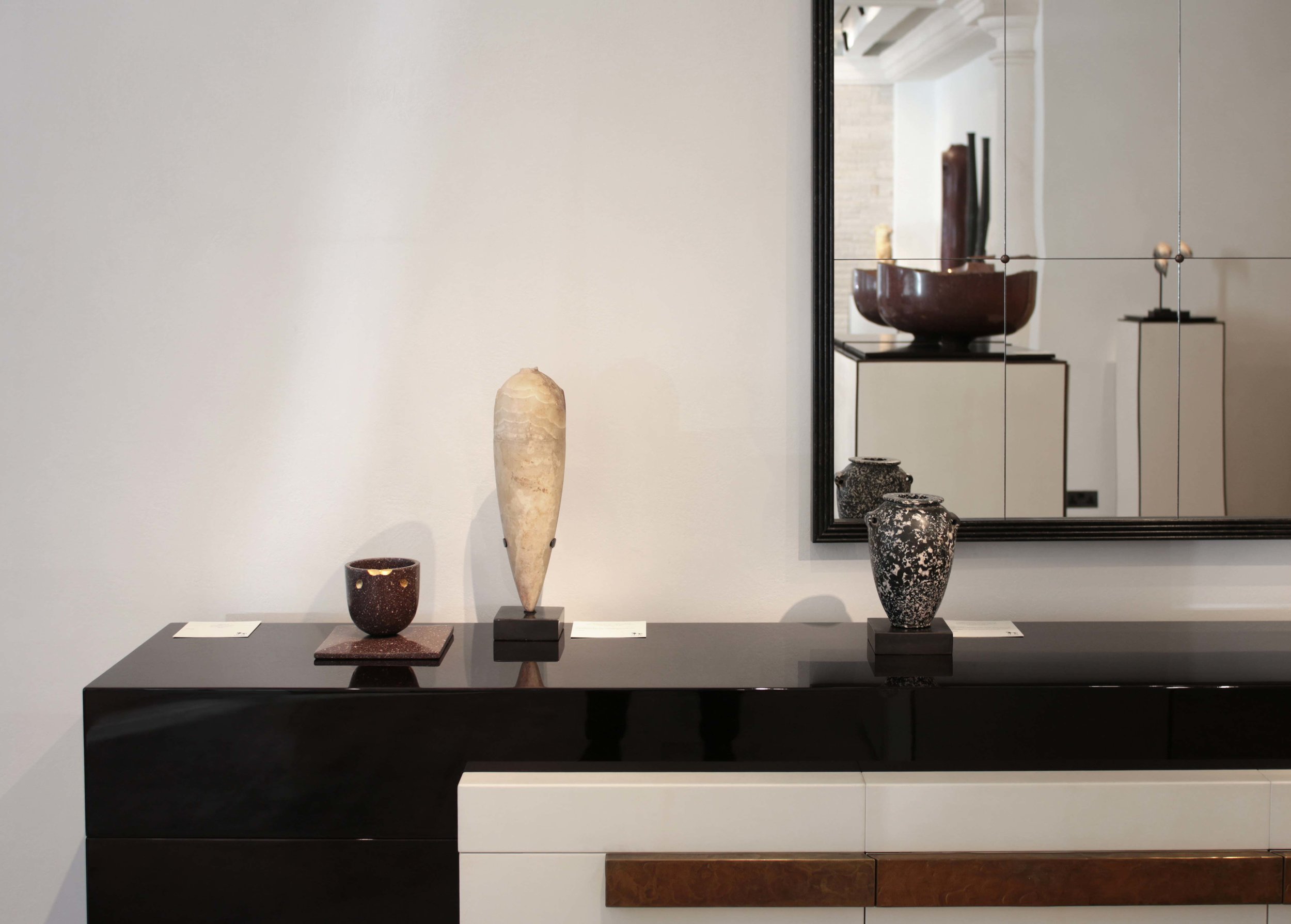
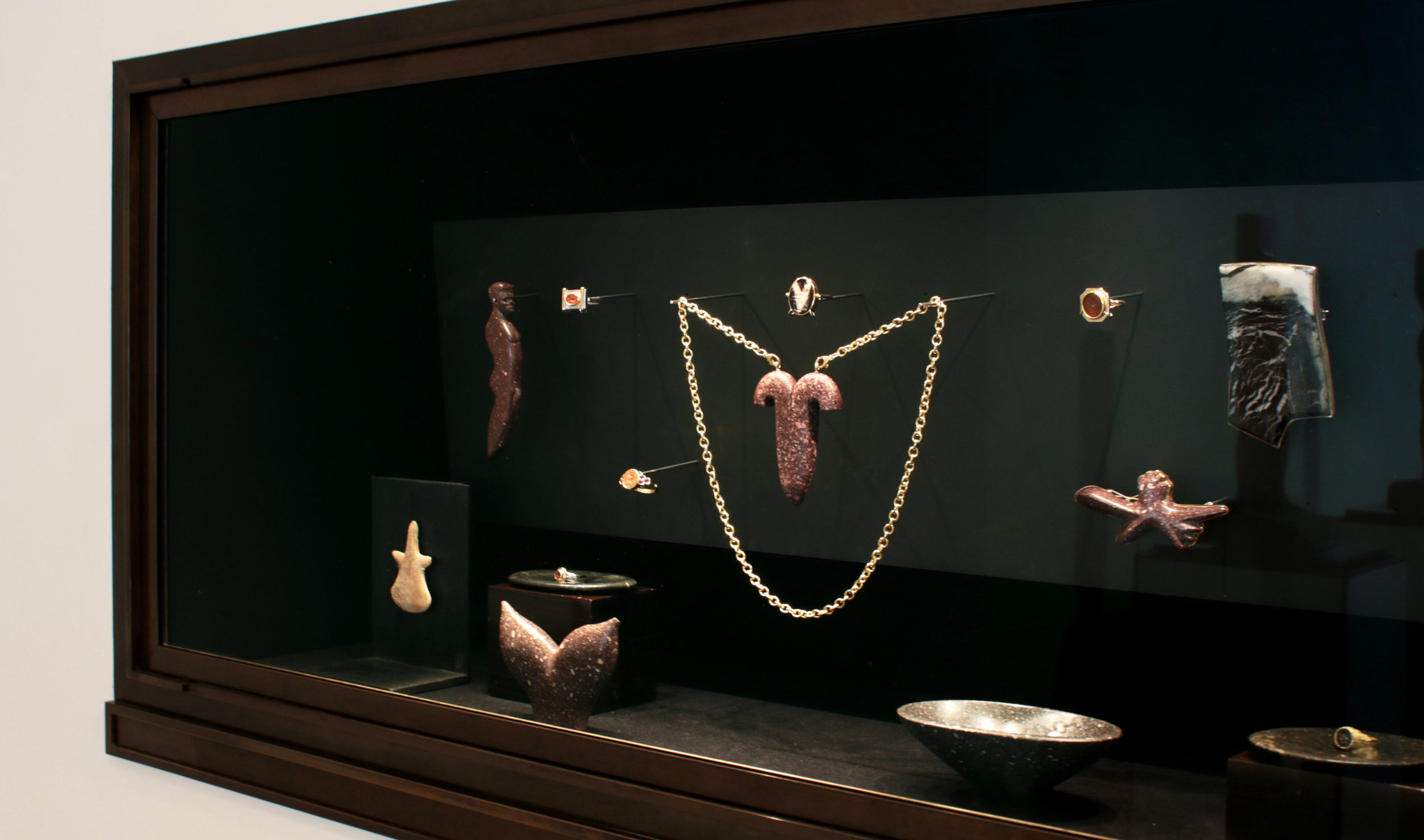
Dots Lines Checks, Kaash Gallery, Bangalore
This show features three bodies of work in Bidri, leather and the Chettinad strap weave. Lighting, seating, art and light works that expand the lexicon of our work and investigate the possibilities of both simple and rarefied materials.
This show features three bodies of work in Bidri, leather and the Chettinad strap weave. Lighting, seating, art and light works that expand the lexicon of our work and investigate the possibilities of both simple and rarefied materials.
Stephen Cox: Dialogues in Stone
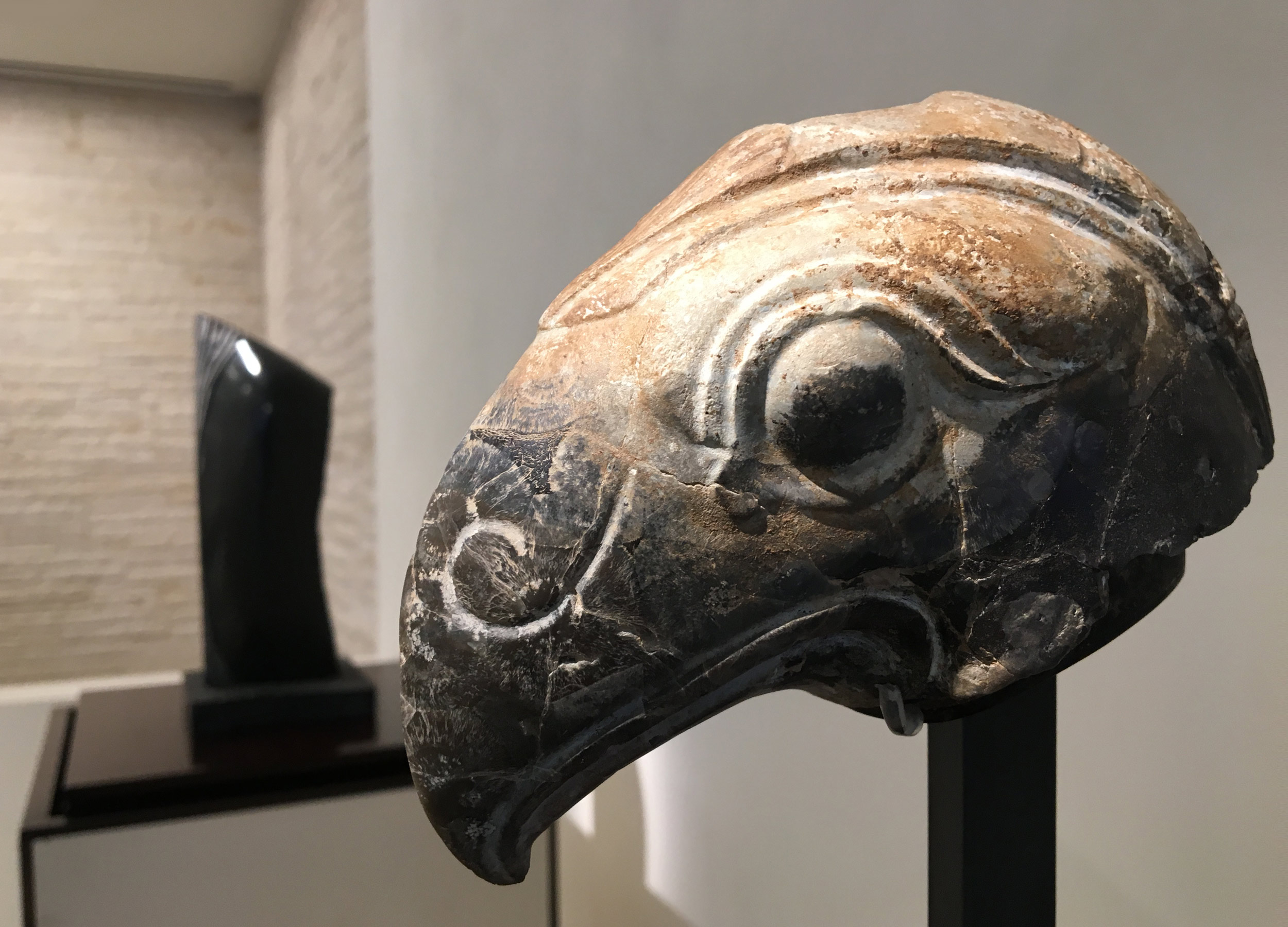
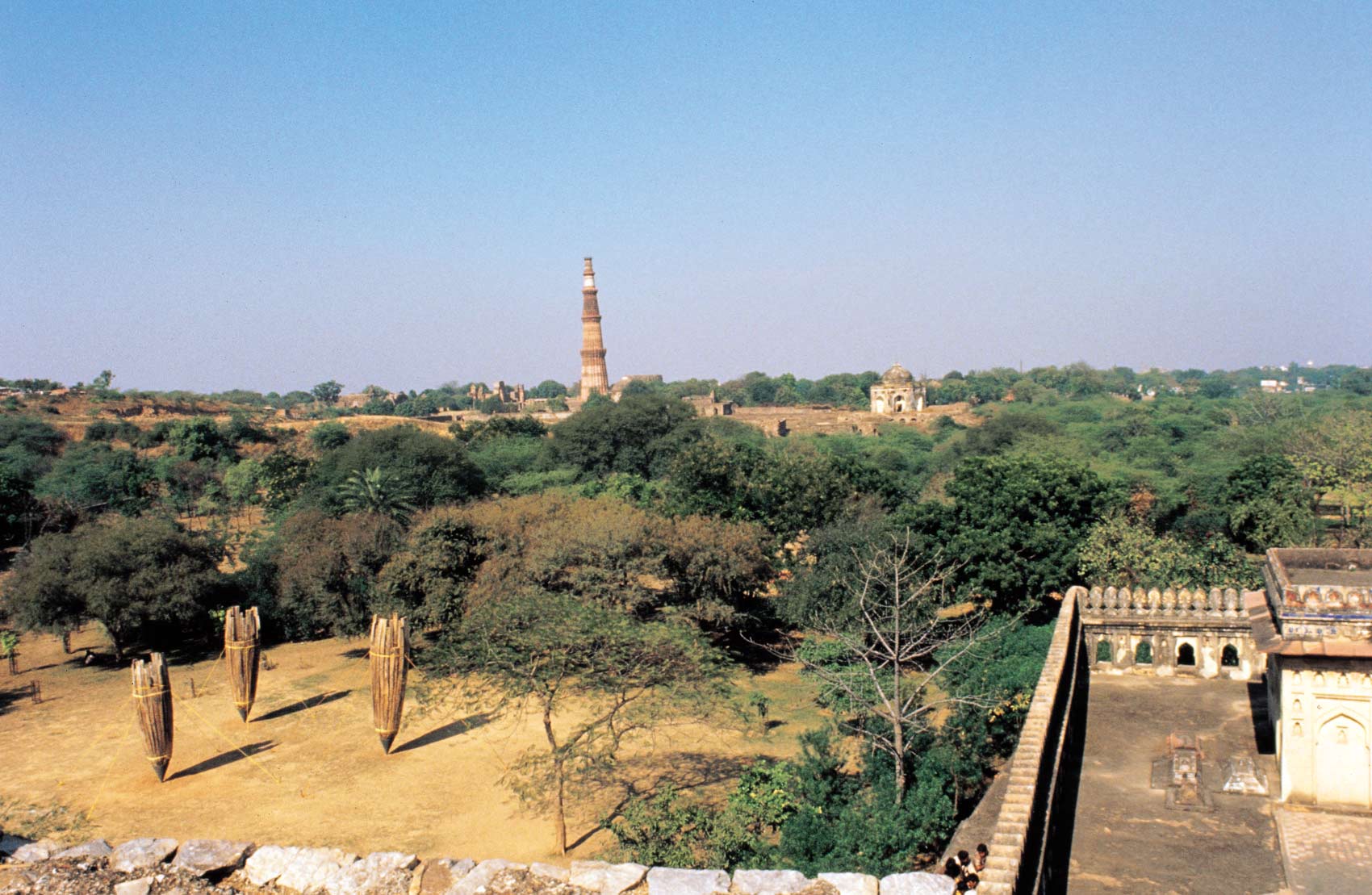
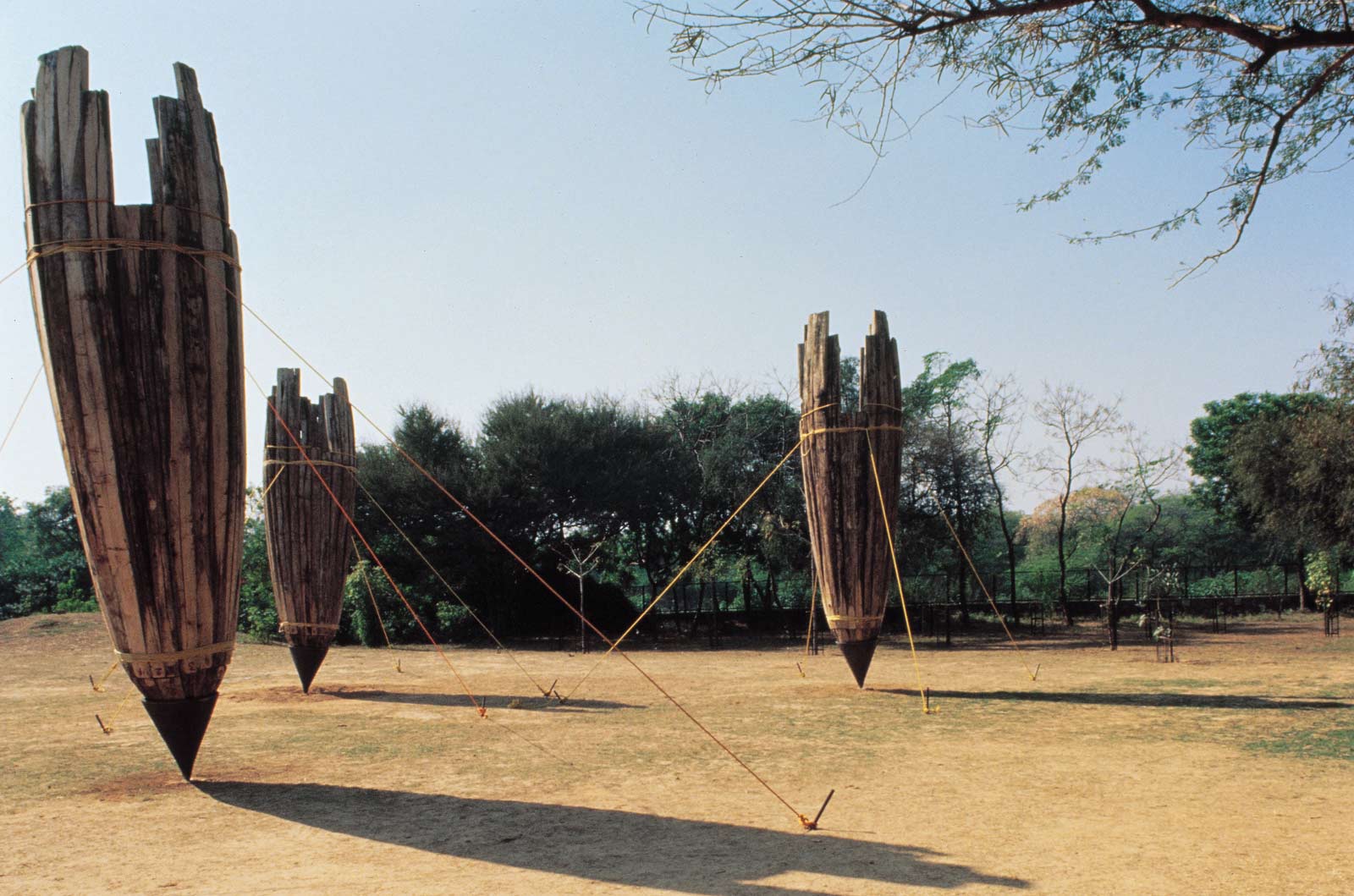
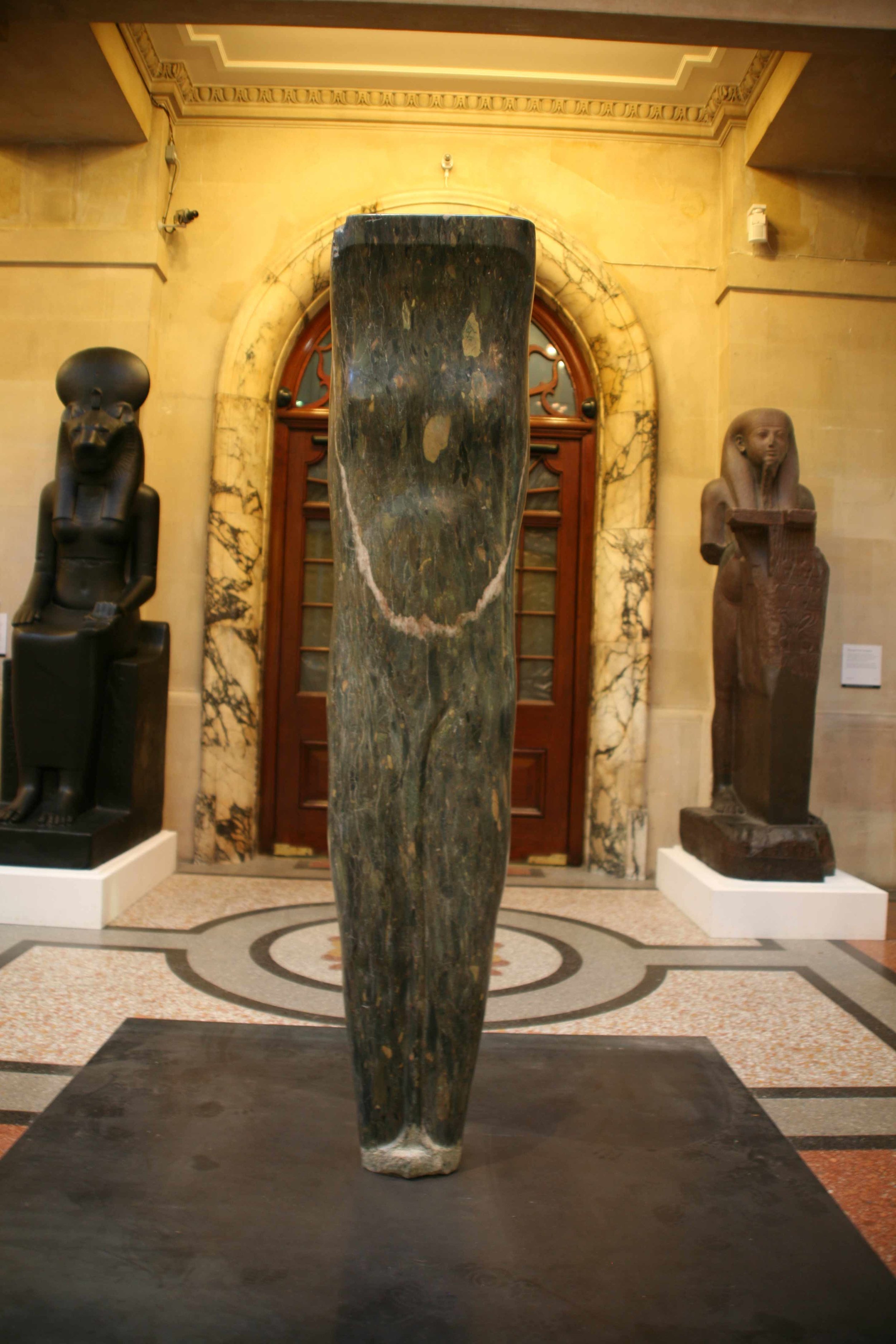
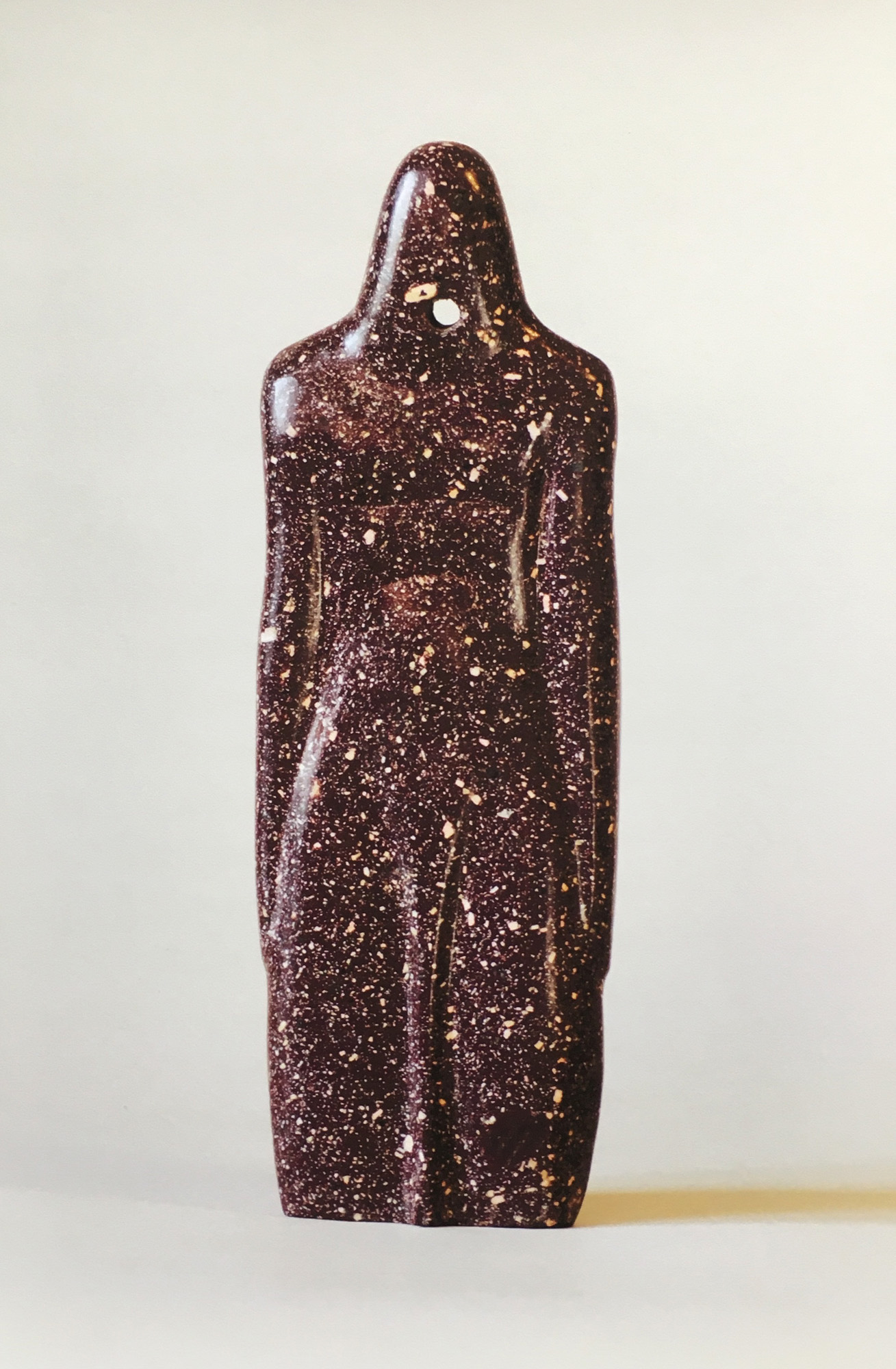
As a part of the inauguration, MAP will be showcasing the sculptures of Stephen Cox, a British sculptor who has spent a considerable amount of time working in India. His sculptures of Yoginis and Rishis carved in basalt greet audiences as they enter the museum. Drawing from Cox’s observations of architectural sites and monuments in the region, they embody mythical beings through minimalist forms.
As a part of the inauguration, MAP will be showcasing the sculptures of Stephen Cox, a British sculptor who has spent a considerable amount of time working in India. His sculptures of Yoginis and Rishis carved in basalt greet audiences as they enter the museum. Drawing from Cox’s observations of architectural sites and monuments in the region, they embody mythical beings through minimalist forms.
The titles of these sculptures – yoginis and rishis – refer to powerful goddesses and sages. The yoginis were part of an esoteric cult, where only a small group of individuals held knowledge about these goddesses. Enshrined in open temples and shrouded in secrecy, yoginis possess magical powers that evoke both fear and awe. Cox’s sculptures are contemporary interpretations of these goddesses, blending animal and human forms, a hybridity referenced in ancient Indian texts and one the artist has encountered in Middle Eastern, Egyptian, Greek and Roman iconography.
The smoothness of stone in the yoginis is contrasted to the rough and textured form of the rishis. Associated with knowledge and truth, the rishis take the form of torsos and other irregular shapes. The minimal intervention to the stone reflects the austere nature of rishis. In doing so Cox breathes life into intractable stone, capturing the essence and spirit of primordial figures.
Cox works with local material, using stone extracted from quarries to the east of Kanchipuram, a city in Tamil Nadu. A team of stone carvers in Mahabalipuram give shape to these sculptures. These stones, known as basalt, were also used in the construction of ancient temples. His sculptures thus bring to light an ancient material into a contemporary setting; the incisions made to these stones are preserved, bearing the marks of time
Museum of Art & Photography (MAP) Bangalore
The exhibition runs from February 18, 2023 - February 18, 2024
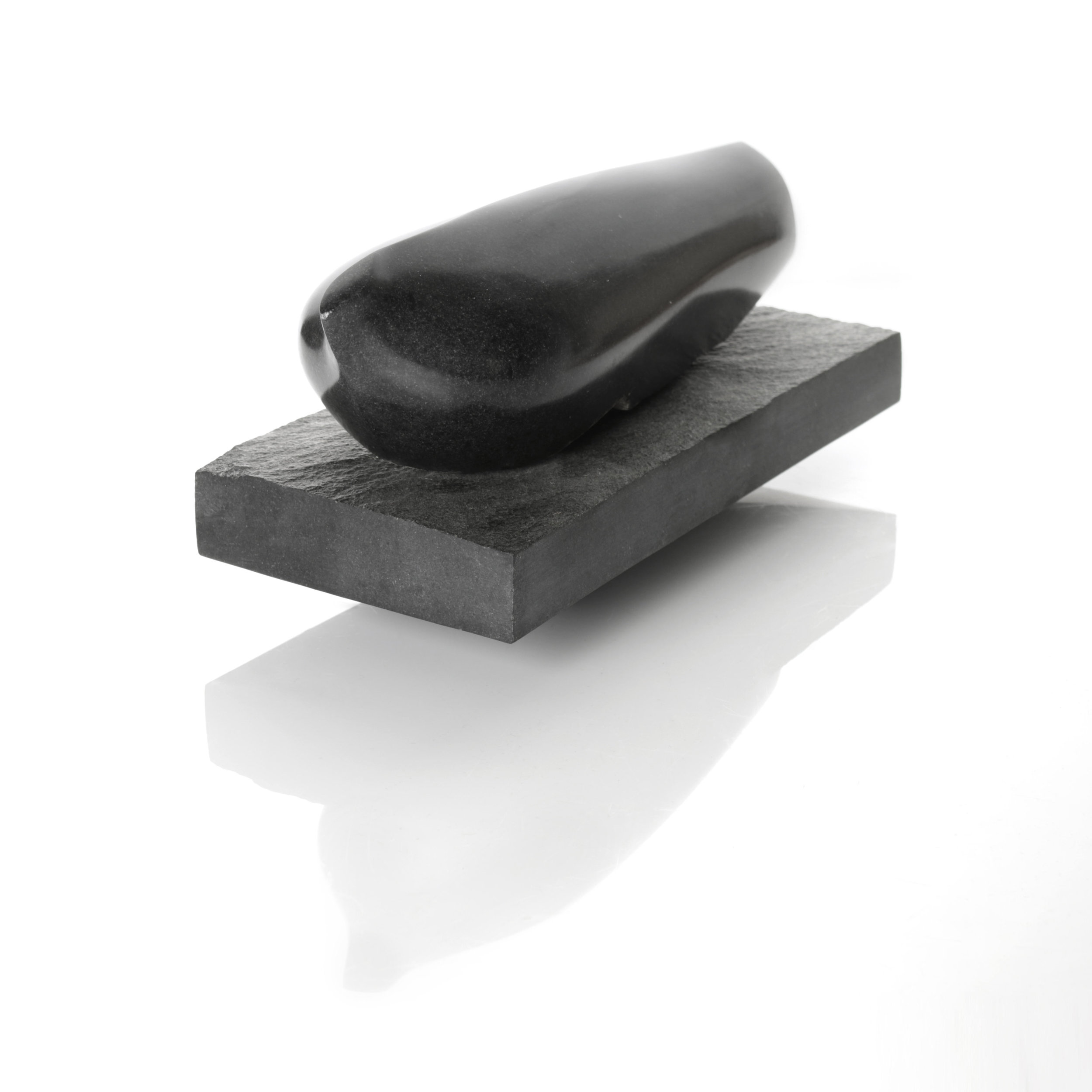
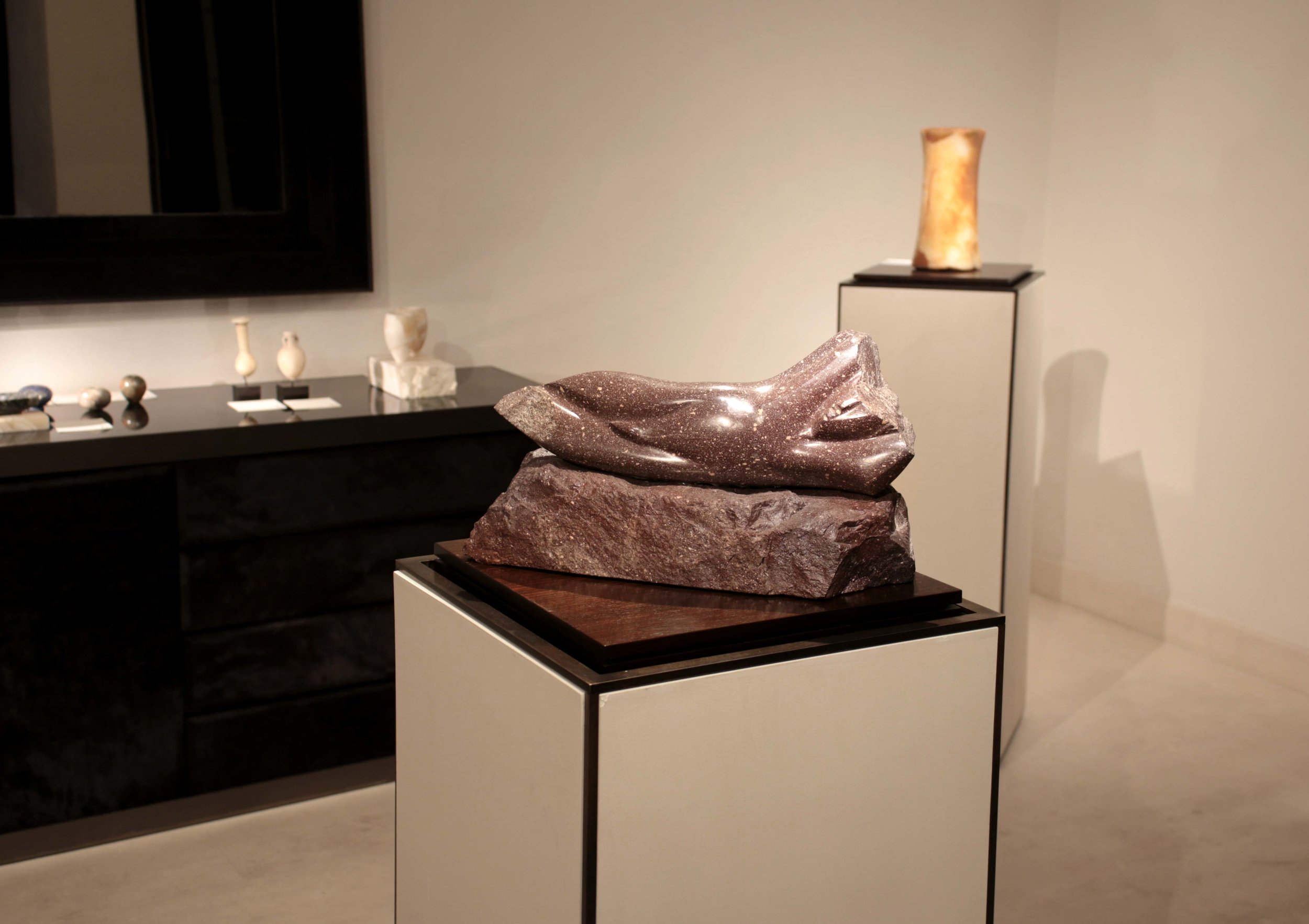
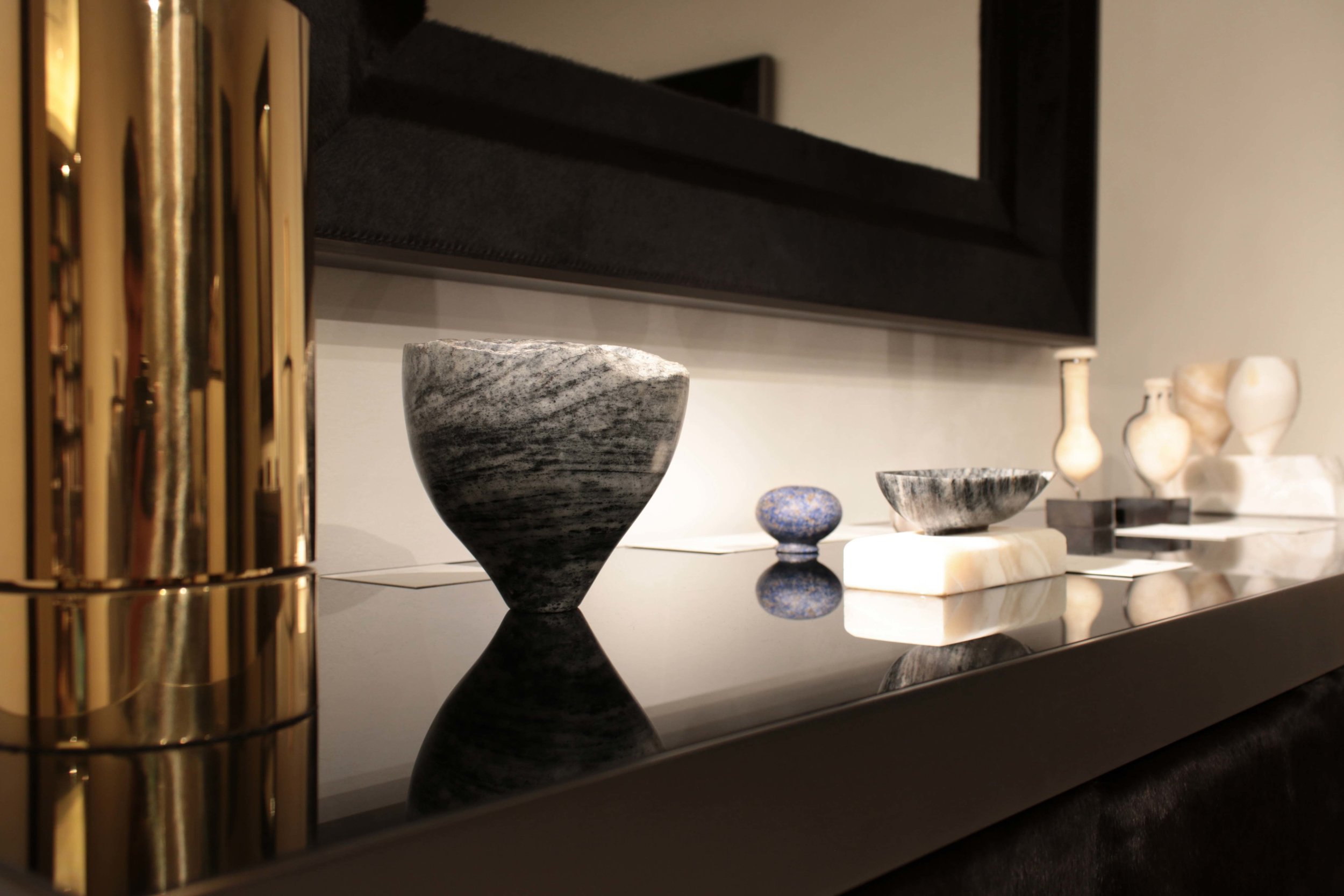
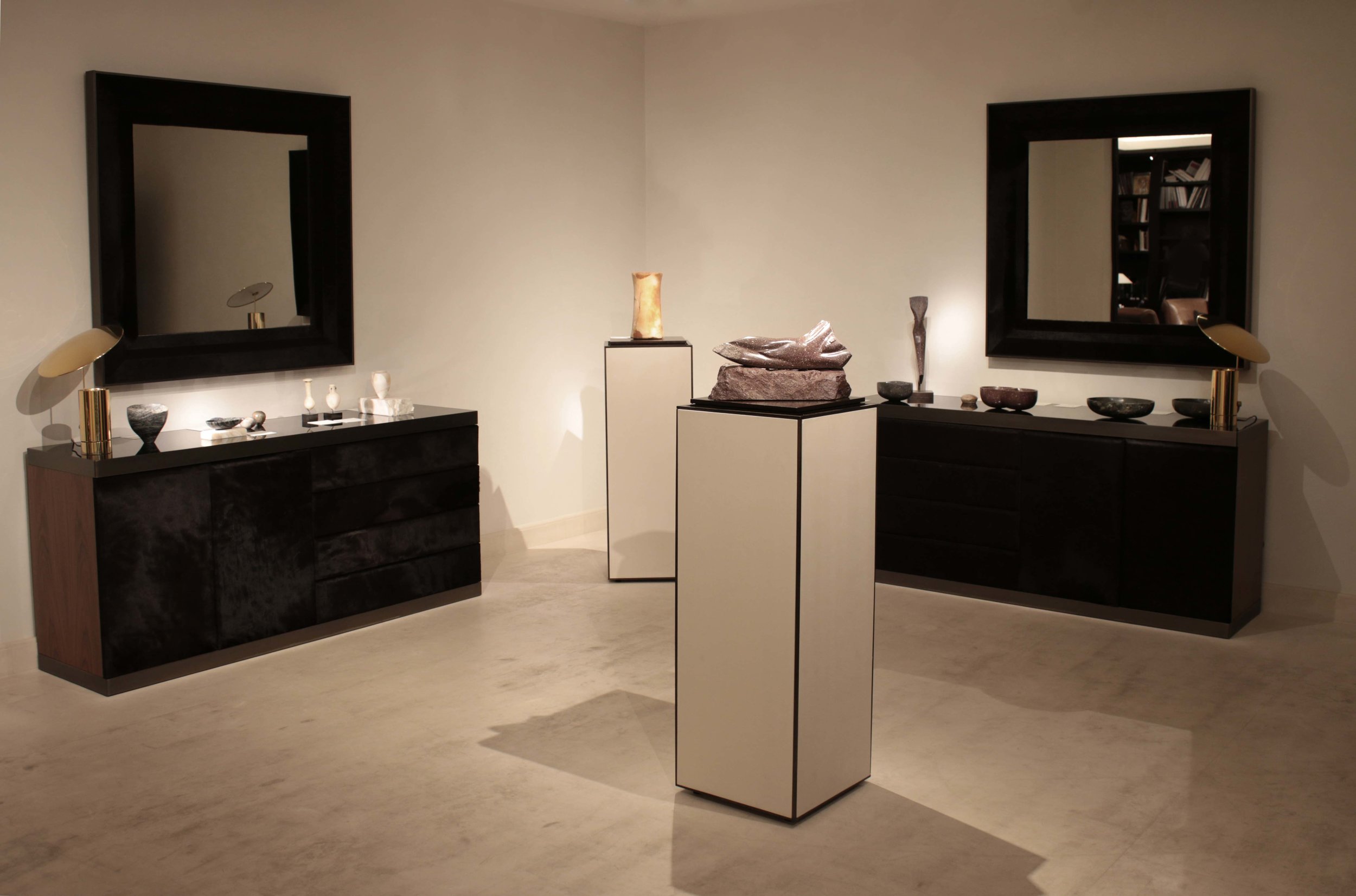
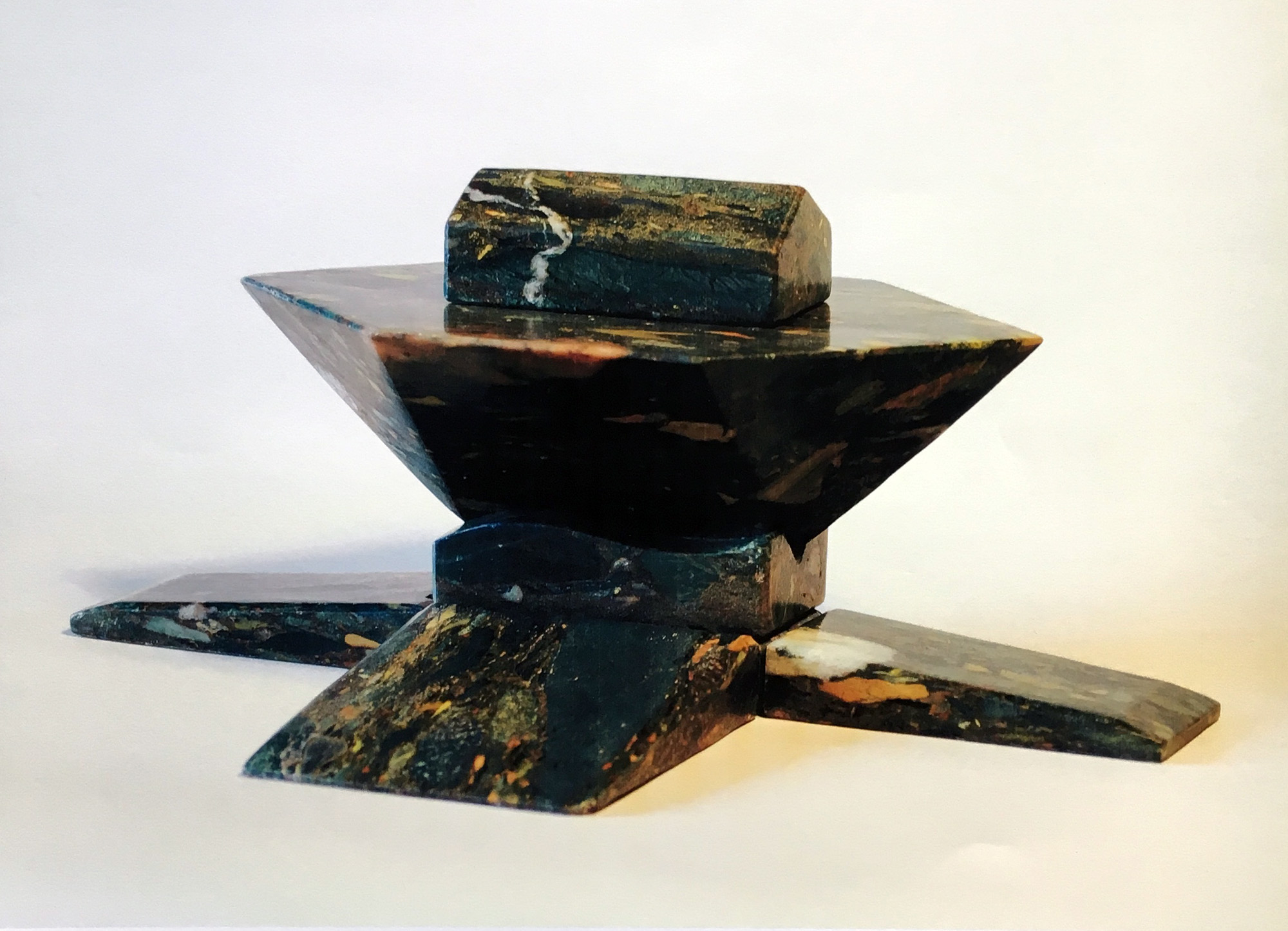
Stephen Cox RA Kallos Gallery Ancient Stone
‘A collaboration inspired by the materiality of stone and featuring sculptures from antiquity alongside contemporary works by Stephen cox Ra, an artist renowned for his knowledge of ancient sculptural techniques, traditions and materials. the exhibition included works in porphyry, marble, alabaster, breccia, gneiss, diorite and flint.’
Text by Kallos Gallery
The Sculpture Show, Hayward Gallery/Serpentine Gallery, London, 1983
The Sculpture Show, Hayward Gallery/Serpentine Gallery, London, 1983
Stephen Cox at the Dulwich Picture Gallery, Dulwich, London
Stephen Cox's Journey
Richard Cork
While other British sculptors thrive on the possibilities suggested by the found object,
whether scavenged or purchased, Stephen Cox insists on meeting the ancient challenge of
cutting into stone, marble and granite. New materials and alternative ways of working
abound in sculptural innovation today, often to the point where 'sculpture' no longer
seems an appropriate term. Indeed, the organisers of the 'Moteriol Culture' exhibition at the
Hayward Gallery asserted that 'the word has recently expanded its meaning so far as to
become almost meaningless.' Cox, on the other hand, is defiant enough to place the idea of
working stone at the very centre of his concerns. And he claims the right to roam through
the history of sculpture at will, discovering nourishment in a heady array of disparate
sources. No era is too distant for him to rule out the prospect of finding inspiration there.
Whether the culture he explores with such commitment originates in the East or the West,
he perpetually renews himself by remaining open to even the most unexpected stimuli
across the world.
Not that Cox's restless journeying arises from a blinkered determination to ignore
the experimental energy of twentieth-century sculpture. His earliest work, produced soon
after leaving the Central school of Art in 1968, is characterised by its alert, questioning
awareness of the modernist legacy. The plasterboard
pieces which first established his reputation during
the 1997’s derived above all from American minimalism. But they were distinctive in their reaction
to the work of Andre and Judd. Despite their often monumental dimensions, they pointed away from a materialist assertion of bulk. Their shimmering surfaces, derived in the latter half of the decade from
a combination of silver sand and lime, possessed a disembodied purity that ran counter to
the American sculptors' assertion of physical substance. in this respect he felt far closer to
abstract painting, and in particular the work of Newman, Reinhardt and Rothko with their
profound spiritual resonance.
Cox was already asserting a powerful need to charge his work with an intense religious
significance. Without in any way associating himself with doctrinal faith, he wanted to
signal his governing belief in art as metaphor, a means of exploring a realm beyond quotidian reality. For all their purity, the finest of these plasterboard pieces implied a desire to
be transported from everyday experience towards a heightened, even ecstatic state of consciousness. They also hovered halfway between painting and sculpture, acknowledging both and yet referring at the same time to the condition of architecture. In short, they manifested
a desire to transcend conventional categories and resist the twentieth-century obsession
with narrow specialisation. Cox had not yet succumbed to the lure of the Mediterranean.
But he must have sensed inside himself a growing fascination with the Renaissance ability
to move, without a sense of strain, between branches of the visual arts which subsequently
became separated from each other.
By t919, Italy had assumed such an overriding importance in his mind that he decided
to leave England and work there. The effect on his work was dramatic. Initially drawn to
the art of the quattrocento, he discovered Agostino di Duccio's carvings in the Tempio
Malatestiano at Rimini through the writings of Adrian Stokes. Impassioned and at the same
time densely informed, Stokes's essays extolled not only quattrocento carvers but the geological evolution of the stones they transformed. His ardent prose convinced Cox that the
Mediterranean is the womb of my civilisation, a limestone basin whose crustacea have
accumulated and been thrust up to form mountains.'He began to meditate on sculptural
tradition rather than concentrating on the specific legacy of post-war American abstraction.
And far from continuing to work in plaster, a medium historically associated with modelling, he turned his attention to carving in stone.
A similar commitment informed the pioneers who had revolutionised British sculpture
earlier in the twentieth century. Epstein, Gaudier-Brzeska. Moore and Hepworth were all
fired by the challenge of 'carving direct', respecting the identity of the block so that it
helped to dictate the form assumed by the finished work. Just as they had once honoured
the idea of 'truth to materials', so Cox accepted the life inherent in the stone or marble. The
rappon he developed with his chosen medium proved energising, releasing him from the
restraint that prevailed in the previous decade. With hindsight, we can see that the extreme
purism he favoured during the r97os became the springboard for a gradual enrichment of
his initial sculptural standpoint. Colour, which had played such a bleached and reticent part
in the freestanding plaster walls, was now allowed an increasingly varied and resplendent
role. Figurative imagery, excluded from the smooth and inviolate blankness of his early
work, began to appear in sculpture that no longer adhered to thoroughgoing abstraction.
And manual mark-making, in the form of delicately carved incisions, lent an element of
individual 'hand-writing' to the work he produced.
The outcome was far removed from the preoccupations of the young British sculptors
who emerged at the beginning of the r98os. Cox displayed no interest in salvaging the plastic detritus that played so prominent a part in Tony Cragg's work. Nor did he follow the
direction pursued by Bill Woodrow, who incorporated the battered and discarded products
of urban life in his deliberately raw assemblages. Compared with them, and other sculptors
of their generation impelled by the belief that virtually anything could now be regarded as legitimate material, Cox's adherence to stone carving seemed the manifestation of an obstinate attachment to the past.
His fascination with the quattrocento even marked him out from the earlier practitioners of 'carving direct.' For Epstein and Moore had both, at their most rebellious, turned
away from the Renaissance in search of other, more 'barbaric' alternatives. Determined to
reject the nineteenth century's veneration of the Greco-Roman tradition, they found fresh
energy in African, Oceanic and ancient Mexican art. Epstein's collection of so-called 'primitive' carvings became renowned, and Gaudier's polemical 'Vortex' credo in the Vorticist
magazine Blast dismissed quattrocento sculpture as 'solid excrements.' Although Cox shared
the desire to regain contactwith directways of tackling the stone, he found the early
Renaissance liberating rather than oppressive. Quattrocento carvers working with flat surfaces had a special significance for him, and the first work he produced under the overt
influence of Italy could hardly be accused of historical pastiche.
Concentrating for the moment on the tondo form, which attracted him because its circularity seemed universal, he restricted himself at first to carvings as simplified as Tondo:
Beyond. Its fossil-like character reflected Cox's desire to evoke a sense of the primordial. The
stone used in Tondo: Beyond comes from the Forest of Dean, and may help to account for
the sculpture's relative sobriety. Within a year, though, Vasari's writings helped him turn
his attention to materials quarried in Italy itself. Their impact on his work was unmistakeable. The title of We Must , lwoys Tum South, an answer to the rhetoricai question posed by
Stokes at the end of his essay'The Qucttro Cento'passionately affirms Cox's willingness to
immerse himself in Mediterranean inspiration. The swollen oval carved on its surface does
not try to ape Renaissance precedent. But as in so many of his Italian works, the colour
emblazoning on this lump of St Ambrogio di Verona marble is, within self-imposed limits,
surprisingly sumptuous. It is redolent of a glowing copper sun, an image reinforced by the
flame-like fingers leaping towards its upper edge.
Although Donatello, Luca della Robbia and Ghiberti were important to Cox at this
stage, he owed Agostino a special debt. Alberti, the architect of the Tempio at Rimini, had
after all been saluted in the titles of a marble relief series as early as 1977. And the carvings
Agostino produced for the temple provided particular inspiration for some of Cox's carvings in the early r98os. Tondo Nuvole, with its evocation of the clouds cut with such economy
in an Agostino relief, can be seen as a homage to the quattrocento artist's understanding of
how the 'vaults of Heaven' appear. But the fragmentation of Tondo Nuvole, ensuring that the
marble seems to have been shattered either by accident or some titanic blow, is prophetic
of Cox's subsequent development. So is the dynamic movement imparted to the carving by
the fissures running through it like seismic fault-lines.
Fragmentation, enabling him to arrange several 'broken' pieces in an ensemble that never quite adds up to a 'complete' sculpture, recurs in his work. Although many of Cox's
reliefs have the appearance of archeological remains. They call to mind Eliot's insistence,
in The Woste Lcnd, that
"You cannot say, or guess, for you know only
A heap of broken images, where the sun beats,
And the dead tree gives no shelter, the cricket no relief,
And the dry stone no sound of water."
This tantalising lack of wholeness surely reflects a belief, on the sculptor's pafi, that the
civilisations nourishing his work will always remain paftially beyond recall, mysterious and
unattainable. The possibility of completion may be suggested by the fifteen irregular pieces
of Peperino stone comprising Gethsemone, especially in the overarching lines of a celestial
canopy running round its upper edge. But each fragment of the sculpture comes from a different piece of stone. They would be impossible ever to unite, and this realisation engenders a sense of Eliot-like melancholy. However vigorously Cox enters into his own meditations on the past, he knows that it is in the last analysis irrecoverable.
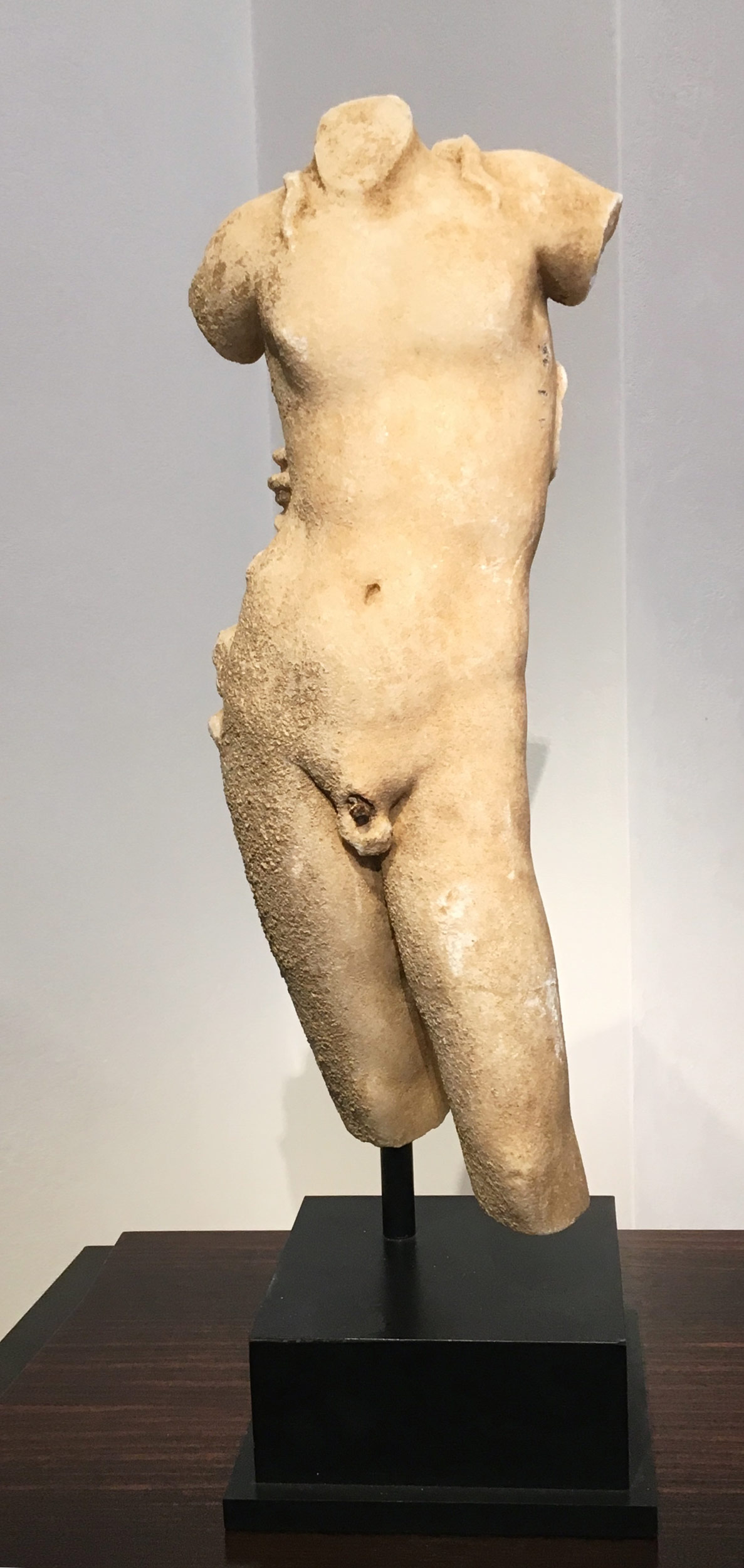
That is why his work could never be confused with the sculpture he regards as his
starting-point. Cox has travelled widely enough to appreciate just how much art from the
past has ended up as ignominiously as Saint Sebastian. Although his martyred body was
recovered after Diocletian's archers had riddled it with arrows, it was afterwards hacked to
pieces and hurled into the Roman sewer. Cox's carving Clooco Moximo presents the butchered
saint as a scattering of anatomical shards. They reinforce the brutality of his death, and at
the same time restore to the grievously degraded figure a semblance of his sensuous,
gleaming presence.
Even when dealing with violence of the most callous kind, Cox is not afraid to admit an
erotic dimension. Italy enabled him to release in his art the sexual element that English
Protestantism had previously repressed. It reaches
extravagant expression in another martyrdom carving, the Ecstosy: St Agotho, a three-part sculpture
where he twists Rosso di Verona marble into shoulders, buttocks and breasts. The bravura drapery
swirling around her is animated by a Baroque flamboyance worthy of Bernini. At first
glance, this unbridled work seems far removed from the quattrocento. But Stokes argued that Agostino at his most uninhibited appears to prepare the way for the Baroque's rhapsodic virtuosity.
Nothing quite so brazenly erogenous had been seen in British sculpture since Eric Gill's
most heated carvings. In his case, the urge to fuse spirituality and sexuality, the sacred with
the profane, was spured by his study of Indian art. In r9r r , at a time when most British
sculptors were still dominated by classical influences, he declared that 'the best route to
Heaven is via Elephanta, and Elura [sic] and Ajanta.'Gill's enthusiasm for Indian artists'ability
to convey divine conviction in the most sexually ecstatic manner encouraged him to carve a
relief of a copulating couple. He knew it was impossible to exhibit the result in England, but
the sculpture would have looked remarkably at home on the facade of an Indian temple.
Ever since the young Cox chose a book about Indian sculpture as a school prize, he had
nurtured a wish to see the art of the subcontinent for himself. He even wonders now if his
father's wartime service in Bombay as a naval petty officer had a genetic influence. At all
events, when the British Council invited him to represent his country at the Sixth Indian
Triennale in 1985, he seized the opportunity to study its great caruing tradition at first hand.
It was a revelation. The influence that Italy had exerted on his work was broken - or rather,
replaced by a growing interest in cultural interaction and exchange. Cox's Italian sojourn
had made him increasingly aware of how ancient civilisations impacted on each other. In
this respect, it is significant that one of the first carvings he made in India dealt with the
theme of overlapping cultures.
The starting-point for Etruscan was a medieval palazzo in Viterbo, where Cox found
himself mesmerised by two eyes staring from a shield high on the wall. Their extraordinary forcefulness prompted him to plan, as an Indian project, a carrying concentrated on the
organs of the senses. In Etrusccn, and its far larger successor produced the following year,
eyes, nose, ears and mouth are successively singled out. The row of four faces is cut from
Black Indian granite, but Cox has focused attention on particular organs by the application
of oil. It turned the pinpointed area of grey stone almost black. The act of pouring also
signified his growing desire to see sculpture not simply as an object scrutinised from afar, but something touched, grasped and even prepared, through libation, for a role in rituals.
The more he stayed in India, the more Cox found himself fascinated by the national custom
of handling and washing carvings of deities. He liked the idea of feeding and dressing his
own sculpture as well - not because he wanted it to assume the status enjoyed by idols in
the temple, but more out of a desire to see stone as a fundamental element in everyday life.
He was equally impressed by the way Indians employ granite for the simplest and most
functional of domestic implements. Watching these pestles, mortars and rolling pins in use
reminded him of Stokes's eloquent passage in 'Rough cnd Smooth', describing how the incessant action of hands and feet on banisters and pavements ended up as an instinctive form
of sculpture.
The idea initially explored in Etruscon continued to intrigue him. By focusing on the
organs of the senses, Cox hoped to heighten our awareness of how we habitually understand our place in the universe swirling around us. The Tonmotrcs [Tanmatras within Samkhaya Philosophy, deals with the subtle elements which identify smell, taste,
sight, touch and hearing with their corresponding elements earth, water, fire, air and ether.] carvings seek to concentrate attention on this process, using the notion of fragmentation as a paradoxical way of
leading us towards a sense of totality. Hinduism harbours similar ambitions, as Cox soon
began to realise. He warmed to the notion of developing 'a conceptual understanding of things beyond one's own place in the cosmos.' The emphasis on fragmentation reminded
him of certain aspects of minimal and conceptual art. So the Tonmatros series attempted to
bring about a fusion of contemporary western thought and historic eastern belief.
Orgons of Action [organs of Action within Samkhaya Philosophy, the gross elements: speach, procreation, evacuation,
grasp and gait deal with Man's physical characteristics] is among the most monumental manifestations of this ambition. As well
as developing the idea originated in Etruscon. it was stimulated by an old translation of the
Bhogovodgito with its diagram of sense-isolation. Indian culture identifies five elements rather
than four, and links them with the five senses. It associates the fifth element, ether, with
hearing. By including it in orgons of Action, he hoped to bring about a synthesis that sharpens
our perception of the universe.
Since Cox has always harboured sffong architectural aspirations, he was bound to find
the unity between Indian sculpture and architecture intensely rewarding. He discovered
that the temple was regarded as a metaphor for the mountain, and several leading modern
sculptors in Britain have seen their own aspirations in a similar light.' I want to carve
mountains' Epstein told his patron John Quinn in 1912, only two years before Gaudier proclaimed that sculptural energy is the mountain.'Moore subsequently advanced the same
notion, as well as deploring modern architects' tendency to force sculpture into a subordinate position. Cox would undoubtedly agree. Hence his admiration for the Indian insistence
on an integral role for sculpture in temples. It is no accident that many of his Italian works
contain references to ruined buildings, and one of his largest Indian carvings is entitled
Thousond Pillored Holl.
Although it recalls the awesomeness of Anselm Kiefer's empty and dilapidated Third
Reich buildings, this imposing sculpture is too lyrical to yie with the brooding moilification of the German's paintings. Using rubbed ochre, faded maroon and rust colours as a
means of conjuring up a patina, Cox brings together the resources of painting and sculpture
in Thousond Pillored Holl to pay homage to the inspiration of architecture. No people can be
discerned among the columns, plentifully embellished with figures in relief. But a woman
strides away from the hall at one side, and her presence is counterbalanced at the other end
by a blank slab of granite. It has a latent power of its own, recalling Cox's awareness that in
'rock-cut' temples a space is hewn out of the mountain. He makes a direct reference to this
inner dimension in Rock Cut: Holy Fomily, where the entire central area is given over to an
Indian devotional group. The possibility that Cox's carving might itself have been excavated, or uncovered in an archeological dig, is strengthened by the rough-hewn boulders surrounding the group.
Cox relishes working in India, and continues to spend a considerable amount of time
there. He likens himself to a lizard, carving on the Bay of Bengal where the sun rises over
the sea every morning and only laying down his chiseis when it sets on the other side of
the peninsula. He feels spiritually regenerated there, and buoyed up too by the realisation
that in the small town of Mahabalipuram, south of Madras, highly skilled craftsmen still
uphold the tradition of carving for temples even today.
AII the same, he remains an inveterate roamer. Sometimes he suspects that his childhood in Bristol, formerly a renowned centre for England's great Merchant Venturers, somehow instilled in him the wanderlust. At any rate, he was delighted when the Foreign
Office invited him, in 1989, to visit Egypt and make a sculpture for Cairo's new opera
house. Epstein once declared that 'in Egypt can be found the perfect example of the alliance
between sculpture and architecture.'Cox clearly venerates it as well. While missing the
sense of a continuing tradition found in India, he savours the skill and camaraderie of the
Egyptian quarrymen who work the stone. Moreover, his previous study of Alberti's writings had alerted him to the mystery of imperial porphyry.
Unlike Italian marble, porphyry daunted Renaissance artists with its intractable hardness. Cox regarded it as a challenge, and embarked as an act of faith on an expedition across
the desert to visit the quarry at Mons Porphyrites in the Eastern Mountains. There, at this
former remote outpost of the Roman Empire, the porphyry reserved exclusively for the
Emperor's use confronted him. Cox was profoundly moved by the encounter, and even
more excited when his Opera House commission granted him the high privilege of access
to the quarry for his own work.
In Chrysalis, one of the most impressive results of his engagement with imperial porphyry, he manages to hint at the new life struggling to emerge from the block It may seem
unfinished, for Cox has left the marks made by Roman cutters who roughed out the stone
in the Emperor's quarry over 2,ooo years ago. But there is nothing unresolved about It presents the intensely dramatic spectacle of metamorphosis, of the image growing out of the primal rock. Cox regards Michelangelo's supposedly unfinished last carving,
the Rondonini Pieto. as the most complete of all his works. In the same way, the tension in
Chrysalis between highly polished refinement and broken, almost inchoate vestiges of the
past is central to the work's meaning.
Even so, it remains a deeply ambiguous work. The promise of new life is countered by
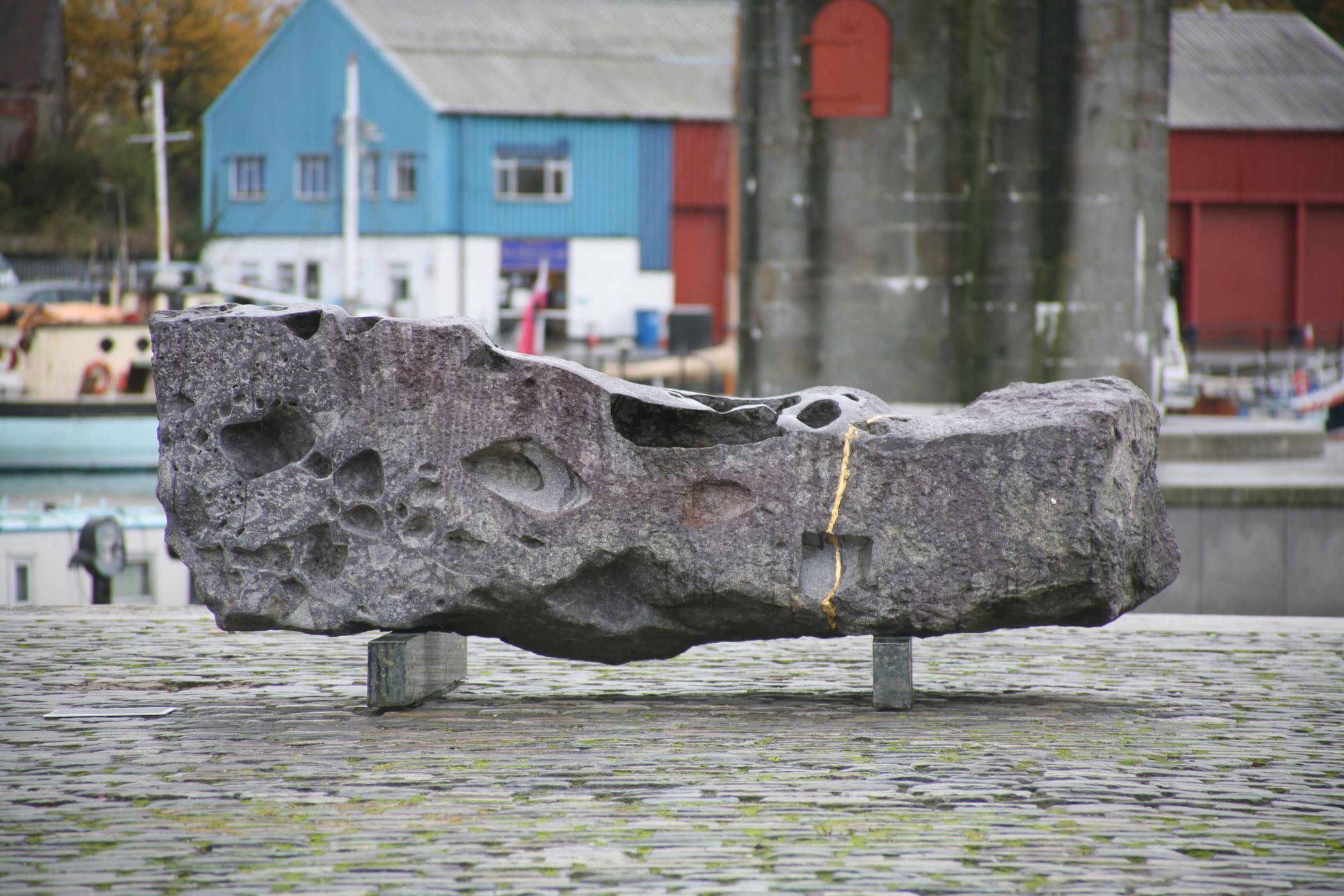
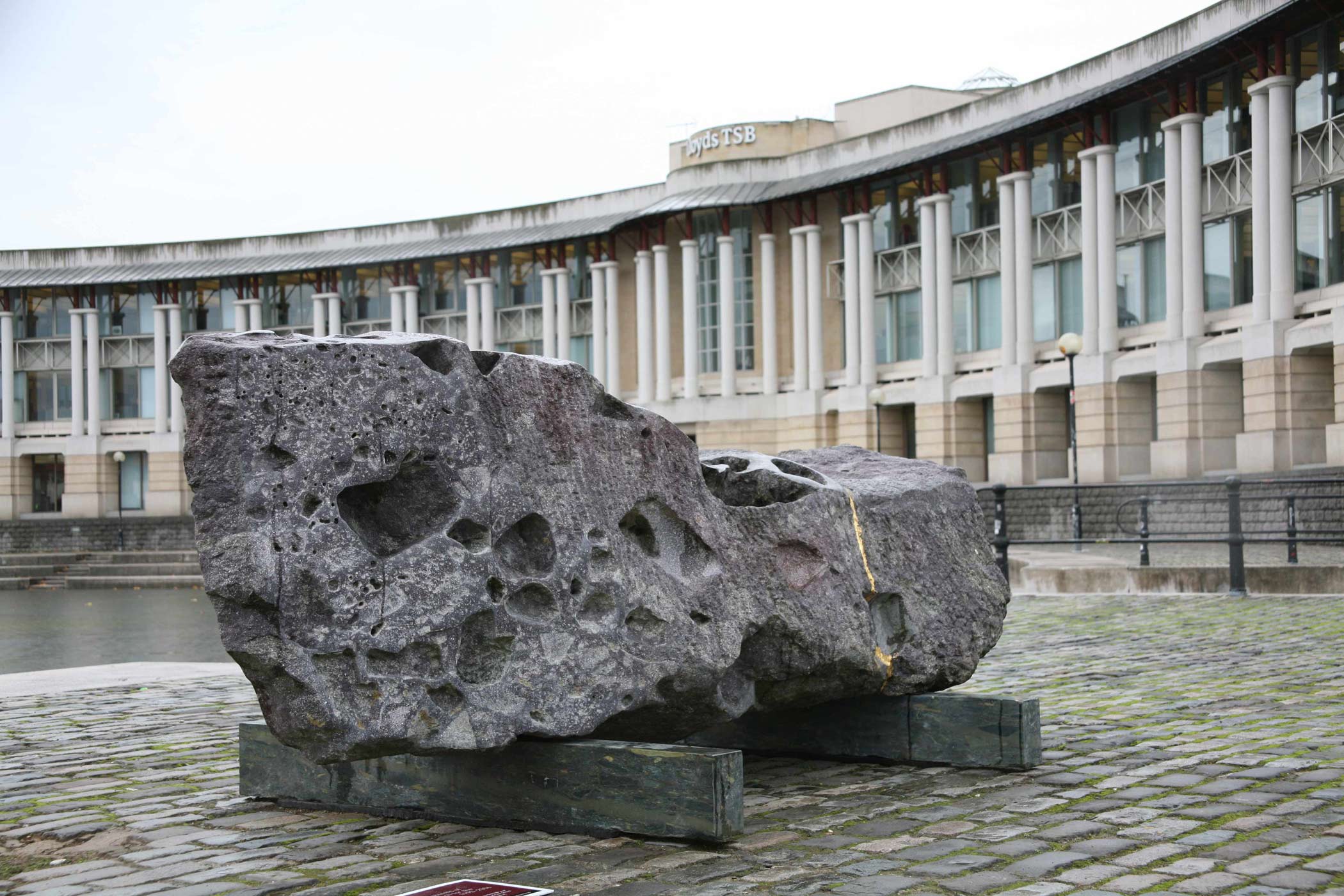
the possibility that death might prevail. Despite its title, Chrysalis is reminiscent of the sepulchre. In this respect, it has a kinship with Interior Space, a fifteen-ton tour de force sliced from a boulder
of Hammamat Breccia. Sculpture here aspires to the
condition of architecture more openly than anywhere else in Cox's work. Inspired by a visit to the
tombs of the Apis bulls near the great stepped pyramid of Sakkara, where the sacred animals were
given ceremonial burlals worthy of a pharaoh, this
gleaming structure appears to offer an invitation. The thin oblong cut from its front lies on
the floor like a pathway. But access is denied: the narrowness of the aperture frustrates any
attempt to penetrate the interior. We are left circumambulating the exterior, noticing how
the rectangular finality of the main block contrasts with the irregularity of the broken stone
above. However thwarted we may feel by our inability to enter this brooding, enigmatic
mass, it is easy to imagine that the darkness within once provided a resting-place for bound
recumbent corpses. At Dulwich, Interior Space's felicitous proximity to Soane's Mausoleum
accentuates its resemblance to a chamber of death.
No essay on Cox's art should conclude on a funereal note, however. The truth is that
his incessant journeying has been an overwhelmingly positive and resourceful affair, conducted in a generous spirit of multi-cultural affirmation. Wherever in the world he elects to
work, the outcome at its finest is always reassuring. By reaching back to the very origins of
sculptural expression, and reinterpreting that impulse according to his own contemporary
imperatives, he endows his art with a feeling of serenity, poise and immemorial wisdom.
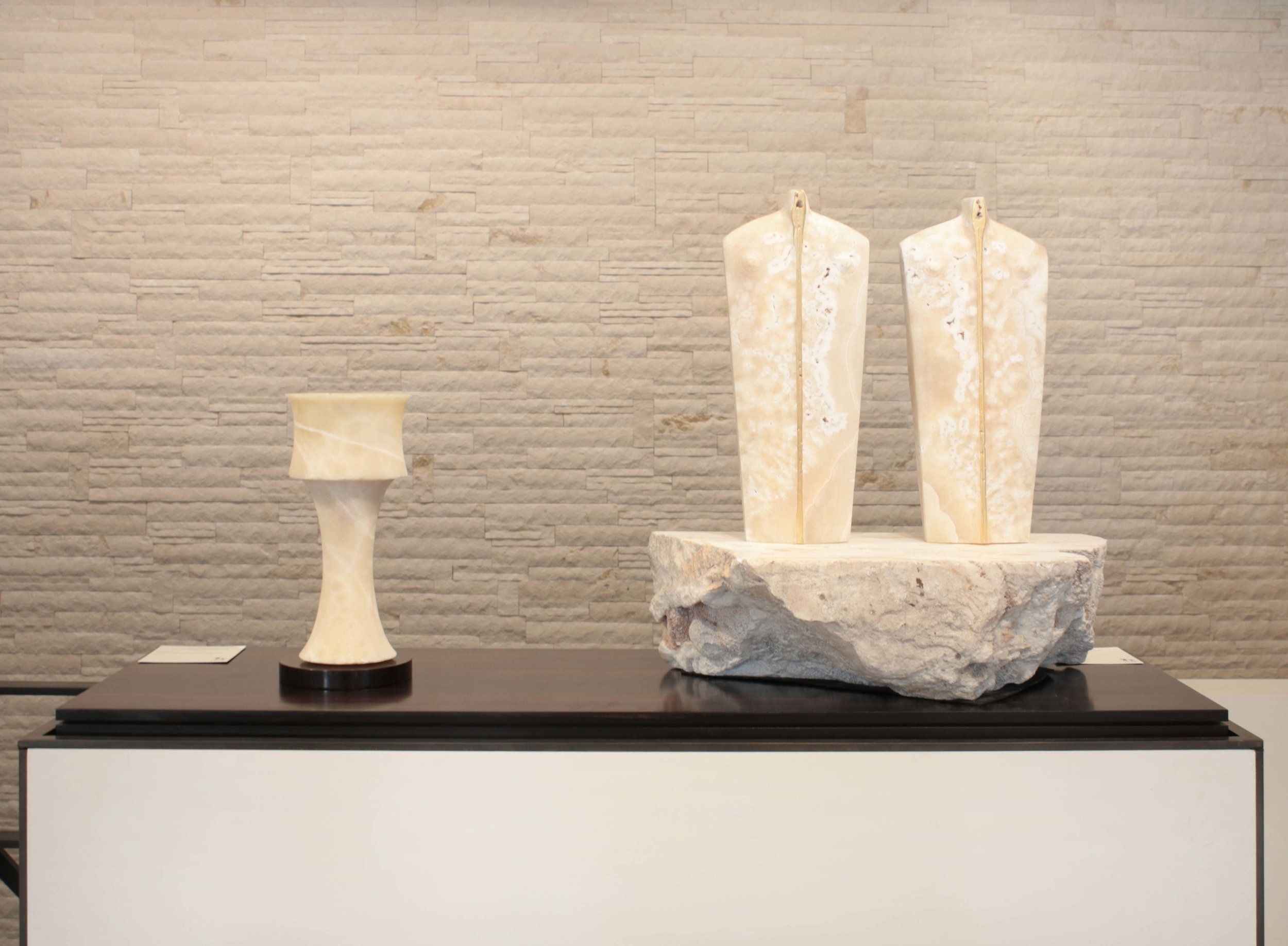
Royal Academy Summer Exhibition, 2016
Stephen Cox has six pieces in the Royal Academy's Summer Exhibition this year:
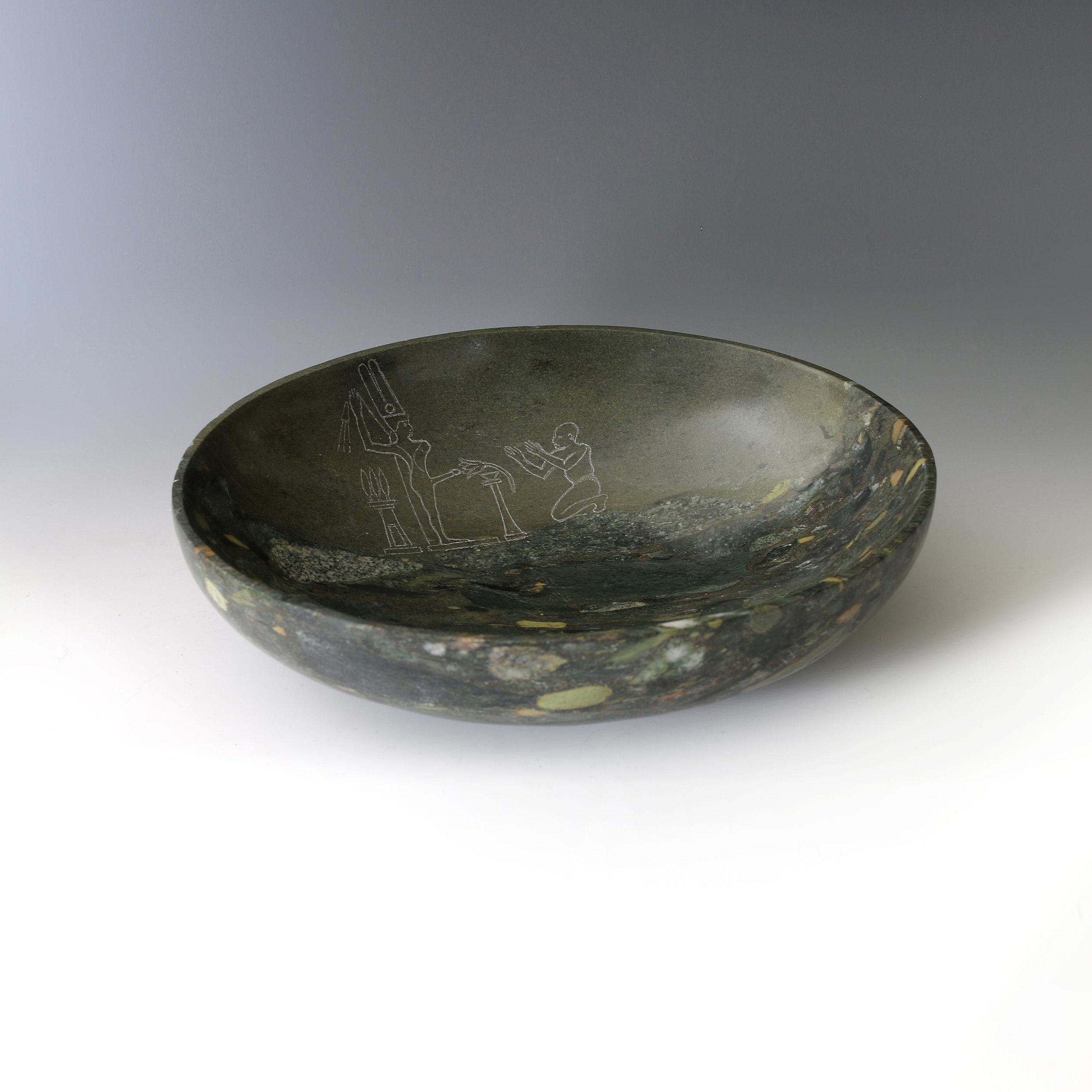
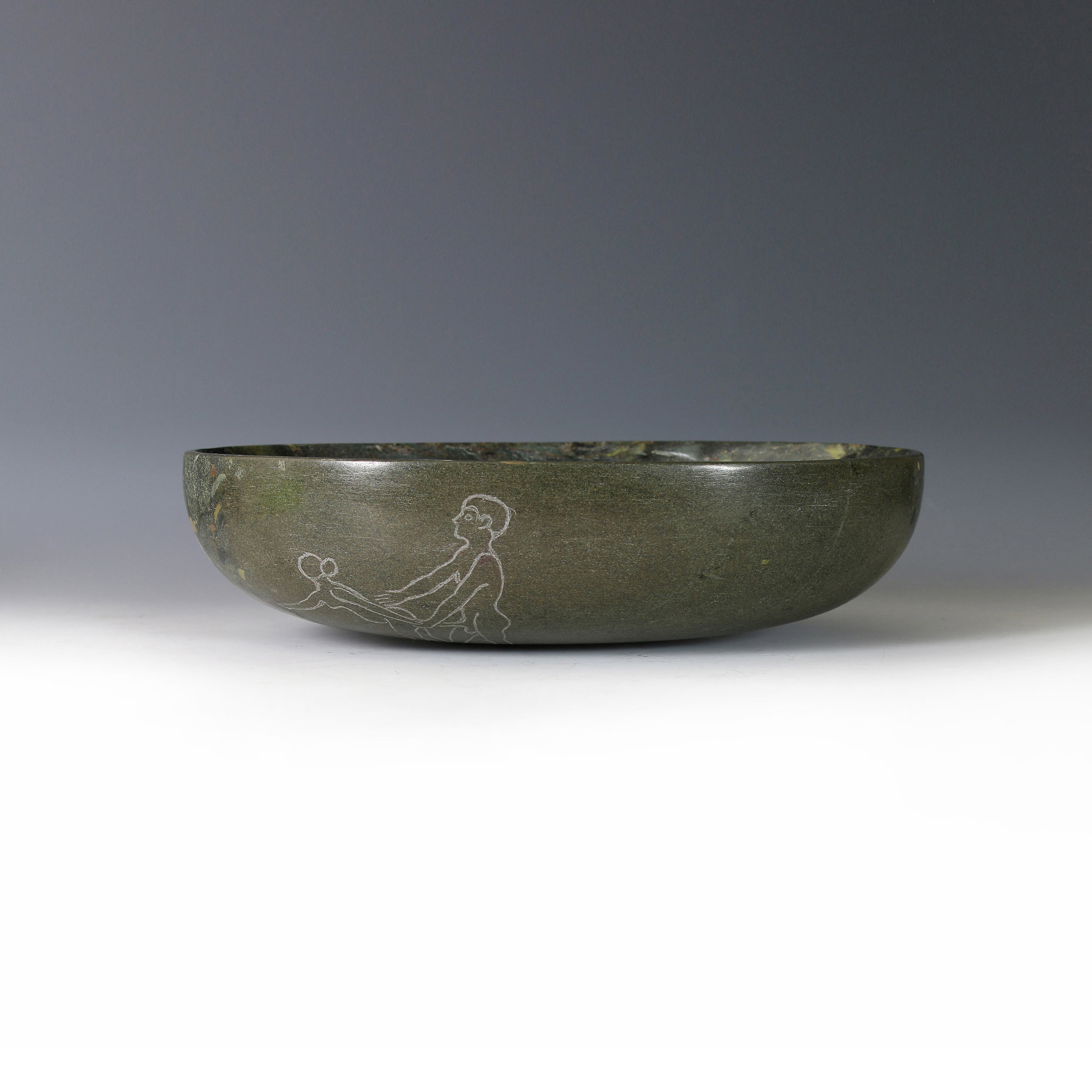
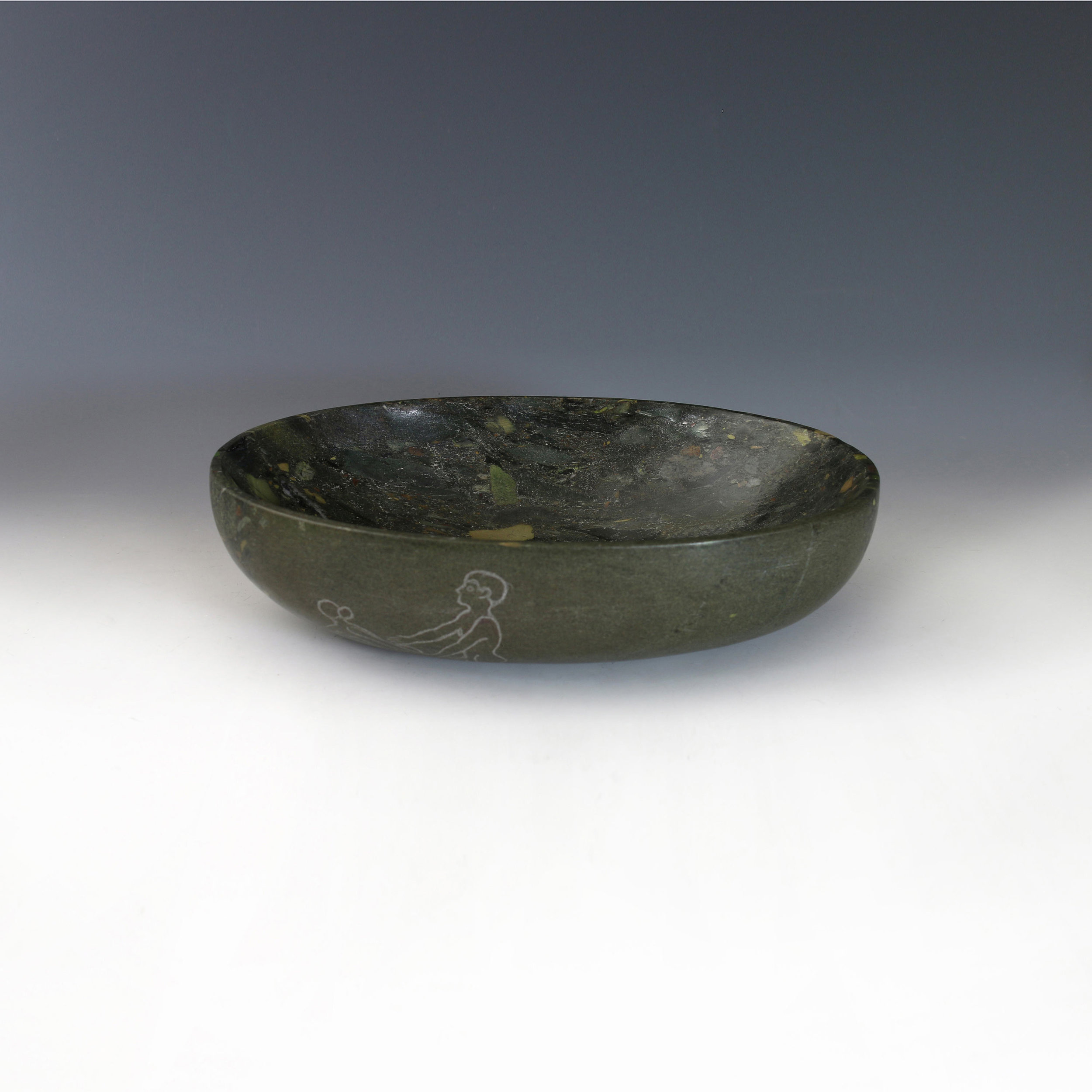
Gemini III is a sculpture consisting of a base and two abstract figures carved from the same block of stone. The stone is known variously as ‘antique Egyptian’ or ‘Hammamat breccia’ and is a conglomerate with bight coloured ‘pebbles’ and fragments of diverse stones: granites, marbles, quartzes, hornblende and hematite of yellow, red, black, pink and white strewn in a greenish matrix. It has been recognised for its beauty since pre-dynastic times making its source one of the oldest, if not the oldest, ‘decorative’ stone quarries in the world. Its fame has yielded up stone to expeditions sent by early kings and pharaohs of Egypt as well as from distant lands including Xerxes and Darius of Persia and Philip of Macedon father of Alexander.
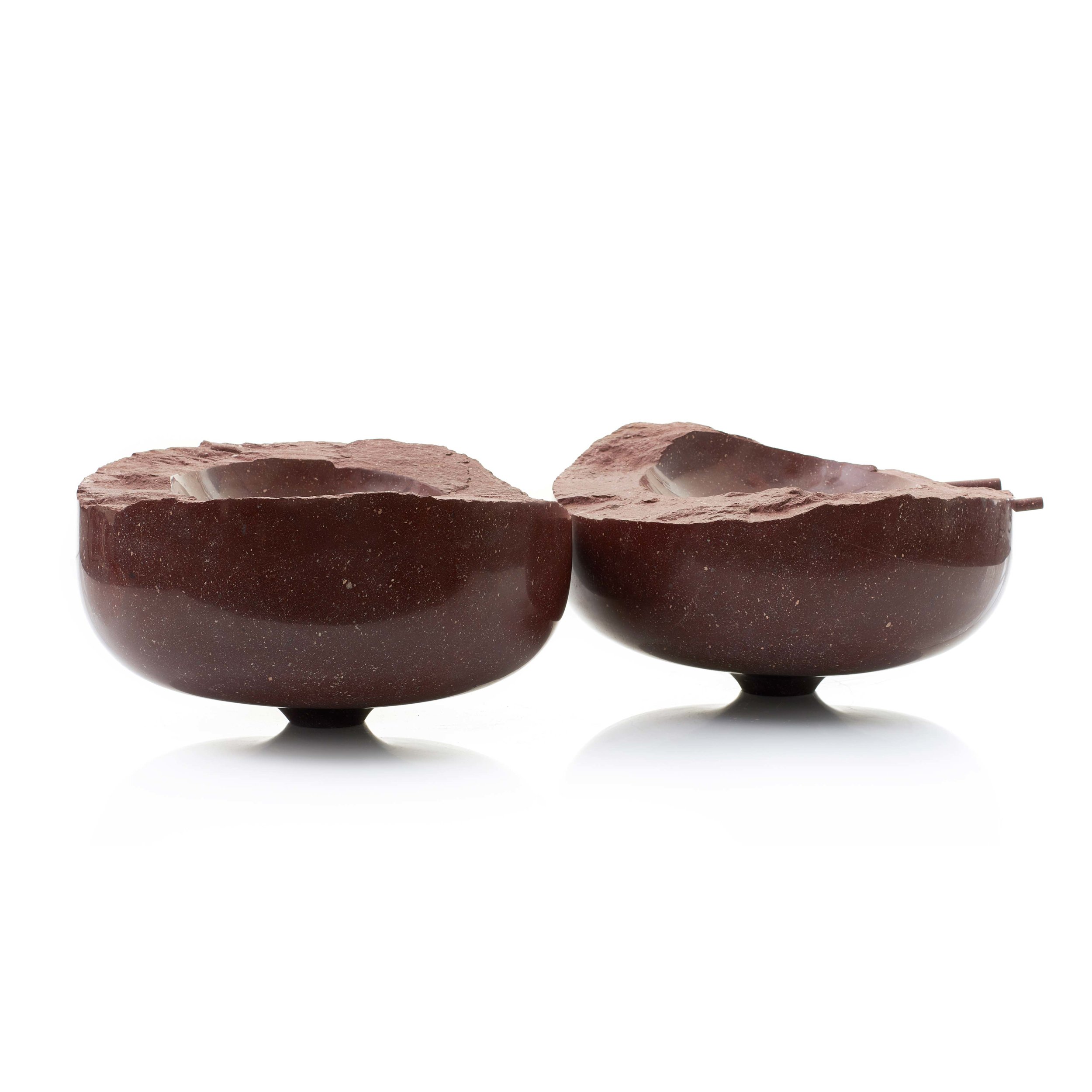
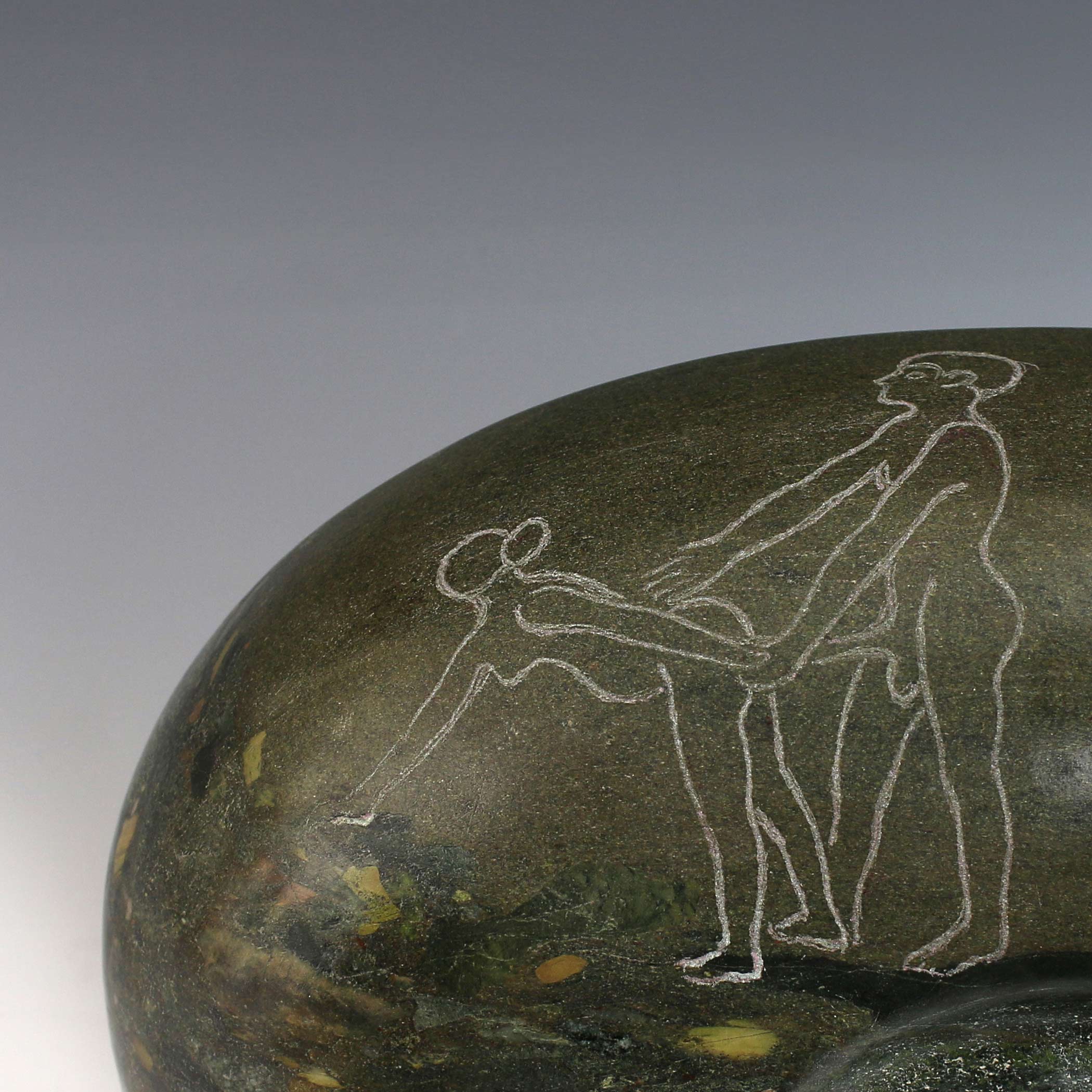
Two recent offering bowls formed from Egyptian breccia are engraved with typical images drawn from the the walls of the valley of the quarries.
The original graffiti was wide ranging in its subject matter. It depicted inventories of men and provisions that were tallied by the masters as well images of idols and offerings some simple, others technically very accomplished. Some of the imagery expressed the yearnings of lonely men in a savage desert environment.
The drawings Louis Khan: Siva / Kali, Black, Orange & Gray are inspired by the magnificent Indian Institute of Management designed by the great architect Louis Khan at Ahmedabad in Gujarat.
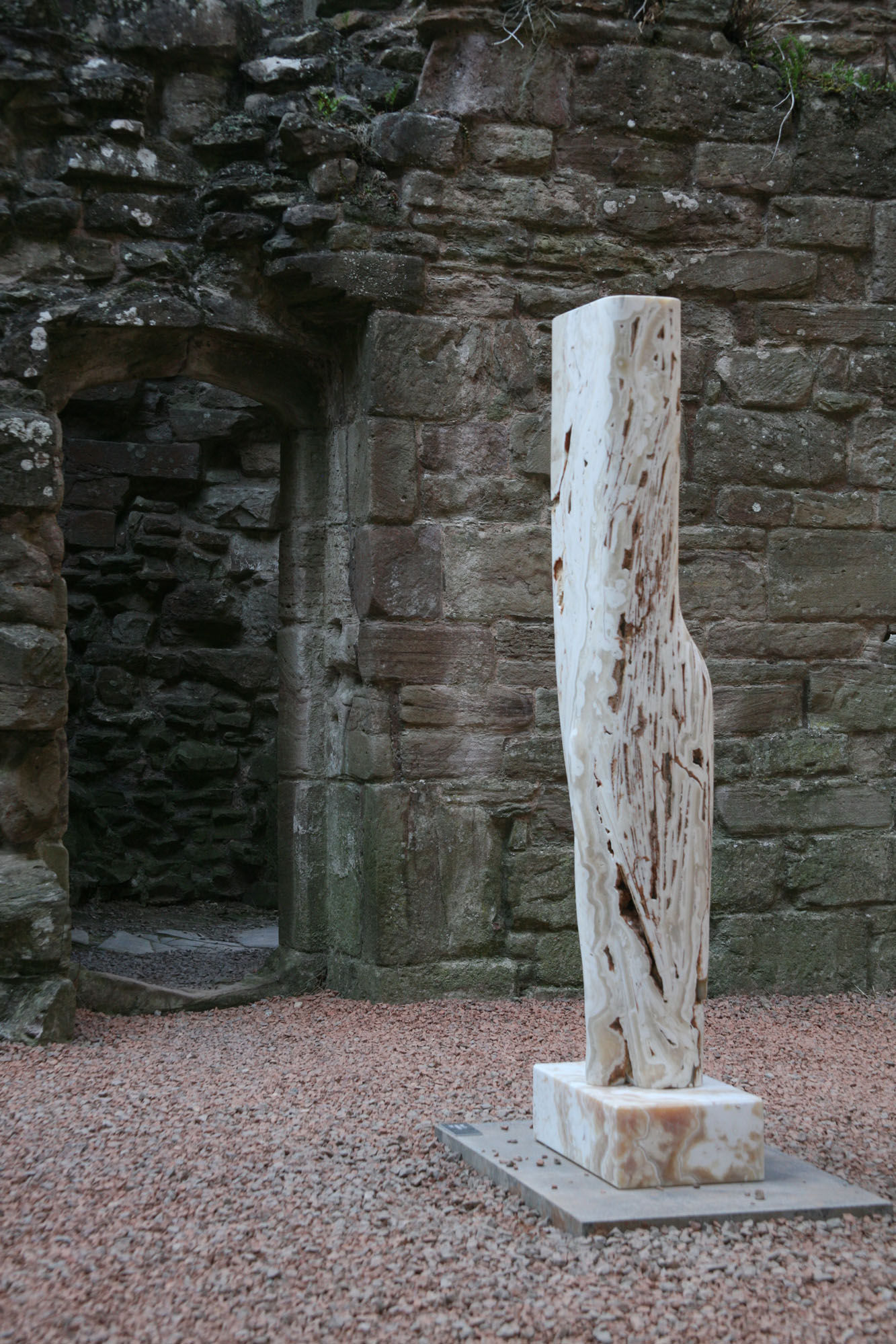
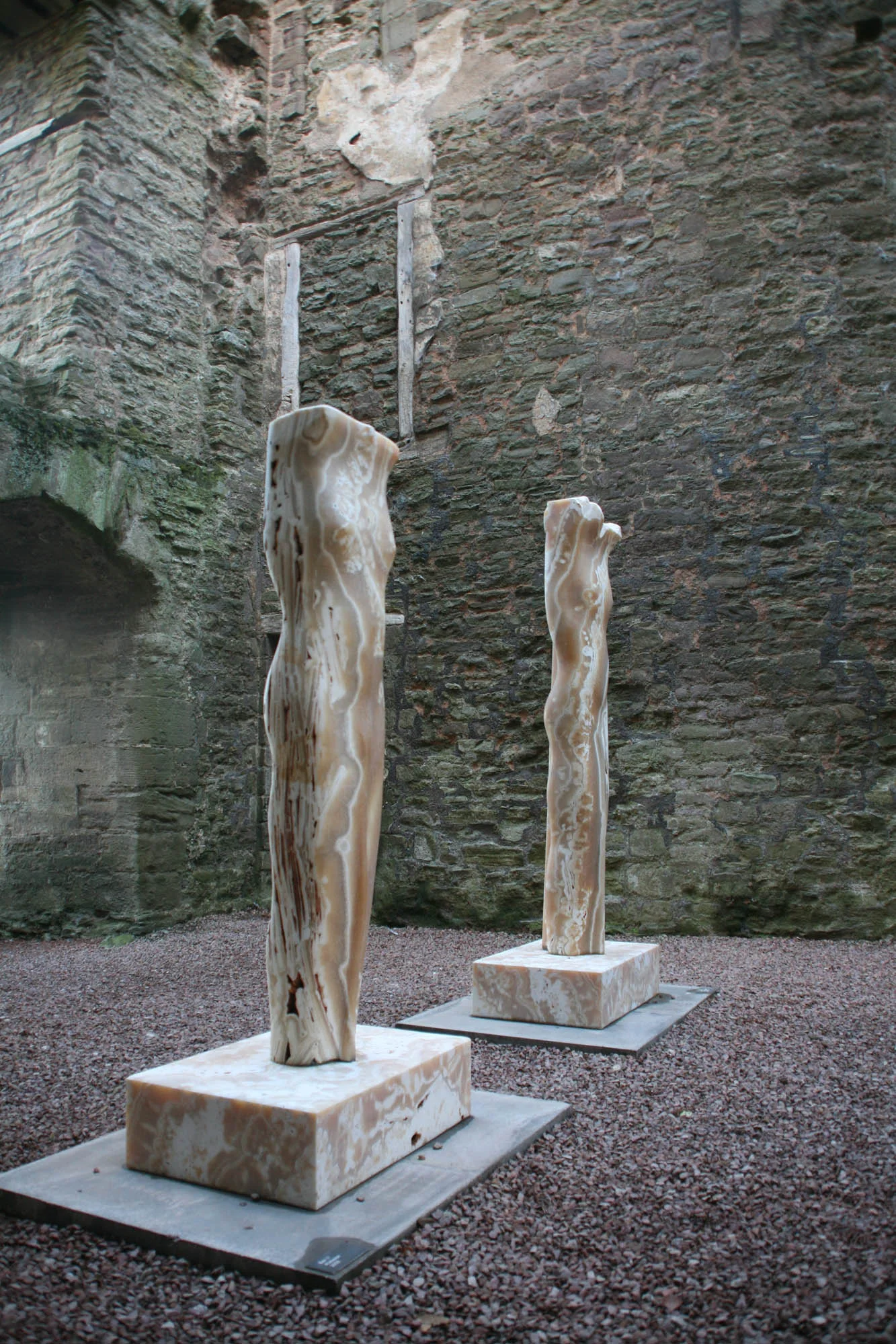
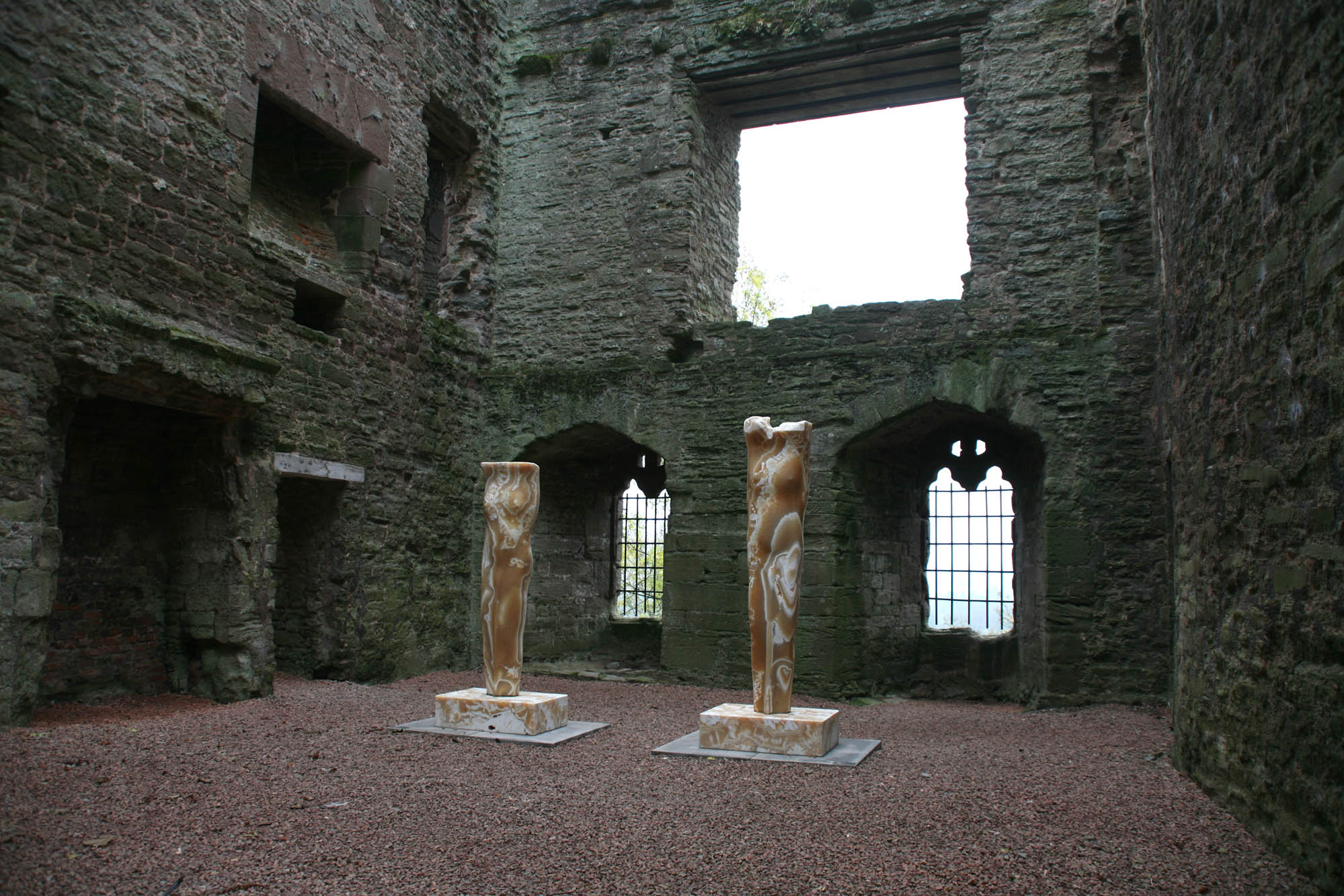
The Meaning of Stone, 2011
This exhibition was held at Ludlow castle and featured large and small scale works that draw inspiration from a wide variety of concepts.
The Meaning of Stone, 2011
Ludlow Castle
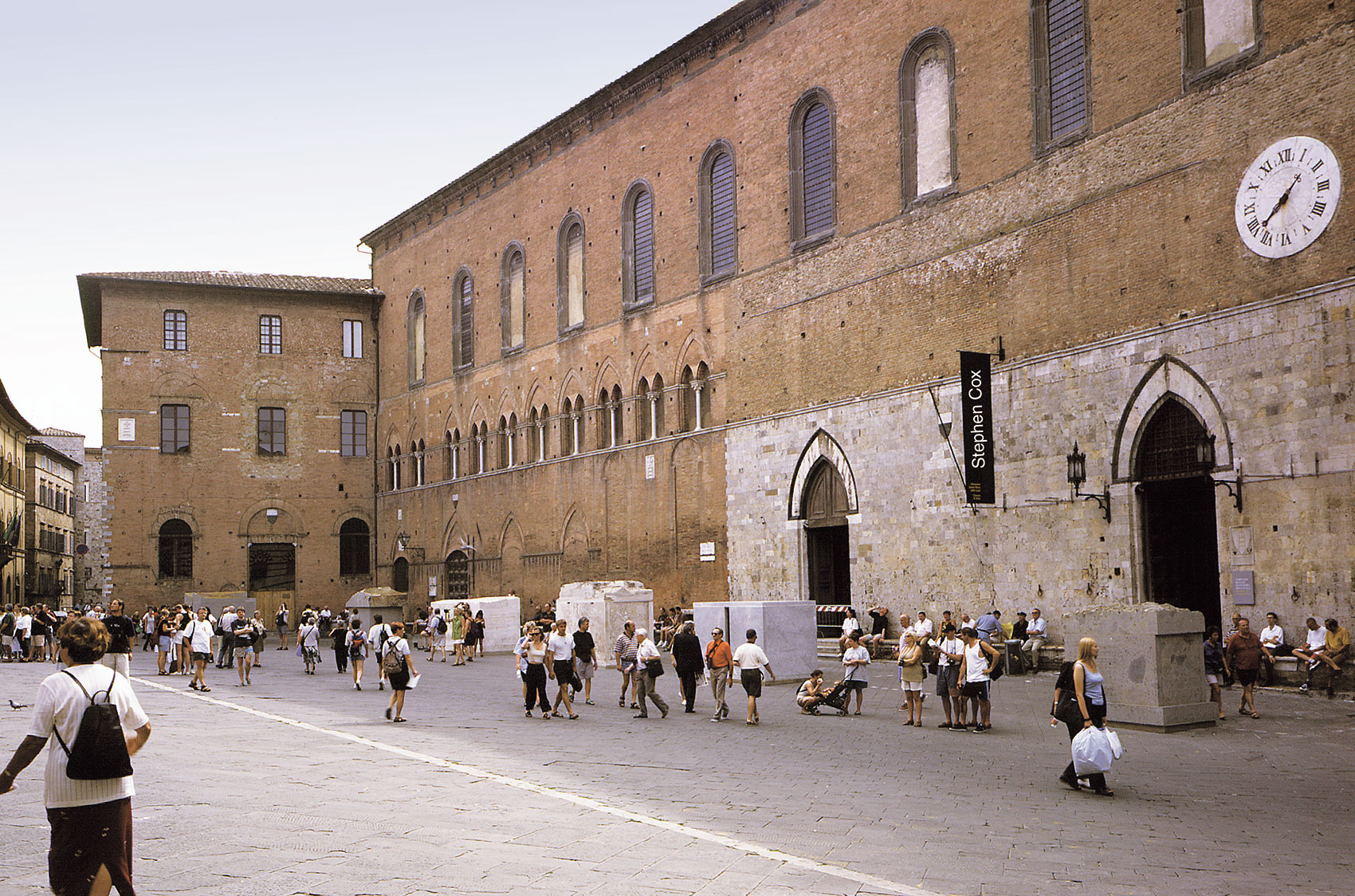
Interior Space, Ospedale di Santa Maria della Scala, 1999
Interior Space, Ospedale di Santa Maria della Scala, 1999
Interior Space, Ospedale di Santa Maria della Scala, 1999
Piazza del Duomo, Siena